* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download sec overview
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
TCP congestion control wikipedia , lookup
SIP extensions for the IP Multimedia Subsystem wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Multiprotocol Label Switching wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Computer security wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Real-Time Messaging Protocol wikipedia , lookup
Routing in delay-tolerant networking wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
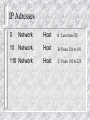
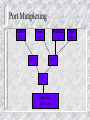
Internet and Network Security Introduction to Network Security Internet and Network Security What you should be able to do Describe the types of security attacks Identify the scope of the security problems Identify the need for establishing a security policy Identify the need to establish a required point of access for security purposes Overview Internet overview Describe the types of security attacks Identify the scope of the security problems Identify the need for establishing a security policy Identify the need to establish a single point of access for security purposes What is the internet ? 50 Million Plus users e-mail Usenet WWW Info super-highway e-commerce Collection of networks How the internet is Funded in the US Internet Services Provider (local) National Service Provider Educational or Research Networks Regional or State Networks Commercial Backbone Networks Network Access Points Internet Security Prevents unauthorized network access to resources Authorizes own personel to use the Internet Increasing use of cryptography to insure: - Privacy - Authentication - Integrity Complements system security Types of Attacks Intrusion Gaining Access Using the System Denial of Service Preventing the use of resources Sabotage Flooding a service or system Information theft Sniffing The Magnitude of Security Problems US Governement “The US DOD expereinced 260,000 computer system attacks last year. In nearly twothirds of the cases, attackers gained entry to the agency’s computer networks, according to a report by the Rand Corp.” IEEE Computer July 1996 Private Industry - According to a survey of 1,320 companies by Information Week/Ernst Young: 78% lost money from security breaches 63% suffered losses from viruses 32% lost money from inside hasckers 73% have no more than three people on secuirty Information Week, October 21, 1996 Don’t Forget 80% of break-ins are with passwords Poor System Configuration File system protection Physical security Internal Security Tapes, Floppies Modem Access Security Policy Set of Rules What is the proper use of resources Follows from the organizational needs Determines firewall design Management should issue a security policy Get RFC 1244 “Site Security Handbook” Providing Controlled Access Point Providing Controlled Access Point Firewall Corporate ip Network Internet TCP/IP Protocols Overview What this section is about This section review the TCP/IP protocol headers and their exposure in terms of security What you should be able to do Describe the following concepts in relation to security Layering Physical Layer IP Layer IP routing ICMP TCP/IP Protocols and Layers Applications Applications Transport TCP/UDP Internet IP Network Interface and Hardware ICMP ARP/RARP Network Interface and Hardware Layering Example: TFTP In each layer the payload contains a header and the payload of the layer above. The TFTP data contains for example 400 bytes of file data. The application protocol adds a TFTP header, which is 4 bytes large. TFTP uses UDP, so UDP header is presented. A UDP header is 8 bytes large. The IP header adds another 20 bytes. Finally, an Ethernet header and trailer are added. Those are 14 and 4 bytes large. If an IP packet arrives whose length is smaller than the combined length of all higher headers, the packet is of no use. If this happens as a result of some malicious intent, this is called the “tiny fragment” attack” File data tftp udp ip Header Ethernet header Ethenet trailer IP Header Version Length Type of Service Identification TTL Total Length Flags Fragment Offset Protocol Header Checksum Source IP Address Destination Address Options IP Options Intended for special handling above and beyond typical situations Many options obsolete Field is typically empty Source routing option specifies route instead of routers - Theory: useful in broken routing environment - Practice: used by hackers to circumvent security measures Recommendation: drop packets with IP option set IP Adresses 0 Network Host 10 Network Host B From 128 to 191 110 Network Host C From 192 to 223 A Less than 128 Fragmentation DF = don’t fragment MF = more fragments Accommodates dissimilar networks Fragment as you go Copy IP header, ID, and compute new (relative) offset Reassemble redone at the destination system using Source address ID Offset, last fragment has MF=0 Proceeding process is CPU intensive IP Forwarding Routers manage internal routing tables Each datagram inspected by router for destination address Router searches Database to determine which interface to forward the datagram IP Forwarding Principles Each packet is forwarded separately Many hops: form router to router Router forwards IP packet to next hop Based on routing table Packets may be fragmented Reassembly done by destination host Router overload - packet is dropped TTL - Time to Live field avoids infinite loops (decreased at each hop) Routing Protocols Every router knows optimal path through network This is used to compute the routing table Routing protocols distribute routing information RIP (Routing Information Protocol) OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) Risk - your router is sent false routing information Don’t allow any routing protocol through firewall Firewall uses static routing ICMP Messages Internet Control Message Protocol Network error messages do not make IP more reliable Essential when diagnosing network problems Each Message includes a type field and related code field Threat - bogus ICMP messages or broadcast storms when something is wrong ICMP Messages Message type Message type 3 code o echo reply 0 Net unreachable 3 Dest unreachable 1 Host unreachable 4 Source quench 2 Protocol unreachable 5 Redirect 3 Fragment needed and DF set 6 Echo 5 Source route failed 9 Router advertisement 10 Router solicitation 11 Time exceeded 12 Parameter problem 13 Timestamp 15 Information request 16 Information Reply Port Mutiplexing Named 53 Telenet 23 UDP Sendmail 25 TCP IP Data link physical Httpd 80 Socket Interface Socket interface to TCP/IP Socket system call Create, bind to address Use file descriptor such as read, write, close TCP Connection Localhost, local port Remotehost, remoteport TCP Reliable Connection Detection of lost data, or dat received twice Retransmissions of lost IP packets Sequence number in TCP header Each byte is numbered and acknowledged ACK (sequence number) in every packet except the first Retransmissions of lost IP packets Flow Control Window size Number of permitted outstanding (non acknowledged) bytes Client/Server Applications with TCP Server (“daemon”) listens on a “socket” (port) Client connects to that port TCP three way handshake SYN SYN, ACK ACK Establishes a connection Bi-directional connection Parties can read/write from/to socket Name Services (DNS) “www.company.com” > 123.45.67.89 telnet host.company.com mail [email protected] UDP- based:vulnerable Exposed internal configuration