* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 1 - William Stallings, Data and Computer
Quality of service wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Packet switching wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunications in Russia wikipedia , lookup
History of telecommunication wikipedia , lookup
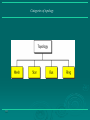
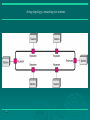
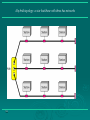
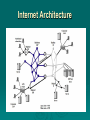
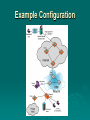
Data Communications Chapter 1 – Data Communications, Data Networks, and the Internet Eighth Edition by William Stallings Data Communications, Data Networks, and the Internet The fundamental problem of communication is that of reproducing at one point either exactly or approximately a message selected at another point - The Mathematical Theory of Communication, Claude Shannon Contemporary Data Comms Trends influenced by: traffic growth at a high & steady rate Requirement / development of new services advances in technology significant change in requirements led to: emergence of high-speed LANs corporate WAN needs Use of digital electronics A Communications Model Key Communications Tasks Transmission system utilization Addressing Interfacing Routing Signal generation Recovery Synchronization Message formatting Exchange management Security Error detection and correction Network management Flow control Data Communications Model Transmission Medium selection internal use entirely up to business long-distance links made by carrier rapid is a basic choice technology advances affects choice fiber optic – high capacity, getting cheaper Wireless - mobility transmission cost is still high hence interest in efficiency improvements – multiplexing and compression Networking growth of number & power of computers is driving need for interconnection also seeing rapid integration of voice, data, image & video technologies two broad categories of communications networks: Local Area Network (LAN) Wide Area Network (WAN) Wide Area Networks span a large geographical area rely in part on common carrier circuits alternative WAN technologies used include: circuit switching packet switching frame relay Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) Circuit Switching uses a dedicated communications path established for duration of communication comprising a sequence of physical links with a dedicated logical channel eg. telephone network Packet Switching data sent out in sequence small chunks (packets) of data at a time packets passed from node to node between source and destination used for terminal to computer and computer to computer communications Frame Relay packet switching systems have large overheads to compensate for errors modern systems are more reliable errors can be caught in end system Frame Relay provides higher speeds with most error control overhead removed Asynchronous Transfer Mode ATM - evolution of frame relay fixed packet (called cell) length with little overhead for error control anything from 10Mbps to Gbps constant data rate using packet switching technique with multiple virtual circuits Local Area Networks smaller scope Building or small campus usually owned by same organization as the attached devices data rates much higher within switched LANs, eg Ethernet wireless LANs Metropolitan Area Networks MAN middle ground between LAN and WAN private or public network high speed large area – city or metro Types of connections: point-to-point and multipoint 1.16 Categories of topology 1.17 A fully connected mesh topology (five devices) 1.18 A star topology connecting four stations 1.19 A bus topology connecting three stations 1.20 A ring topology connecting six stations 1.21 A hybrid topology: a star backbone with three bus networks 1.22 # In a network with 25 computers, which topology would require the least extensive cabling? Mesh Star Bus Ring # For six devices connected in mesh, how many cables are needed? How many ports are needed for each device? # What is the consequence if a connection fails for five devices arranged in: a) Mesh b) Star (excluding hub) c) Bus d) Ring The Internet Internet evolved from ARPANET first operational packet network applied to tactical radio & satellite nets also had a need for interoperability led to standardized TCP/IP protocols Internet Elements Internet Architecture Example Configuration MCQ The protocol/medium/signal/all the above is the physical path over which message travels. The information to be communicated in a data communications system is the medium/protocol/message/transmission. Frequency of failure and network recovery time after a failure are measures of the performance/reliability/security/feasibility of a network. Summary introduced data communications needs communications model defined data communications overview of networks introduce Internet