* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Presentation: the internet layer, IP, the Internet Protocol
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Net neutrality wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Net neutrality law wikipedia , lookup
Multiprotocol Label Switching wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
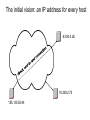
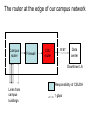
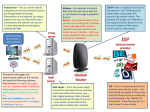
The internet layer Skills: None IT concepts: layered protocols, the internet layer, IP protocol, router, dumb (“end-toend,” “neutral”) networks This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoncommercialShare Alike 3.0 License. Where does this topic fit? • Internet concepts – Applications – Technology (Communication) – Implications for • Internet skills – Application development – Content creation The initial vision: an IP address for every host 63.80.4.26 18.238.2.75 155.135.55.94 The TCP/IP protocol layers There are two transport layer protocols, TCP and UDP. Web applications use TCP because it checks for errors and controls speed. Application Get useful work done – retrieve Web pages, copy files, send and receive email, etc. Transport Make client-server connections and optionally control transmission speed, check for errors, etc. Internet Route packets between networks Data link Route data packets within the local area network Physical Specify what medium connects two nodes, how binary ones and zeros are differentiated, etc, The Internet consists of connected networks Each network has a router at its edge The router at the edge of our campus network Campus router Firewall CSU router AT&T Data center Downtown LA Responsibility of CSUDH Links from campus buildings 1 gbps A client has a packet to send to a server The client and server are on different, Internet connected networks, so the packet must be routed across the Internet. It is sent across the LAN to the router (using a data link protocol) There are four possible outgoing routers. The LAN router picks the “best” of the four It uses information in local tables and makes a new decision for each packet. Each router does the same thing The next “hop” ... The packet reaches the destination network’s router And is delivered to the server (using a data link protocol) The complete route What happens if something goes wrong? Perhaps a router breaks or is over capacity or a cable is cut IP routes around the problem By design, the Internet is dumb The Internet The telephone network The telephone network is smart The internet layer Skills: None IT concepts: layered protocols, the internet layer, IP protocol, router, dumb (“end-toend,” “neutral”) networks This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoncommercialShare Alike 3.0 License. A few questions • We asked what happens when something goes wrong – what sorts of things might go wrong? • Would the route from host A to B necessarily be the same as the route from B to A? • Might routes between two hosts change during the day? • Might the time to traverse a route vary during the day?