* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download งานนำเสนอ PowerPoint
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Computer security wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
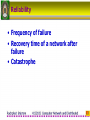
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
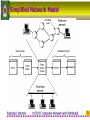
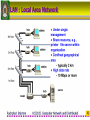
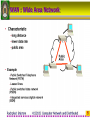
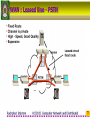
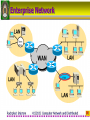
4122102 : Computer Network & Distributed Computer Network and Distributed Rachphat Sriprom Rajabhat Institute Chandrakasem 1 Computer Network • A network is a set of devices (nodes) connected by media links • A node can be a computer, printer, etc. • The links are called communication channels 2 Simplified Network Model 3 LAN : Local Area Network 4 WAN : Wide Area Network 5 WAN : Dial On Demand-PSTN 6 WAN : Leased line - PSTN 7 WAN : PSDN 8 WAN : ISDN 9 Enterprise Network 10 Network Criteria 11 Performance The performance of a network depends on a number of factors ; • • • • Number of users Type of transmission medium Hardware Software 12 Reliability • Frequency of failure • Recovery time of a network after failure • Catastrophe 13 Security • Unauthorized access – For a network to be useful, sensitive data must be protected from unauthorized access. Protection can be accomplished at a number of levels • Viruses – A good network is protected from viruses by hardware and software designed specifically for that purpose. 14 Computer Networks & Computer Communications • Computer Networks: two or more computer interconnected via a communication network • Computer Communications: the exchange of information between two computers for purpose of cooperative action 15 Communications Tasks • Transmission system utilization • Interfacing • Signal generation • Synchronization • Exchange Management • Error detection and correction • Flow control • • • • Addressing Routing Recovery Message formatting • Security • Network management 16 Protocols • Protocol - a set of rules governing the exchange of data between two entities in a system • Must speak the same language • Entities • Systems – User applications -Computer -Terminal – e-mail facilities -Remote sensor – terminals 17 Key Elements of a Protocol • Syntax – Data formats – Signal levels • Semantics – Control information – Error handling • Timing – Speed matching – Sequencing 18 Protocol Data Unit (PDU) 19 Protocol Data Unit (PDU) • The sending application generates a block of data and passes this to the transport layer • Each of these blocks the transport layer appends a transport header, containing protocol information • The combination of data from the next higher layer and control information is known as a protocol data unit (PDU) 20 Encapsulation in PDU • Addition of control information to data – Address information – Error-detecting code – Protocol control 21 Protocol Data Unit (PDU) 22 Standard or Nonstandard 23 OSI Model • The Open Systems Interconnection model is a layered framework for the design of network systems that allows for communication across all types of computer systems • It consists of seven separate but related layers • An ISO standard ISO is the organization. OSI is the model. 24 OSI seven layers • • • • • • • Application layer Presentation layer Session layer Transport layer Network layer Data Link layer Physical layer 25 OSI layers 26 The OSI Environment Headers are added to the data at layers 6, 5, 4, 3, and 2. Trailers are usually added only at layer 2. 27 Functions Of The Layers • Physical Layer – Physical interface between devices • Information Transmission • Medium & Signal • Mechanical (Connector) 28 Data Link Layer • Control the information transfer over Physical link • Physical addressing • Framing • Flow control • Error control • Synchronization • Access control 29 Data Link Layer Figure shows Framing 30 Data Link Layer Example 31 Network Layer • The network layer is responsible for the source-to-destination delivery of a packet possibly across multiple networks (links) • Switching & Routing • Logical Addressing • Higher layers do not need to know about underlying technology • Not needed on direct links 32 Network Layer Example 33 Network Layer Example 34 Transport Layer • Control for information transfer between end user system • Segmentation & Reassembly • In sequence • Connection control • Flow control • Error control • Quality of service (QoS) 35 Transport Layer 36 Transport Layer Example 37 Session Layer • Control of dialogues between applications in end systems • Dialogue discipline (full duplex or half duplex) • Grouping • Recovery 38 Presentation Layer • The presentation layer is concerned with the syntax and semantics of the information exchanged between two systems – Data formats and Encoding – Data compression – Encryption (senders transforms the original information to another from and sends it out over the network) 39 Presentation Layer 40 Application Layer • The application layer provides user interface and support for services such as electronic mail, remote file access and transfer, shared database management, etc. – Network virtual terminal (allows a user to log on to a remote host) – File transfer, access, and management (FTAM) – Mail services – Directory services 41 Application Layer 42 Summary of Layer Functions 43