* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Physical and Data Link Layer
Telecommunications engineering wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Quality of service wikipedia , lookup
Communication protocol wikipedia , lookup
History of telecommunication wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunication wikipedia , lookup
Number One Electronic Switching System wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Number Five Crossbar Switching System wikipedia , lookup
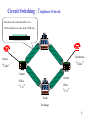
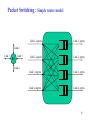
Physical and Data Link Layer Computer Network System Sirak Kaewjamnong 1 Network Devices 2 Circuit Switching A Source B Destination It’s the method used by the telephone network. A call has three phases: 1. Establish circuit from end-to-end (“dialing”), 2. Communicate, 3. Close circuit Originally, a circuit was an end-to-end physical wire. Nowadays, a circuit is like a virtual private wire: each call has its own private, guaranteed data rate from end-to-end. 3 Circuit Switching : Telephone Network Each phone call is allocated 64kb/s. So, a 2.5Gb/s trunk line can carry about 39,000 calls. Destination “Callee” Source “Caller” Central Office “C.O.” Central Office “C.O.” Trunk Exchange 4 Packet Switching A Source B R2 R1 R3 Destination R4 It’s the method used by the Internet. Each packet is individually routed packet-by-packet, using the router’s local routing table. The routers maintain no per-flow state. Different packets may take different paths. Several packets may arrive for the same output link at the same time, therefore a packet switch has buffers. 5 Packet Switching : Simple router model Link 1 Link 2 Link 3 R1 Link 4 Link 1, ingress Link 1, egress Link 2, ingress Link 2, egress Link 3, ingress Link 3, egress Link 4, ingress Link 4, egress 6 Why does the Internet use packet switching? • Efficient use of expensive links: – – – • The links are assumed to be expensive and scarce. Packet switching allows many, bursty flows to share the same link efficiently. “Circuit switching is rarely used for data networks, ... because of very inefficient use of the links” - Gallager Resilience to failure of links & routers: – “For high reliability, ... [the Internet] was to be a datagram subnet, so if some lines and [routers] were destroyed, messages could be ... rerouted” Tanenbaum Source: Networking 101 7 Packet Switching A B R2 Source R1 Destination R3 R4 Host A TRANSP1 R1 R2 R3 Host B “Store-and-Forward” at each Router TRANSP2 PROP1 TRANSP3 PROP2 TRANSP4 PROP3 PROP4 Minimum end to end latency (TRANSPi PROPi ) i 8 Packet Switching Why not send the entire message in one packet? M/R M/R Host A Host A R1 R1 R2 R2 R3 R3 Host B Latency ( PROPi M / Ri ) i Host B Latency M / Rmin PROPi i Breaking message into packets allows parallel transmission across all links, reducing end to end latency. It also prevents a link from being “hogged” for a long time by one message. 9 Common Data Link 10 LAN and WAN Layers Physical and Data Link layer for LAN and WAN 11 Medium Access Control • Protocol for controlling access to transmission medium • Defined as part of Data Link layer • The protocol performs: – Perform functions related to medium access (MAC sublayer) – Concerned with the transmission of a link-Level between two node (LLC sublayer) 12 IEEE 802.3 Operation • Every node can receive a transmission by all other nodes • Need addressing scheme to identify destination • Only destination copies frame to it, all other nodes discarded the frame 13 Token Ring / IEEE 802.5 14 IEEE 802.5 Operation Token ring LANs continuously pass a token or a token ring frame 15 Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI) Devices on FDDI maintain connectivity on dual ring 16 WAN Protocols • SDLC : Synchronous Data Link Control for IBM SNA network • HDLC : High Level Data Link Control common WAN data link • LAPB : Link Access Protocol, Balanced DTE to DCE data link for X.25 • Frame Relay framing for higher speed, reduce checking for higher speed • PPP : Point to Point Protocol part of TCP/IP stack for WAN links 17 SLIP : Serial Line IP • Method for encapsulation IP datagrams on serial line • Popular for connecting home computer to Internet, via modem • RFC 1005 de facto standard 18 SLIP Deficiency • Need manual configuration of IP address both side (no negotiation mechanism ) • Only one protocol can be used because there is no field to specify type of protocol • No checksum, bad for protocol that depend on CRC • Slow line make inefficient to carry only 1 byte data with 40 bytes overhead(IP + TCP header) – CSLIP (compress SLIP) reduces 40 bytes header to 3-5 bytes – smaller header greatly improve the interactive respond time 19 PPP : Point to Point Protocol • Methods for encapsulation IP datagrams on serial line, correct all deficiency in SLIP • Support either an asynchronous link with 8N1 or bit oriented synchronous link • Two parts: – LCP :(Link Control Protocol ) to establish, configure and test connection – NCP :(Network Control Protocol) support different network layer protocols 20 PPP Advantage • • • • Support multiple protocols CRC for every frame Dynamic negotiation of the IP address for each end Link control protocol for negotiating data-link options 21 Loopback Interface • • • • Channel for client and server on the same host use to communicate Class A network ID 127 is reserve for the loopback interface Most system assigns IP 127.0.0.1 with the name “ localhost ” Loopback interface appears as another link layer to the network layer 22 Summary • The physical layer provides access to the medium of an internetwork • The data link layer provides support for communications over several types of data links: – LAN (Ethernet, IEEE 802.X, FDDI) – Dedicated WAN (SDLC, HDLC,PPP,LAPB) – Switches LAN (X.25, Frame Relay, ISDN) 23