* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Part I: Introduction - University of Pittsburgh
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Backpressure routing wikipedia , lookup
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol wikipedia , lookup
TCP congestion control wikipedia , lookup
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Multiprotocol Label Switching wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.1aq wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
UniPro protocol stack wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
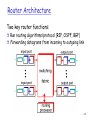
Final Review CS1652 Jack Lange University of Pittsburgh Final Thurs 12th: 12-2PM This room Not Cumulative One page of notes 2 Chapter 4: Network Layer Network layer service model Forwarding vs. Routing IP addressing, NAT & DHCP Router architecture Routing algorithms Handling scale - CIDR and BGP ICMP, traceroute 3 Network layer service model Unreliable, connectionless data delivery Q: is UDP more reliable than IP? Q: do TCP packets receive more special treatment than UDP packets? Host-to-host packet delivery Q: Difference from transport layer? All systems implement network layer End systems + routers Q: Why not routers implement transport layer? 4 Forwarding vs. Routing Definition? Switch vs. router? How routing affects forwarding? Routing algorithms Intradomain routing algorithms • Distance vector, Link state Interdomain routing algorithms • BGP Longest prefix match 5 IP addressing, DHCP and NAT 32-bit IPv4 address Subnet part + host part Subnet part is used for forwarding decision CIDR Subnet portion can be an arbitrary size Why CIDR? • IP allocation efficiency & supernetting DHCP How it works? Where is it useful? NAT Pros. and Cons. 6 IP datagram format IP protocol version number header length (bytes) “type” of data max number remaining hops (decremented at each router) upper layer protocol to deliver payload to how much overhead with TCP? 20 bytes of TCP 20 bytes of IP = 40 bytes + app layer overhead 32 bits type of ver head. len service length fragment 16-bit identifier flgs offset time to upper header layer live checksum total datagram length (bytes) for fragmentation/ reassembly 32 bit source IP address 32 bit destination IP address Options (if any) data (variable length, typically a TCP or UDP segment) E.g. timestamp, record route taken, specify list of routers to visit. 7 Router Architecture Two key router functions: Run routing algorithms/protocol (RIP, OSPF, BGP) Forwarding datagrams from incoming to outgoing link 4-8 Routers Input ports (line cards) Forwarding table lookup – line speed Queuing packets if switching fabric is busy • Head-of-line blocking? Switching fabric Via memory, bus, special interconnection Output ports Buffering & scheduling 9 Link state algorithm Broadcast local link info to all routers Dijkstra’s algorithm Greedy algorithm Compute the least cost path to every node Each loop finds at least one node whose least cost path is found Algorithm complexity? O(nlogn) Oscillation problem 10 Distance vector algorithm Distribute one’s view of network to neighbors Bellman-ford algorithm Dynamic programming Asynchronous update Problem? Count-to-infinity & routing loops Possible solution? 11 Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Autonomous System (AS) AS number – 16 bit id BGP contains full path from src to dest AS AS PATH – list of AS numbers How to prevent routing loops? Hot potato routing? One reason for routing path asymmetry How to deliver a packet from one AS to another? Intradomain (Intra-AS) routing Interdomain routing Forwarding table (FIB) 12 Chapter 5: Link Layer Delivering frames to a direct neighbor Error detection and correction Sharing a broadcast channel Reliable data transfer & flow control Hop-by-hop vs. end-to-end 13 Error detection & correction Parity checking Single bit vs. two-dimentional bit parity Odd/even parity Internet checksum – IP/TCP layer Why is error checking needed in the upper layer? Cyclic Redunancy Check (CRC) CRC32 is widely used (e.g., Ethernet) 14 Multiple Access Protocol How to share a broadcasting media Medium Acccess Control (MAC) protocol Channel Partitioning Random Access Taking turns 15 Random Access Protocol Slotted ALOHA Fixed time slot – synchronized If collision, retransmit with a probability of p for each slot ALOHA No slot synchronization CSMA, CSMA/CD, CSMA/CA CSMA – sense carrier before sending CD – detect collision while sending and cancel it CA – avoid collision by getting permission first Ethernet and Wi-Fi? 16 MAC addresses Ethernet: 48-bit MAC addresses Burned into hardware Globally uniquely assigned Why not use MAC address instead of IP? Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) Determining MAC address with IP address ARP table = <IP address, MAC address, TTL> Broadcasting mechanism (make sure to know!) 17 Ethernet & Switch Access protocol: CSMA/CD Old Ethernet hubs used to share access Understand the exponential back-off algorithm Most current devices are switches Connectionless, unreliable Frame format Preamble, 2 MAC address, type, data, CRC32 Switch Make sure you understand self-learning algorithm 18 Chapter 6: Wireless Difference from wired environment Signal attenuation Hidden terminal problem Interference from other sources (phone, microwave) SNR (Signal-to-Noise ratio) The larger, the better BER (Bit error rate) CDMA 19 Wi-Fi Access protocol : CSMA/CA Reserve the channel first before sending No collision detection – why? Understand the sending protocol Access Point(AP) Link layer device (may run DHCP) Passive/Active scanning for association 802.11 frame format Why we need three MAC addresses? 20 Chapter 7: Multimedia Quality of service guarantee Providing performance guarantee required by app Current Internet does not directly support it Delay sensitive, loss tolerant application Video streaming vs. Email? What is jitter? Multimedia application Stored streaming Live streaming Real-time interactive 21 Internet Phone, CDN Internet phone Network loss vs. delay loss Content distribution networks (CDNs) Definition? DNS redirection for finding the near server? 22