* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CBA Hardware,Software, and - CBA-Survival
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
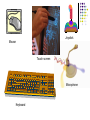
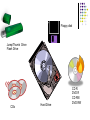
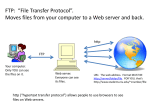
Hardware/Software Telecommunications Introduction A computer system consists of hardware and software Hardware is anything you can touch (ex. Mouse, monitor, and keyboard) Software is step by step instructions that performs a specific task (ex. Internet, Games, Word) Executing is when the computer uses software to perform a specific task You must have both hardware and software to make a computer work. System unit – a computer case that contains the CPU, power supply, memory, and storage HARDWARE Input Devices Peripheral device Mouse Keyboards QWERTY is standard Ergonomic– helps relieve stress caused by repetitive actions. Carpal Tunnel Speech recognition– talk into the computer Roller ball Optical Must have software and microphone. Touch screens– Self check at Walmart Joystick Mouse Touch screen Microphone Keyboard Output Devices Output device – allows the user to view or listen to the data a computer processes. Monitor– produces a soft copy Printers– produces a hard copy Impact– strikes paper– dot matrix Non-Impact– laser and inkjet Plotters– pens to draw graphics on paper Speakers Monitor Speakers Laser Printer Plotter Inkjet Printer The Central Processing Unit Central Processing Unit (CPU) – executes commands from a computer's hardware and software; the principal computer chip that contains several processing components, which determines the computer's operating speed; CPU- two parts ALU– Arithmetic and Logic Unit– Math Control Unit– the boss CPU– the brain of the computer Placed on a silicon chip known as the microprocessor Machine Language Machine Language– Binary number system 0’s and 1’s. 1 is electric current is on O is electric current is off Bit is a 0 or 1 Byte is 8 bits ASCII– American Standard Code for Information Interchange Primary Storage Memory - computer chips that store data and programs while the computer is working; often called RAM or Random Access Memory Main storage, Main memory RAM– Random Access Memory– can be changed—volatile ROM—Read Only Memory– cannot be changed– non-volatile KB– 1 thousand MB—1 million GB- 1 Billion Secondary Storage Storage device – external hardware used to store and retrieve data. Magnetic Media– Hard disks, disks, and tapes Hard disks—stack of round disks Diskettes---3 ½ Tape – sequential access—used for backup Optical Storage CD’s—uses laser to write data CD-Rs and CD RW must have a cd burner DVDs Jump Drives and Memory Cards Floppy disk Jump/Thumb Drive Flash Drive CDs Hard Drive CD R DVD R CD RW DVD RW Categories of Computers Supercomputers– fastest– used by scientist and weather Mainframes– slower, less powerful– used by businesses, hospitals, and colleges Minicomputers– slower– used by small businesses Microcomputers– what we use Portables– Laptops, PDAs Compatibility Software must be compatible with hardware and vice versa. Examples Microsoft and IBM compatible Macintosh compatible Software System software – software responsible for the general operation of a computer system, including the operation of hardware, running application software, and file management OS– operating systems/System Software Examples: BIOS, Microsoft Windows, Mac OS X, Linux, or utility software Booting– starting up a computer system by loading the OS Warm boot– CTRL+ALT+DEL Cold Boot– use power button Operating System Operating system - system software that acts as a "go-between", allowing computer hardware and other software to communicate with each other DOS– command Line Interface GUI– Graphical user interface– Windows Multitasking– ability to do more than one task at a time Windows Vista Windows 7 Application Software Application software – computer software created to allow the user to perform specific a job or task Examples: Word processing, Spreadsheets, Database, and Graphics software Office 2007 is a integrated software package Includes Outlook--Email Word—Word Processing Excel--Spreadsheet Access--Database PowerPoint--Presentation Publisher—Desktop Publishing Frontpage– creates web pages PowerPoint 2007 Excel 2007 Office 2007 Word Save and Save As Save – storing data for later use Save As – a feature that allows the user to change the attributes of a file (such as location, file name, or file type) before saving it. File management – A program on a computer that allows the user to create, edit, view, print, rename, copy, or delete files, folders, or an entire file system File type – an extension at the end of a file name, indicating which application was used to create a document Examples: Word files end in .doc and Excel files end in .xls Network Network– two or more computers connected together to share information. Can be Wired or Wireless Logon – the action of gaining access to a computer or a network by entering a username and password; also called Login/Sign In LAN– Local Area Network. Limited geographical area. WAN– Wide Area Network– City, State, Country Networks Telecommunications – transmitting information and communicating electronically Intranet – a company's private network of computers Example: School Network. Protocol – the rules that must be observed for two electronic devices to communicate with each other. HTTP: Hypertext Transfer Protocol You can send and receive Web pages over the Internet because Web servers and Web browsers both can understand HTTP. Networks Online – computers that are connected and ready to receive and/or transmit data Stand alone – a computer that is not connected to a network Electronic mail (e-mail) – transmission of messages and files using a computer network Fax – a document generated by using a facsimile machine Internet Internet is the largest network ISP– Internet Service Provider– Verizon, WASP wireless, WildBlue, Ritter Examples include Dialup Cable DSL Wireless WWW. World Wide Web (WWW) – a system of computers that share information by means of links on web pages Internet Uniform Resource Locator ( URL) – Internet address that identifies hypertext documents Every Web site has a unique address called a Uniform Resource Locator or URL. The first part of an URL indicates the protocol required to access the page. The second part of an URL specifies the IP address or a domain name. The top-level domain at the end of the URL indicates the type of organization or business. The Parts of an URL The protocol indicates what rules are used to transmit and interpret the Web page codes. The domain name http://www.smithsonian.org This indicates that the site is on the Web. The domain extension indicates what type of organization sponsors the Web site. Careers in Computers All careers involve a computer School degrees Computer programming Computer Engineering Computer Repair Software Design CAD– Computer Aided Design CAM– Computer Aided Manufacturing Web Design Computer Game Designer Popular Jobs Systems analysts Computer operators– use programs and devices to conduct business with computers. Teachers Office Management Computer Programmers– write software Microsoft Game Designers Future New technology changes everyday. Technology is updated every 72 hours. Cell Phones– Smart phone– Had laptop possibilities. Netbooks– small, portable computers Wireless Internet McDonalds, Burger King, Starbucks, etc Computers are becoming smaller, powerful, and have more memory and hard drive space. Touch Screens The End