* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BCS433 Data Communication & Networking
Net neutrality law wikipedia , lookup
Computer security wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Multiprotocol Label Switching wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
UniPro protocol stack wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
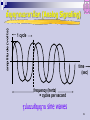
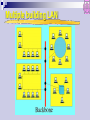
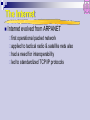
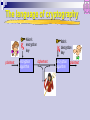
ICT+ Introduction to Networks ั ์ ม ังสงิ ห์ ดร. สุรศกดิ URL: E-mail: [email protected] [email protected] http://www.spu.ac.th/~surasak.mu 1 ICT+ Agenda SUN 06/07/51 (0900-1200): Overview (1300-1600): Network Topology and Basic Protocols SAT 12/07/51 (0900-1200): Principle of Data Communication SUN 13/07/51 (0900-1200): Guided and Wireless Networks (1300-1600): Networking Devices and Software and the Internet SAT 19/07/51 (0900-1200): Switching and Routing SUN 20/07/51 (0900-1200): Network Security (1300-1600): Examination ICT+ Introduction to Networks Overview ื่ สารระยะไกล: โทรคมนาคม การสอ ั หลักการทางไฟฟ้ าเพือ อาศย ่ ทาให ้เกิดการสง่ ผ่าน ข ้อความติดต่อ ี ง อัตราเร็วของแสง vs ความเร็วของคลืน ่ เสย ี ง : ~ 670 ไมล์ ต่อ ชว่ ั โมง - ความเร็วคลืน ่ เสย - ความเร็วของแสง : ~ 186,000 ไมล์ ต่อ วินาที Bandwidth (แถบความกว ้าง): เกีย ่ วข ้องปริมาณข ้อมูล ่ งทางการ และ ความสามารถในการสง่ ผ่านข ้อมูลผ่านชอ ื่ สาร (channel) ทีน สอ ่ ามาใช ้ แต่ไม่เกีย ่ วข ้องกับคุณภาพ ื่ สาร ของการสอ 4 ื่ สารข้อมูลทางอิเล็คทรอนิคส ์ การสอ ให ้ความสนใจกับอุปกรณ์ทางานในลักษณะเก็บบันทึกข ้อมูลพักไว ้ ก่อนทีส ่ ง่ ผ่านต่อไปด ้วยความเร็วสูง (store and forward) ้ ตัวอย่างการสง่ ผ่านข ้อมูลทีใ่ ชเทคนิ ควิธแ ี บบ ่ E-mail, voice mail, Store-and-forward เชน Facsimile, file transfer และ WWW 5 amplitude (volts) ั สญญาณอะนาล็ อก (Analog Signaling) 1 cycle time (sec) frequency (hertz) = cycles per second ั ญาน sine waves รูปแบบสญ 6 ั สญญาณอะนาล็ อก (Analog Signaling) 7 ข้อมูลดิจต ิ อล (Digital Data) ั ลักษณ์ เชน ่ (1 หรือ 0) แทนข ้อมูลด ้วยสญ ่ งทางสอ ื่ สาร (channel) วัด อัตราและความสามารถในการสง่ ผ่านชอ ่ โมเด็ม มีอต อยูใ่ นหน่วย บิท ต่อ วินาที (bit per second) เชน ั ราการ สง่ ผ่านข ้อมูล 56 Kbit / sec. (56 * 1000 bps) ข ้อมูลดิจต ิ อลถูกแทนในรูปแบบไบนารี โดยใช ้ 0,1 ข ้อมูล 0, 1 ได ้มาจากการแทน ระดับแรงไฟฟ้ าทีเ่ ปลีย ่ นแปลงใน ชว่ งเวลาหนึง่ Bit: มาจาก Binary Digit คือ เลขฐานสองหนึง่ ตัว ิ 1 คือค่า 1 ในระบบเลขฐานสบ ิ 10 คือค่า 2 ในระบบเลขฐานสบ ิ 10011001 คือค่า 153 ในระบบเลขฐานสบ Byte ประกอบด ้วย 8 บิท 8 จานวนบิต และจานวนค่าทีส ่ ามาถแทนได้ Number of outcomes Number of bits Typical uses 1 2 Basic unit of information 4 16 Hexadecimal digit 10 1,024 Byte: character with parity bit 20 1,048,576 Number of bytes in kilobyte of storage 32 4,294,967,296 Address size 64 18,446,744,073,709,551,616 Modern address size หน่วยของข้อมูล Storage Term Abbreviation Number of bytes Kilobyte KB 1 thousand Megabyte MB 1 million Gigabyte GB 1 billion Terabyte TB 1 trillion Petabyte PB 1 quadrillion 10 ื่ สาร VIViD รูปแบบข้อมูลสอ Voice Image Video Data text graphics video audio 11 Communications Tasks Transmission system utilization Interfacing Signal generation Synchronization Exchange management Error detection and correction Flow control Addressing Routing Recovery Message formatting Security Network management A Communications Model Data Communications Model Transmission Medium selection is a basic choice internal use entirely up to business long-distance links made by carrier rapid technology advances change mix fiber optic wireless transmission costs still high hence interest in efficiency improvements Networking growth of number & power of computers is driving need for interconnection also seeing rapid integration of voice, data, image & video technologies two broad categories of communications networks: Local Area Network (LAN) Metropolitan Network (MAN) Wide Area Network (WAN) Local Area Networks smaller scope Building or small campus usually owned by same organization as attached devices data rates much higher switched LANs, eg Ethernet wireless LANs LAN Topologies BUS STAR RING STAR-BUS Multiple building LAN Metropolitan Area Networks MAN middle ground between LAN and WAN private or public network high speed large area Metropolitan Area Networks Wide Area Networks span a large geographical area cross public rights of way rely in part on common carrier circuits alternative technologies used include: circuit switching packet switching frame relay Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) The X.25 Network 23 Circuit Switching uses a dedicated communications path established for duration of conversation comprising a sequence of physical links with a dedicated logical channel eg. telephone network Public Circuit Switched Network 25 Packet Switching data sent out of sequence small chunks (packets) of data at a time packets passed from node to node between source and destination used for terminal to computer and computer to computer communications Datagram Diagram 27 Virtual Circuit Diagram 28 Frame Relay packet switching systems have large overheads to compensate for errors modern systems are more reliable errors can be caught in end system Frame Relay provides higher speeds with most error control overhead removed Simple Frame Relay Network A Simple Frame Relay Network Connects Various Devices to Different Services over a WAN 30 Asynchronous Transfer Mode ATM evolution of frame relay fixed packet (called cell) length with little overhead for error control anything from 10Mbps to Gbps constant data rate using packet switching technique with multiple virtual circuits ATM Network Device An ATM network is made up of one or more ATM switches and ATM endpoints. An ATM endpoint (or end system) contains an ATM network interface adapter. Workstations, routers, data service units (DSUs), LAN switches, and video coder-decoders (CODECs) are examples of ATM end systems that can have an ATM interface 32 The Internet Internet evolved from ARPANET first operational packet network applied to tactical radio & satellite nets also had a need for interoperability led to standardized TCP/IP protocols The Internet: “nuts and bolts” local ISP router server regional ISP workstation mobile enterprise network Internet Elements Internet Architecture Example Configuration Network Security Alice data Friends and enemies: Alice, Bob, Trudy channel data, control messages secure sender secure receiver Trudy Bob data The language of cryptography Alice’s KA encryption key plaintext encryption algorithm Bob’s decryption B key K ciphertext decryption algorithm plaintext 40