* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 2 - William Stallings, Data and Computer
IEEE 802.1aq wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
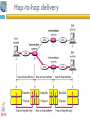
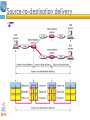
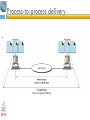
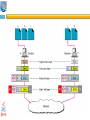
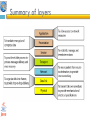
1 Protocol Architecture, TCP/IP, and Internet-Based Applications Data and Computer Communications by William Stallings Eighth Edition Networks and Communication Department Click to 2edit Master subtitle style Chapter Need For Protocol Architecture data exchange can involve complex procedures. better if task broken into subtasks implemented separately in layers in stack each layer provides functions needed to perform functions for layers above using functions provided by layers below layers communicate using a set of rules known as a protocol. TCP/IP Protocol Architecture developed by US Defense Advanced Research Project Agency (DARPA) •for ARPANET packet switched network •used by the global Internet • 1) TCP/IP Layers 5.Application layer 4.transport layer 3.Network layer 2.Data link layer 1. Physical layer Physical Layer The physical layer is responsible transforming data into bits. concerned with issues like: • characteristics of transmission medium Representation of bits and signal levels: how 0,1 are changed to signals. data rates: number of bits sent per second and duration of bits. Synchronization of bits. Data link Layer The data link layer is responsible for moving frames from one hop(node)to the next •It adds a header to the frame to define the sender and the receiver of the frame. •Using physical address(MAC) : the local address of a node as defined by its LAN pr WAN. •concerned with issues like: -Flow control -Error control • Data link Layer The data link layer is responsible for moving frames from one hop(node)to the next Hop-to-hop delivery Network layer Network layer is responsible for the delivery of packets from the source host to the destination host across multiple networks. •using IP address: 32-bit address that uniquely define a host connected to the internet. •routers connect two networks and relays data between them • Source-to-destination delivery Transport Layer (TCP) Delivery from a specific process on a computer to specific process on the other •Using Port address: 16-bit address to choose among multiple processes on the destination host. • Process-to-process delivery Application Layer Enables the user to access the network • Addressing Requirements Three levels of addressing required: •each host on a subnet needs a unique global network address its IP address •each application on a (multi-tasking) host needs a unique address within the host known as a port address • Physical address 2) OSI Open Systems Interconnection •developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) •has seven layers • OSI Model Session layer •The session layer is responsible for dialog control and synchronization . •Establish, manage ,terminate session Presentation layer •The presentation layer is concerned with the syntax and semantics of the information exchanged between two systems Summary of layers