* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Networks, Interfacing & Handshaking
Computer security wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
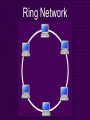
A-Level Computing networks, protocols and interfacing Objectives • Know what a basic network consists of • Understand the benefits of using a network • Know how devices connect and communicate over a network Interfacing • Computer devices all work differently • Need to connect to each other and same computer • An interface is the hardware and software needed for the processor to be able to communicate with a device Interfacing • Processors and in turn computers are being developed all the time • Devices on one computer must be able to talk to another • It is important to adopt standards so that if the processor changes then the device can still communicate Interfacing • Sometimes the interface hardware comes on an interface board, which has to be fitted into a computer • The device can just be connected to a socket. This is the port through which signals to and from the device travel Interfacing • Most PCs come with at least a serial port (for mouse or modem) • Being replaced by a USB (Universal Serial Bus) port. Handshaking • When two devices need to communicate, one device sends a message to the other.... 'Are you ready to receive data?' • When the other is ready, it sends a signal back to the first device.... 'Yes, I am ready to receive data' • ...and then communication can begin Networks • A network consists of a number of computers and peripherals connected together Networks • hardware can be shared (eg.a number of computers can use the same printer) • software can be shared (eg a number of workstations can all load up a program from a file server) • data can be shared (eg a number of computers can access the same database stored on a file server) • computers may communicate between each other (messages / email Networks • viruses can be spread to all computers on a network • hackers may access computers on a network. • network failure means nobody can use the computers • networks may be slower than using standalone computers • complex cabling may be expensive to install Local Area Network • A LAN (local area network) is a method of connecting computers together in a small area • Building or small site • Computers and peripheral devices are linked via physical connections (cables) Topologies • The physical layout of a network • How computers (nodes) connect to one another • Bus Network • Star Network • Ring Network Star Network Star Network • Each node is connected to a host computer • The host controls the network • WAN with big mainframe computers use this topology Star Network • Pros: • If one cable fails, the whole network doesn’t • Easy to isolate faults • Consistent performance • Each node has its own connection to the server • Messages sent directly, more secure • Simple to extend Star Network • Cons: • Costly to install (length of cable) • Cabling is major cost in networking • Distributed star networks are collection of ‘stars’ connection boxes linking a ‘string’ of stars Bus Network Bus Network • Common in a LAN • All devices share a single cable • Data travels in all directions from one computer to another • Works well if ‘channels’ on network are too crowded Bus Network • Pros: • Very cheap and easy to install • Easy to add more nodes to network without disruption • Cons: • Cable goes down....whole network breaks! • Hard to isolate faults • Heavy load of traffic slows network down Ring Network Ring Network • No central computer controlling the network • Every computer communicates with any other in the ring • Sends messages with an address • Messages passed in one direction Ring Network • Pros: • No depending on central computer • Transmission of signals nice and simple • Can send lots of signals • Cons: • one node breaks....cant send signals Mesh Network Mesh Network • Every computer acts as a router to every other computer • Nodes can break down but signals can still be passed to others • Very expensive when using network with lots of nodes Wide Area Network • A WAN (wide area network) is a network over a large scale (city-city, countries etc.) • Can be made up of connected LAN’s • Connected by telephone or satellite links Wide Area Network • Public telephone network • Dedicated leased lines • Radio Waves • Fibre Optic Cable • Microwaves (limited to 30 miles apart) • Satellites orbiting planet Earth Modems • Sending data over long distances • Internet using phone lines • Modems convert digital signals on computer to analogue to transmit over phone lines • Modem at other node converts analogue back to digital Standards • It is important that networks adopt standards • Common methods of sending data and consistent data formats. • If they did not operate in the same way the workstations would not be able to communicate with each other. Standards • http://www.bbc.co.uk • HTTPs: HyperText Transfer Protocol, used for a website over the internet • FTP: File Transfer Protocol • VoIP: Voice over Internet Protocol Wireless Networks • Radio waves can be used to transmit data from one computer to another. • Wireless networks are becoming very popular as there is no need to lay a lot of cables. • Each computer in a wireless network needs a wireless network card installed. • A wireless hub is connected to the network and transmits and receives data from the computers. Wireless Networks Wireless Networks • Pros: • no need for cabling. • computers can be used anywhere within range of the signal. • For example laptops can be moved around and still use the network. Wireless Networks • Cons: • data transmission speeds can be slow. • data signals can only be received within a limited range. • security may be a problem as people may be able to pick up the data signals outside your premises. • Careful setting up of the network is needed.