* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download IDS
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
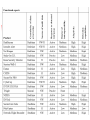
A survey of commercial tools for intrusion detection 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Introduction Systems analyzed Methodology Results Conclusions Cao er Kai. INSA lab. 2003.09 1. Introduction Intrusion Detection Systems generic ID architecture Common Intrusion Detection Framework (CIDF) - DARPA (Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency) • Event generators (E-boxes) • Event analyzers (A-boxes) • Event databases (D-boxes) • Event response units (R-boxes) event generators obtain information from sources and transformed into a standard format (gido) event analyzers statistical analysis and pattern recognition searching event databases storage of events and information (gidos) response units initiate the proper response 2. Systems analyzed 3. Methodology Comparison criteria Granularity of data processing Source of audit data (raw events) network-based : Ethernet (see all traffic) host-based : security logs Detection method 1. 2. IPSEC rule based anomaly based Response to detected intrusions passive active System organization Security : withstand attacks againstitself Degree of interoperability Exchange of audit data records Exchange of audit data records Exchange of misuse patterns or statistical information about user activities Exchange of alarm reports and event notifications Manageability Centralized : data analysis Distributed : data collection HP Openview , BMC Patrol Adaptivity System and network infrastructure requirements TCP/IP Classification of comparison criteria 4. Results Functional aspects Granularity of data processing real-time T-Sight Source of audit data (Raw events) host-based (H) both host-based and network-based (NW/H) network-based (NW) switched networks network encryption Response to detected intrusions Passive responses Active response sending e-mails, paging or displaying alert messages. network-based systems : terminating transport level sessions Host-based systems : control processes, terminate network sessions Interfaces to network management applications : SNMP (send traps) Interfaces to network elements : firewall control sessions/connections Service availability aspects Legal aspects : “returning fire” Degree of interoperability 1. 2. 3. 4. Exchange of audit data records Exchange of security policies Exchange of misuse patterns or statistical information about user activities Exchange of alarm reports, event notifications and response mechanisms Adaptivity (customization) Detection method Adding new intrusion patterns Adopting rules for site specific protocols and applications Rule based detection anomaly based detection Detection capabilities Physical and data-link layer Network and transport layer Operating Systems Applications, databases, management and support systems, office automation Security aspects 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Confidentiality of audit data Integrity of audit data : using encryption Confidentiality of the detection policy Integrity of detection policy Protection of response mechanisms Availability Encrypted communication channels Heartbeat functions Stealth behavior Access control Weaknesses of network-based systems Architectural aspects System organization distributed environment single host or network segment System and network infrastructure requirements Operating systems Network technology Operational aspects Performance aspects Communication overhead network-based intrusion detection, the overhead is caused by the distribution of audit data and the communication between the various subsystems of the IDS. Computational overhead host-based IDS execute and collect audit data on the target they monitor. Management aspects Configuration management management of the detection capability and the corresponding response mechanisms Security management Access security Audit trails and security alarms Security of management 1. 2. 3. 4. Authenticity Integrity Confidentiality Availability Management interfaces Management model Many-to-Many One-to-Many One-to-one 5. Conclusions The role of IDS in corporate security infrastructures: IDS are not a substitute for other security services such as firewalls, authentication servers etc Host-based versus network-based IDS. Security of IDS Lack of modularity and interoperability Background of vendors RealSecure RealSecure Architecture: RealSecure Engines Network interface Packet Capture Module Ethernet, fast Ethernet, FDDI and Token-ring Windows NT: network service Solaris: Data Link Provider Interface Filter Module Attack recognition Module Response Module RealSecure RealSecure Agents RealSecure Manager Central real-time alarm Central data management Central engine configuration Intruder Alert Intruder Alert Architecture Interface console Manager interface console and manager only runs on Windows NT/95 Agents Intruder Alert Intruder Alert Domains: groups of agents/hosts Intruder Alert Policies Drop & Detect Policies Detect and respond Policies Custom-configurable Policies Carte Blanche NetRanger NetRanger Architecture Sensors Ethernet, Fast Ethernet, Token Ring and FDDI Director Post office Stake Out I.D Stake Out I.D Architecture Network Observation Intrusion Detection Evidence logging Alert Notification Incident Analyzer/Reporter Kane Security Monitor Kane Security Monitor Architecture Monitoring Console Collection Auditor and Alerting Engine Intelligent Agents Session Wall-3 Session Wall-3 Architecture Network Usage Reporting Network Security WEB and Internal Usage Policy Monitoring and Controls Company Preservation Entrax Entrax Architecture Command Console Assessment Manager Alert Manager Detection Policy Editor Audit Policy Editor Collection Policy Editor Report Manager Target Agent CMDS (Computer Misuse Detection System) SecureNET PRO CyberCop CyberCop Architecture CyberCop Sensors CyberCop Management Server INTOUCH INSA T-sight NIDES ID-Trak SecureCom POLYCENTER Network Flight Recorder