* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download cfghk - WOCC 2015
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
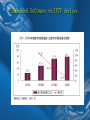
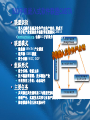
Embedded Computing and Software Platform for Wireless Networks Prof. Zhaohui Wu, Ph.D College of Computer Science Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, P.R.China Outline Embedded Software in China Embedded Software Industry in China: Status and Challenges Key R&D Projects about Embedded Software in China: 863 plan on software subject Embedded Computing: Status and Trend Sensor Networks are new Challenges Application Opportunity Technical Challenges for Embedded Computing Our Works on Embedded Software for SmartPhone Computing and Sensor Network Software Market in China (2004y) Package software(478亿元, 478,000,000,000) System Software(89亿元,89,000,000,000) OS(44.19亿元, 44190,000,000) Database Management System(20.06亿元, 20060,000,000) Software tools(25.71亿元, 25710,000,000) MiddleWare (6.98亿元, 6980,000,000) Application Software(304.53亿元,304,530,000,000) General Application Software(Security 、OA、MIS、 Game Software、CAI) Domain-Special Application Software(Telecom、 finance、government ) Embedded Software(673.62亿元, 673,620,000,000) Software Service and System Integration (937.48亿 元,937,480,000,000) Embedded Software Market in China(1) Embedded Software Market in China(2) Embedded Software in China : Summary The industry of embedded software is growing dramatically and plays a more and more important roles in software industry of China. The biggest market of Embedded Software is Telecom, including cell-phone, switch-class and Router-class devices. The three new domains for Embedded Software in next 5 years in China: Smart-phone(ep. For 3G), IPTV, and e-auto Embedded Software on mobile-phone Embedded Software: various Hand-held Devices within wireless connection for mobile computing Tablet PC Pocket PC Desktop PC Phone PC Wrist PC 无线连接 Embedded Software on IPTV devices Home-internet: new kind network for e-home IA Digital Home Renderer (DHR) Devices Digital Home Server (DHS) Devices Transparent Connectivity LCD TV Digital Media Adapter • • • • • Wi-Fi / Wireless Protocol Internet Protocol (IP) Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) Infrared Connectivity Streaming Media Video Transmitter Personal Video Player PC Multimedia Center MP3 Player DVD Player Personal Video Recorder Home Gateway Media Storage IP Camera Wireless Video Router Embedded Software on Auto-electron Embedded Software: mesh network for e-Auto 汽车电子:占整车价值的45%; 围绕嵌入式LAN的改造是未来汽车电子发展的趋势 The market of Embedded Software for Medical Device is also huge, wireless embedded network for Medical Device will have a new chance Medical Xray system – Dicom, Imaging Biomedical Instrumentation Medical Infusion Pump Embedded Software for Wearable Computing will become more important in future: body wireless network Overview about 863 plan on software subject 应用软件层 应用示范 开 源 社 区 测 试 体 系 技 术 标 准 中间件软件层 网络软件 运行环境 网络软件 开发环境 智 能 手 机 通 信 设 备 信 息 电 器 汽 车 电 子 面向领域的 嵌入式 软件平台 基础软件层 2017年5月25日星期四 数据库管理系统 办公软件 服务器操作系统 桌面操作系统 嵌入式 操作系统 15 The Goal and Tasks for 863 subject on Embedded Software Real-time Embedded OS and Component Ware Application-Specific Embedded Software Platform For Telecom, for e-home and e-Auto Telecom-Oriented Embedded Software Platform funded by 863 in the amount of 80,000,000RMByuan Cell-phone or smart-phone Switch-class Telecom Device Router-class Telecom Device Software Platform for new era network such as Ad hoc and Sensor Network will be considered next 5 years 863手机嵌入式软件联盟 863手机嵌入式软件联盟CMSTA 联盟宗旨 嵌入式操作系统及软件平台的产业化, 形成面 向手机产业链的技术辐射型联盟组织CMSTA (www.cmsta.org, 也称863手机软件技术联盟); 联盟模式 独裁制: WinTel 产业联盟 联邦制: OMG联盟 联合国制: W3C, GGF 组织形式 联合国型:轮值主持 技术辐射型联盟:技术辐射产业 开放性的工作组:动态运作 主要任务 共同制定共性规范接口与数据交换格式, 研制平台,实现技术共享与知识产权保护, 推动联盟单位互补双赢合作 863手机嵌入式软件联盟的主要工作 联盟工作 2003年4月科技部领导提议,2003年8月四家单位发起成立 目前联盟单位36个: 手机厂商:12家(中兴通信、波导股份、普天东信、海尔通信、TCL移 动通信、联想移动、南方高科、海信通讯、大唐移动、华为科技、康 佳、科健) 操作系统厂商:3家(凯思Hopen,科银京成Delta,SmartOs) 应用软件厂商:16家(汉王科技、中科模识、茁壮网络等); 运营商: 2家(中国移动、联通) 手机设计集成商:德信无线 召开联盟全会及工作组会议21次 制定了二个规范 863手机软件联盟CMSTA的嵌入式基础平台软件参考模型与规范 接口(推行版 1.0.4) 制定了手机软件联盟CMSTA的API符合性认证规范(A/B/C三级认 证) Trend of Embedded Computing Embedded OS: More tiny and flexible, component ware, real-time, high-performance, high reliability, More Security Power Aware Support: Just In time Power Development Environment IDE for Embedded Software: Model-based Design Visualization Integration Trend of Embedded Computing Embedded Software Platform Domain Specific Platform Open Standardization Common Component Builder Open Source Driver Java/Linux based Solutions Systematism Driver Integration of OS, Embedded Middleware, and Domain-Specific Platform Trend of Embedded Computing New areas: new challenges SOC(System on Chip): SoC and IP create new opportunities for embedded software industry. Internet integration: Deep-Embedded Network Sensor Network and Ad hoc network: upsetkind network need a new genus of embedded software Ubiquitous Computing Environment and Smart World Sensor Network: Ongoing features and Goals Tight constraints Computation power Storage Power supply Traffic pattern Little activity in life period Tense traffic in short time Highly correlated traffic Environment Dynamic changing Potential Applications Biomedicine Surgically implanted sensors monitoring a patient’s health Environmental monitoring Forest fire monitoring Local temperature gradients Spatially correlated temperature gradients Hazardous environment exploration Chemical concentrations Monitoring safety of children in neighborhood Military tracking, targeting Intrusion detection, identification (acoustic, imaging sensors) Spatially correlated troop, tank movement (seismic sensors) Monitoring foot paths: “Smart breadcrumbs” Inventory control Monitoring location of valuables in home Tracking inventory in ship-board containers Technical Challenges for Embedded Software Tight resource constraints Energy Communications range, bandwidth Computation, storage (but not as constrained as energy and communications – computation is often used to reduce communication) Dynamically changing bandwidth, range, and computation power Dynamically changing network topology Battery depletion Node failure Node mobility Unreliable links (noise, jamming) Interactions Computation constraints lead to uneven power depletion which leads to network topology changes Correlated bursts of traffic across neighboring nodes -- not a collection of independent point-to-point flows – violating the design assumptions of common media access protocols Ongoing Projects in Our Lab SMART: Our Vision about Embedded Computing and Systems SmartOS: Embedded Software infrastructure for Smart-phone Computing SmartScud: A Context-Aware Lightweight Embedded Software Platform for Sensor Network SMART:Our Vision SMART (Sub-coMponet ARchiteTure) Guidelines Embedded systems based on components of thingranularity flexible, optimized and customized Objectives high-quality codes high reliability real-time customized applications Application-specific OS SMARTOS: An CMSTA-compatible Embedded OS for Smartphone SMART Reference Model of SmartPhone System Application Software Cross-platform IDE Dynamically Application Abstract Layer G U I Multimedia Security Embedded DB Java & Internet SMART-EOS Resilient Communication Protocol Stack Process/Thre ad Management Time Management File Management Power Management Device Management Data Communication Communication Synchronization & Exclusion Management Universally Adjustable Hardware Abstraction Layer Embedded Operating System SMARTOS Highly reliable & component-based embedded OS ASOS (Application Specific OS) Model "Pipeline kernel" of 3rd-generation micro-kernel CMSTA-compatible Cross-platform IDE Model-based Design Tools Model Visualization SMART-IDE Editor Linker Debugger Simulating environment Plug-in toolkit Memory leaking analyzing tools Coverage checking tools Performance measuring tools Static code checking tools Embedded DBMS Concurrent control Real-time transaction commit protocol Data migration Online data update Database backup and recovery tools Memory-resident DBMS Flexibility design of DBMS Embedded Multimedia Multimedia network communication protocol stack component library Multimedia network communication device 26 BREW cellular phone games Embedded OS based audio, video, stream media support MP3 Cooperative Enterprises Bird(波导) UTStartcom(UT斯达康) Huawei technology(华为) ZTE(中兴) Start(实达) EASTCOM(东信) Ningbo Samsung(宁波三星) General Electric(美国通用 电气) Putian(普天) Mitsubishi(三菱) Holly Group(华立) Supor(苏泊尔) DITEL (迪科) SOYEA technology(数源科技) Cellular Phones DSP-based Video phone PDAs IP TV: internet-based Digital TV SmartScud: Lightweight Embedded Software Platform for Sensor Network SmartScud SmartOSEK: Tiny OS for Sensor Network ScudWare: Lightweight Middleware for Sensor Network Routing Algorithms for Sensor Network Applications Demo for Smart Space for Driver Further Applications on Environment Sensing and Monitoring SmartOSEK: embedded OS Project abstract: SmartOSEK Applications SmartDesigner OSEK-compliant Real-time Tiny Operating System Platform ECU The size of kernel <10k. The context switch time is less than 10us. Processors: AT89C51、 Intel 196、 FreeScale MPC555、 68HCS12、MSP430、Philips LPC2119、TI TMS320C2407、ADI Blackfin 533 etc. SmartOSEK IDE preemptive, non-preemptive group-based preemptive scheduling. CAN SmartEditor Project features Supporting three schedule schemes: AMT SmartOSEK OS SmartOIL SmartAnalyser SmartOSEK OS Kernel BSP SmartDebugger CAN Bus Driver SmartTracer SmartOSEK COM ADC Driver 8051 MPC555 HCS12 ARM MSP430 DSP SmartOSEK IDE SmartDesigner: the graphic modeling tool with graphic interface, component operation, automatic code generation and error detecting. SmartOIL: the graphic configuration tool with configuration and parsing of OIL files, graphic scalability and customization of the system kernel. SmartAnalyser: the graphic schedulability analysis tool. SmartTracer: the graphic tool which traces the running processes of the OS kernel and enables users to observe the kernel status in a step-bystep manner. The Context-based Lightweight Middleware Architecture for Sensor Network Project: ScudWare LightWeight Context-aware Reconfigurable Middleware Project overview The project is oriented to the heterogonous sensor network computing environment in dynamic changing. Scudware has the the properties of configurability, reusability, security and is compliant to mini-CCM specification. The research focuses on adaptive scheme with non-monotone QoS requirements and restricted resource and context management system. Features of ScudWare Component management Service Construction and Programming Mechanism Contextual infrastructure for Dynamically Changing Resource Adaptive resource configuration Demo for Sensing SmartSpace of Driver – ZCCM-based design – CAN Bus control devices Routing Algorithms for Sensor Networks(1) EDC[1]: An Event-Driven Clustering Routing Algorithm for Sensor Network suitable for the event-driven static distributed Sensor Networks ACHGT[2] :A Clustering Routing Algorithm Using Game-theoretic Techniques Individual sensors of the algorithm are modeled as players to make decisions about whether electing to become clusterhead nodes by using node energy payoff functions to weigh their own costs and benefits. This strategy can keep sensor nodes of lower remainder energy out of being used up quickly. Routing Algorithms for Sensor Networks(2) CRAM[3]: An Energy-Efficient Clustering Routing Algorithm using Multi-CHs-One-Cluster method for Sensor Networks selects Multi-CH nodes in every cluster together as one CH node to perform data fusion and data transmission to the BS so as to improve energy efficiency and enhance data transmission reliability Since one CH node in a cluster may be unreliable and cause energy losing in case of node failure or communication error. Thanks! Technical Challenges --Sensor Node Design Simplicity Cost Battery power battery replacement Deployment Resolution, accuracy, etc. Data sampling rates Clock sync Technical Challenges --Data communication and aggregation Wired vs. wireless communication Distances, bandwidth, multiple sensors Shared vs. dedicated channel access simple MAC protocol Routing through multi-hop networks Sensors are possibly stationary Sensors go into “sleep mode” to conserve energy Re-routing Technical Challenges --Sensor localization Each device has an factory-configured ID Network deployment is unplanned Location determination GPS-based Triangulation Etc. Technical Challenges -- Others Security (integrity, authentication, confidentiality) Data compression References [1] Zheng Zeng-wei, Wu Zhao-hui, Lin Huai-zhong, “An EventDriven Clustering Routing Algorithm for Wireless Sensor Networks”, 2004 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 2004), Sendai, Japan, September 28 - October 2, 2004. [2] Zheng Zeng-wei, Wu Zhao-hui, Lin Huai-zhong, “CLUSTERING ROUTING ALGORITHM USING GAMETHEORETIC TECHNIQUES FOR WSNs”, IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS 2004), Vancouver, Canada, May 23-26, 2004. [3] Zheng Zengwei, Wu Zhaohui, Lin Huaizhong, Zheng Kougen, “CRAM: an Energy Efficient Routing Algorithm for Wireless Sensor Networks”, 19th International Symposium on Computer and Information Sciences (ISCIS 2004), Kemer - Antalya, Turkey, October 27-29, 2004.