* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Networking
Net neutrality law wikipedia , lookup
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Policies promoting wireless broadband in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Computer security wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.11 wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Virtual LAN wikipedia , lookup
Network Concepts and Troubleshooting:
A field guide for understanding IP networks
Laren Metcalf - Dir. IP Services
Networking History
Ethernet – Started as 10 Mbit
Ethernet shared topology using coax cable, RG58 for thin net, RG-8 for thick net,
terminated with a resister on each end. Connect a station using a tap into the coax
10 Base 5 Thick net
Signalling
10 Base 2 Thin net
CSMA/CD –
Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detect
Shared media- Collision Detect
Check for idle on media
Send
Max distance 500 meters
(1640 ft) Max nodes 100
If collision stop transmission frame
Send Jam signal (32 bit binary pattern)
Wait a backoff period
Retry
NIC – Network Interface Card
MAC – Media Access Control. Each
device has a unique MAC address
Max distance 185 meters
(607 ft) Max nodes of 30
Networking History
Ethernet – 10 Base T, 100 Base T, 1000 Base T
Power Over Ethernet IEEE 802.3 af/at/
Ethernet over Coax was not flexible enough so 10 BASE-T developed using 8 wire standard
twisted pair cabling using pins 1, 2, 3, and 6. Gigabit uses all four pairs.
10 Base T RJ45 8 wire
Network Switch
Every port is a separate bridge domain.
Packets don’t go out all ports, only to the
destination MAC address
POE/POE+ Power Over Ethernet IEEE 802.3 af/at
IP Phone getting power from
network switch over RJ45
connection 5 Volts @ 7 Watts
Distance is 100 meters, 328 ft., extenders for distance
802.3 af max 15.4 Watts, 802.3at max 34.20 Watts
Voltage Range 44-57 V
Max Current 350 mA – 600 mA
4 Power class levels negotiated at initial connection
Wireless Access Point getting
Class/mA 0/0-4, 1/9-12, 2/17-20, 3/26-30, 4/36-44
power from the RJ45
Power extenders – boost power, boost noise
connection @ 15 Watts
Can use to go 200 meters, 300 meters, +
Better to get power and POE switch closer to device
Home Network
The fastest growing segment of the market. Simpler but still has to follow the rules
Outside carrier connection comes in through a modem
Connections are made in the back of the home router. It
could be a wireless device as well
WAN port
Speed issues, applications are driving speeds up on the edge,
then to the provider, then across the provider network.
Broadcom is coming out with a 2X2 MIMO chip, BCM4354 for
smartphones, Called 5G WiFi MIMO. Current chips are 1x1 MIMO.
Tablets
Smartphones
Smart TV
Appliances
Networking
Classification of Traffic
Each application on a network, data, voice, video, can have separate QoS
VLANS, virtual LANs, used to separate each application
Access Point
When using multiple applications that require isochronous,
consistent communications, Classify your data
Video VLAN – Traffic needs to be identified and prioritized
Voice VLAN – Devices need to be in a vlan with high priority
Data VLAN – Low priority data, web browsing, email
Access Point – Just like a switch offering connections
Voice VLAN – HIGH QoS
Data VLAN – Low QoS
Networking
Trunk vs. Access Ports
Trunk ports have multiple vlans and connect switch to switch, multiple vlans
If only one vlan is required on the port they can assign a vlan that applies to all traffic.
Untagged means no vlan embedded in them, port assigns vlan
Tagged Packets have the vlan imbedded in the packet using 802.1q
802.1q packet
Access Tagged
Voice vlan
Trunk
Access Tagged
Data vlan
Networking Media Types
Gigabit/10 gigabit/40 gigabit/ 100 gigabit Ethernet
10 Gbit SFP+ Fiber
1 Gbit SFP Fiber
550 m
10 GBASE-SR Short Range 850nm
400 m
SX
black/beige lever
850nm
LX
Blue extractor lever
1310 nm 10 Km
10 GBASE-LR Long Range 1310 nm 10 Km
EX
Blue extractor lever
1550 nm 40 km
10 GBASE-ER Ext Reach
1550 nm 40 km
ZX
Blue extractor lever 1550 nm 80 km
10 GBASE-ZR ZR Reach
1550 nm 80 km
40 Gbit QSFP+
40GBase -SR4 Short Range OM3/OM4 100/125m
40GBase-LR4 Long Range 1310 nm
10 Km
40GBase-ER4 Ext Reach
1310 nm
40 km
40GBASE-T Cat8 copper
4 pair Copper 30m
100 Gbit Fiber*
100GBase-SR4 Short Range OM3/OM4 00/125m
100GBase-LR4 Long Reach 1310 nm 10 km
100GBase-ER4 Ext Reach
1310 nm 40 km
* Remains a carrier platform. Vendors with products – Arista, Brocade, Huawei, Cisco (limited), Juniper (limited)
Wireless Networking
WiFi - 802.11 a/b/g/n/ac
802.11 a/b 11Mbit Old and slow. Devices using this require other wireless devices capable of faster speeds to slow down. 3 non overlapping channels.
802.11 g 54 Mbit (22.5 Mbit X 2), uses 2.4 GHz radio. Wide band (2 20MHz channels for a 40 MHz channel) for higher speed (simulated n), but it will
conflict with channels in multiple AP environment. 3 non overlapping channels. 802.11n in 2.4 GHz uses 82% of the channels – 40 MHz wide channels
802.11 n 72Mbit/150 Mbit MIMO allows 300Mb, 450Mb, and 600Mb. 5GHz. MIMO Most common is 3X3:3, 3 Tx antennas, 3 Rx antennas, 3 streams
802.11 ac 433.3 Mbit per stream, 1300Mbit total. 80 or 160 MHz channels versus 40 MHz in 802.11 n. Limited distance. Wider channels, more steams
Future – 802.11ad “WiGig” 60 MHz channels and 7 Gbit speed, 802.11af based on 802.11ac, geo discovery for optimal connection, 568.9 Mbit
MIMO - Spatial Multiplexing using multiple antennas Tx Rx : Strms
Requirements:
Adaptive Beamforming manipulates the phase and amplitude of the signal at each transmitter and
rejects unwanted signals
Precoding – Multi-stream beamforming, improves the received signal quality at the decoding stage,
spatial multiplexing creates spatial beam patterns in same frequency channel
Space-Time coding/processing – separates each antenna element
802.11n has max of 4X4 MIMO and channel width of 40 MHz.
8 spatial streams with 80 MHz channel width
256-QAM modulation, up from 64-QAM in 802.11n
Quadrupling spectral efficiency over 802.11n
Wireless Networking
WiFi – 2.4GHz
2.4GHz only has 13 channels (US) with 3 that don’t overlap.
Power and channel are critical for it to function in multi radio environment.
SNR –
Power determines the signal
to noise ratio critical for
communication
SNR of -40db Excellent, -25 to 40 very good, -15 to 25 low, -10 to 15 very low
Wireless Networking
802.11n 5GHz 7x more channels
5 GHz 24 non overlapping channels, use dynamic frequency selection (DFS) and transmit
power control (TPC) to avoid interference with weather radar and military applications.
Wireless Wifi
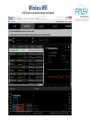
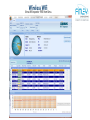
inSSIDr tool to see wireless power and channel
Wireless Wifi
Xirrus Wifi Inspector FREE from Xirrus
Break?
Next Section
OSI 7 Layer model
OSI 7 Layer model
Soup to Nuts - Everything
OSI 7 Layer model
Simplify - Break it Down
Load Balancers
Firewalls
Network Access
Specialized
Applications
OSI 7 Layer model
The dividing line between the end device and the network
Network Access
Example: TCP/IP
Transmission Control Protocol /
Internet Protocol
Example: LAN, WAN,
Wireless LAN, SONET, ATM
OSI 7 Layer model
TCP/IP Protocols
Example – FTP connection
Server
Client
Example – Email
Outlook client requests email data from the mail server
Security
Are Firewalls enough?
They’ve been around for 20+ years!!
Perimeter Defense is still needed, they’ve evolved and aren’t perfect.
Stateful Inspection – CBAC Context Based Access Control
Inspects packets from the external network, only allowing traffic when the connection is initiated
from the inside network. Examines network, transport, and application layer information, deep
packet inspection, DPI.
Platforms New platforms – Palo Alto, FireEye, granular network and device permissions. Application aware
Older - Checkpoint, Cisco, Juniper, Sonicwall, Fortinet, Watchguard
Linux – iptables Basis for most linux firewalls, packet filtering, IPCop, Shorewall (iptables with a
GUI), UFW (iptables netfilter). Don’t ignore Vyatta, m0n0wall,
Access List
Filter by IP address or transport protocol. Not a secure method to block traffic, no monitoring and
tracking of sessions, only ability to see hits on the access list rules.
NAT – Network Address Translation
One to one NAT, one to many NAT (conserve Ip addresses). Not a secure method to block traffic.
Security
Intrusion Detection/ Intrusion Prevention IDS/IPS
Detect it and you can address it
•
•
•
•
Systems are inline with traffic and monitor for attacks as they occur.
Must have a signature database – updates are critical
Day Zero attacks – How can they be detected?
Forensics – Capture the traffic and reconstruct what was compromised,
understand the scope and extent of the attack
• Seen as high end appliances, only in large enterprise and uber secure networks
• IDS/IPS components in security/firewall devices including wireless
• It only takes a signature database and DPI…
Security
Small and Midsize Companies vs Large corporations
• They do what they can – Anti Virus, Perimeter Firewall, compliance requirements
• Viruses and malware are spreading and evolving, attack patterns are changing
• Since 2008 viruses have taken off, come in through mobile device with corporate
email
• Do it yourself hacker kits, identify what they want to do – a whole new level of
sophistication
• Security companies get called in and block known attacks and find unknown
attacks only after forensics (decoding packet traces to and from devices)
• The nature of Wireless makes it easiest target. Aircrack tools for WEP and WPA
cracking just needs enough data to sift through to figure out the keys.
Types of threats
Malware
• Android OS – HEUR.Trojan-Spy- intercept SMS messages and upload to a server with encrypted URL –
Appears on Android phone as a Blue shield named Android Security Suite Premium
• Adobe PDF reader used to deliver malicious payloads which evade malware and intrusion detection
software, prior to version 9.
• Linksys/Cisco “Moon” worm connects to port 8080, loads a worm 2MB in size, scans for 670 different
networks, try to infect other systems, new code for fix, disable remote management.
• DDoS attacks – 100 Gbpsec using an old NTP command requesting data be sent to another server.
Amplification directs thousands of NTP servers to a targeted system. Up 371% in last 30 days.
• Mt.GOX, the worlds largest bitcoin exchange, coin stealer on MAC or Windows, TibanneSocket.exe,
seeks out bitcoins.conf and wallet.dat and send them to a command server in Bulgaria. Hackers
posted a zip file supposed to be a data dump and tools found on Mark Karpeles (Bitcoin’s CEO)
personal blog and reddit account that would allow access MtGox data but they turned out to be
Bitcoin wallet stealing malware.
• Facebook – ‘See your friends naked’ Over 2 million people fell for this. It showed a picture of one of
your contacts saying click here to see a video of them naked. Brought the user to a youtube page
stating they needed to upgrade their flash player, if they downloaded it malware loaded that steals
your photos and adds a browser extension to spread the scam.
Companies offer rewards
• Facebook and Microsoft rewards hackers finding security holes
• Wurm online offering $13,000 bounty for info on a DDoS attack
• Most hacking not reported, banks and institutions fear publicity
If you get caught…
• Hacker joined a DDoS attack for one minute and fined $183,000 for
causing website to be down for 15 minutes
• Hacker could face 10 years in prison for breaking into a intelligence
company, Stratfor
• Aaron Swartz’s worldwide attention for felony charges for hacking
MIT academic files led to his suicide.
Financial Malware most popular threat in 2013
1400 Financial Institutions in 88 targeted by Banking Trojan in 2013 337% increase
Antivirus firm Symantec has released a Threat report, called “The State of
Financial Trojans: 2013”. Over 1,400 financial institutions have been targeted
and millions of computers have been compromised around the globe with
71.5% of US banks as the most targeted of all analyzed Trojans.
First 3 quarters of 2013
Number of computers
compromised:
2M – Zbot + Gameover
125K – Cridex
33K – Shylock
The Botnet Population is Huge
26K – Spyeye
According to a study by McAfee, "at least 12 million computers around the world (are) compromised
21K – Bebloh
by botnets." That means the botnet operators are controlling a population rougly the size of
Guatemala
9K – Mebroot
2K - Tilon
* Source: thehackernews.com
Understanding TCP Syn Attack
Sender transmits a volume of connections that can’t be completed
TCP works like a phone call, called connection oriented protocol
It can be used for nefarious activity, same scenario with a phone call
In a SYN flood attack the malicious client sends
the SYN packet to the server without the intent of
setting up a connection. It doesn’t wait for a SYNACK packet, it sends another SYN packet trying to
setup another connection. The server keeps the
connection active for 2 minutes before letting it
go and as new SYN requests come in the server
will eventually be unable to keep up and will
either refuse new connections or reboot.
About DDoS attacks
DoS attack multiplied
Multiple attacks launched from many computers unknowingly infected with a virus or Trojan allowing them to be
controlled by a ‘bot herder’. An attacker can issue commands to the entire herd ordering them to attack a specific target.
Immediately the target goes down and doesn’t come back up until
Low Orbit Ion Cannon
LOIC – ‘Hive Mind’ allows a single user to control a
network of LOIC deamons distributed globally
Tools like Low Orbit Ion Cannon make it easy for
anyone to maliciously take a nearly any size target
anywhere offline. DDoS attacks are escalating and
occurring for reasons of extortion, political and
ideological agenda, anti competitive intitatives, and
suppression of free speech.
Mitigation of DDoS – Filter/Control/Back Hole Traffic
Purpose Built packet filter
Linux Server
ps –aux | grep –I HTTP|wc -1 Identify the traffic, if it’s port 80
Netstate –lpn|grep :80|awk ‘{print $5}’ |sort If there are more than 30 sessions you are under attack
Iptables – A INPUT –s <Attacking Network IP Address> -j DROP Stop the attacking network
OR
Route add <IP> gw 127.0.0.1 lo
Route add –net <IP/mask> gw 127.0.0.1 lo
*This can be used to implement a bogon, bogus IP address block list
Screen traffic on border routers
Drop packets that –
• Have internal IP addresses from your network
• Are from known black hat sources
• Incomplete or malformed
• Are for services not utilized
- Only allow traffic you should see, i.e. HTTP/port 80
• Utilize a DNSBL list
- A known list of IP addresses associated with spamming, zombie computers
Cisco has a white paper on RTBH, remotely triggered black hole filtering
Use IP route statement to black hole a route
Ip route 192.0.2.0 255.255.255.0 Null0
Use BGP to map a route prefix to null
in the redistribute static section STATIC-TO-BGP
match tag 66
route-map STATIC-TO-BGP permit 10
set ip next-hop 192.0.2.1
…
Ip route 171.xxx.xxx.1 255.255.255.255 Null0 Tag 66
Simple hosts file blocking using 127.0.0.1
• Hosts file – the first internet dns. On all Windows, Unix, Macs…
• Located – C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc
Anything Else?
Target PoS systems, credit card info scraped to an internal server compromised by hackers
Eset, a company based in the Czech Republic, found a worm designed to steal AutoCAD drawings
and transmit them to China. More than 10,000 ACAD/Medre.A infections have been found in
Latin America
NSA spies on Huawei servers, communication between top company officials, internal
documents, and source code of individual Huawei products – The US and Australia have barred
Huawei from broadband projects over espionage fears
Cisco’s own VPN product has a vulnerability in the client enabling access to malicious sites and
allow an attacker to execute remote code using ActiveX or Java. They issues a patch and also
warned of a software downgrade vulnerability allowing a hacker to change to an earlier
exploitable version of the software
US-CERT issued an advisory that some 64-bit Intel based systems are susceptible to local privilege
escalation attack to allow control over virtual machines
AhnLab, Inc., a South Korean security vendor, issued a warning about variations to the SpyEye
Trojan and ZeuS bot that attempts to steal personal banking data
Stuxnet, Flame both used against Iran stunting it’s ability to build nuclear weapons
New Security Products
ThreatSecure from ThreatTrack Security detects malware based on anomalous network
behavior. This is the next generation of day zero countermeasures a step above using
signature based defenses.
McAfee unveiled new next generation firewall defense leveraging acquisition StoneSofts
malware detection engine. It updates endpoint protection for endpoints when threat is
detected.
Fortinet upgrades OS to version 5 adding integrated reporting, protection vs. targeted
attacks, faster SSL inspection, and strong authentication.
HP unveils Threat Central, a security intelligence platform allowing sharing of threat data
integrating with HP Tippingpoint and Arcsight appliances.
Huawei Rolls out Anti-DDoS appliance for carriers and datacenters. 1 Tbpsec, and
protection from application layer mobile devices and outbound DDoS
Barracuda announces NG Firewall for Windows Azure cloud platform coupled with the
Web Application Firewall to provide app security and secure remote access.
Best Practices
Layered Protection – Perimeter Firewall, antivirus, IDS/IPS, desktop firewall, OS patches
Reduce the attack Surface – Restricting applications, devices access to resources and
allowed to connect – example BYOD – only access to outside facing portal and internet
Browser plugins – Patch them and monitor and eliminate the holes. Most hacked is
Microsoft Internet Explorer, Adobe Reader, Acrobat, and Flash. Vulnerabilities are
documented and maintained, stay up to date and try alternatives.
Block P2P – The simplest method to distribute malware is hidden files in peer to peer
networks. Eliminate any P2P file sharing with resources including Application and Device
Control (ADC) component at the desktop.
Turn off Autorun – Stop Conficker/Downadup and other network based worms from
jumping from USB keys and network drives
Monitor, Analyze, Patch, Repeat…
Calix MSAP
Multi Service Access Platform
GPON – Gigabit Passive Optical Network.
• Supports multiple services in their native formats
• Gigabit Ethernet 2.448 Gbit downstream/1.25 Gbit upstream
• Equal, fixed time slots for all endpoints using TDM
Home Network
Every home is an IP network with an outside IP to the Internet
There are two parts to an IPv4 address
Network and Mask
Almost all network devices have default
IP of 192.168.168.1 with subnet mask
of 255.255.255.0
ONT
Internal IP subnet used for home
network
In IPv4 this is represented as
192.168.168.0/24
Network | Hosts
IP Address 192.168.168.0
Mask
255.255.255.0
External IP on Internet
through Carrier connection
?
Device
?
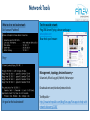
Network Tools
What to do to test local network
Do I have an IP address?
Ipconfig –
Test the outside network
Ping DNS Server IP, ping a known web page –
www.yahoo.com
Now check your browser -
Ping –
Management, topology, device discovery –
Solarwinds, What’s up gold, NetInfo, Netsurveyor
Download.cnet.com/windows/network-tools
I’m good on the local network!
TechRepublic –
http://www.techrepublic.com/blog/five-apps/five-apps-to-help-withnetwork-discovery/1230/
Wireshark – Protocol analysis
Free download – Capture traffic – Wired, wireless, Bluetooth, USB…
Solarwinds
S-flow monitoring protocols
IPv4 Address Primer
Each Number in an IP address represents an Octet
192.168.5.1
There are 4 octets in an IP address. Each octet
can be represented in an 8 bit binary number
The mask represents the dividing line where the network number ends and the host identifier begins
The last octet is used for identifying hosts. In this example the host is 130. Hosts can be numbered from 1-254
The last octet can be used as the broadcast to all hosts in a subnet using 255, all 1’s in binary
IPv4 Address Primer
Using variable Masks
By manipulating the mask you can conserve IP addresses, only using what you need.
You can break up your 192.168.5.0 subnet into multiple subnets using a longer mask
IPv6 Addressing
Intended to replace IPv4 to deal with long anticipated IPv4 address exhaustion
2013 only 2% of users reaching Google services used an IPv6 address
IPv6 allows 2128, or 3.4 X 1038 address using a 128 bit IP address vs. IPv4 using 32 bit addressing
Uses 8 groups of four hexadecimal digits separated by colons
2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334 - All leading zeros can be dropped shortening the address to
2001:db8:85a3:::8a2e:370:7334
3 Types of networking methodologies:
Unicast – Identifying each individual network interface
Anycast – Identifies a group of interfaces, usually at different locations using nearest first
Multicast – Used to deliver one packet to many interfaces
Broadcast is not implemented in IPv6
Questions
?