* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Overview of Communications Technologies
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Multiprotocol Label Switching wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Remote Desktop Services wikipedia , lookup
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Serial digital interface wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Packet switching wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
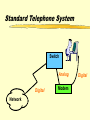
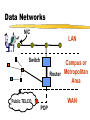
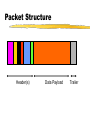
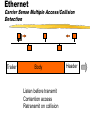
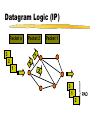
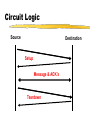
Basic Communications Overview of communication technology. Communications Electronically exchanging data or information. Voice interactive communication Data large volume batch transmissions Image encoded graphics Video streaming media Telecommunications History Pre 1984 Local and long distance monopoly 1984 AT&T settlement Intense long distance competition 1996 Telecommunications Act Local access competition Standard Telephone System Analog Switch Analog Digital Digital Network Modem Digital Telephone Changes Rapidly decreasing long distance rates Value added telephone services Cellular access Flat rate long distance? Data and voice convergence. Issue: Access Dedicated lines Standard voice Integrated Services Digital Network Digital Subscriber Lines Cable Modem Wireless Voice vs. Data Voice Delay Sensitive Constant bit rate Not error sensitive Growth stable (video ??) Data Delay insensitive Variable bit rate Error sensitive Demand growing Data Networks NIC LAN Switch Campus or Router Metropolitan Area WAN Public TELCO POP Packet Structure Header(s) Data Payload Trailer LAN Operating Protocols (layer 2) Ethernet open standard, cheap, most common Token Ring IBM proprietary, high quality, expensive Others Network Interface Cards Build, send out and accept frames Usually a daughter board on PC Must match LAN and CPU Require drivers to operate Network Interface Cards (NIC) Ethernet Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection Trailer Body Listen before transmit Contention access Retransmit on collision Header Network Routing Protocols for internetworking. Two major types Packet switching (or datagram) Usually layers 3 and 4 Circuit switching Usually layers 1 and/or 2 Packet switching or Datagram Protocols Best effort Frames take individual routes Packet assembly devices needed Error Control Traffic Management Buffering Discard Datagram Logic (IP) Packet n Packet 2 Packet 1 3 2 1 3 1 PAD 2 IP Best Effort Addressing Variable packet lengths (1500 bytes or less) IPv4 vs IPv6 Frame and Header TCP and UDP Transmission Control Protocol Connection oriented Assures that packets arrive in order and that they are correct. User Datagram Protocol Connectionless Sends packets out without confirming that they arrive Ethernet/TCP/IP Header Structure Circuit Protocols All packets take the same route No packet assembly device to reorder packets Normally layer 2 connection May be permanent or switched Allow guaranteed service quality levels May be used to carry datagram protocols Circuit Logic Source Destination Setup Message & ACK’s Teardown Internetworking Technologies Common WAN technologies. ISDN Circuit Switched Data and Voice Service Digital Subscriber Lines DSL uses packet switching technology that operates independent of the voice telephone system, allowing the telephone companies to provide the service and not lock up circuits for long calls. WAN Costs Circuit Charges Committed Bandwidth Peak Bandwidth Discard Priority Latency Representative Prices per MB of traffic (Qwest, Dec. 98) Frame Relay Non-discard eligible Discard eligible 4 cents 3 cents ATM Constant bit rate Variable bit rate (real-time) Variable bit rate (non real-time) Available bit rate Unspecified bit rate 2 cents 1.2 cents .75 cents .55 cents .4 cents Representative Prices per port (Qwest, Dec. 98) 56 Kb Frame Relay T-1 Frame Relay T-3 Frame Relay $190 $1,595 $3,190 Client/Server Architecture An architecture in which the client (personal computer or workstation) is the requesting machine and the server is the supplying machine, both of which are connected via a network. Client/Server Architectures FAT CLIENT FAT SERVER SERVER PROCESSING CLIENT PROCESSING CENTRALIZED STAND-ALONE Client/Server Scalability Interoperability User buy-in Increased cost Multi-tier One Tier System Two Tier Client/Server Three Tier Client/Server Application Issues Interoperability (e.g. ODBC) OS support Multi-threaded or single threaded Network impact (e.g. chattiness) QoS demands Delivery: centralized, clien/server, web Application Management Standards Supported Accepted Prohibited Version Control and Distribution License Management Virus detection and inoculation