* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study guide for exam 2
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
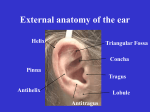
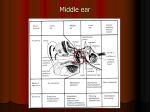
SPPA 6030: Study Guide for Exam 2 Notes: This study guide is intended to give you a general idea of some of the kinds of questions that might appear on the exam, and to help you organize your studying. It is not intended to cover all of the topics that might be appear on the exam. However, some of the exam questions may be taken almost verbatim from the study guide. In addition to the kinds of questions that are shown below, there may also be multiple choice questions, matching items, and diagrams that you would be asked to label. NOTE: The study guide is based on a guess about how much material we will cover prior to the exam. There may be material covered here which we do not get to and which, therefore, will not be on the exam. For example, I think it’s unlikely that we will get to the central auditory system, although this topic is covered on the study guide. If you are unsure, ask me. 1. What are the three functional subsystems of the auditory system? What functions are performed by each subsystem? 2. What does it mean to say that there is an impedance mismatch between the outside air and the inner ear? How large is this mismatch: (a) expressed as a ratio, and (b) expressed on a decibel scale? How does the middle ear overcome this mismatch? 3. What does it mean to say that the auditory system is a spectrum analyzer? Give a general explanation of how the auditory system performs spectrum analysis. 4. What is the acoustic reflex? What muscles participate in this reflex? What is thought to be the purpose of this reflex? 5. Where is the Eustachian tube located? What are the functions of the Eustachian tube? 6. What are the six surfaces of the tympanic cavity, and what structures are located on each surface? 7. The tympanic membrane is composed of what three layers? 8. What is a transducer? What transduction functions are performed by the auditory system? 9. Explain what causes the "pop" that you hear when riding down (or up) an elevator in a tall building. 10. The labyrinth contains what two sensory systems? 11. The membranous labyrinth portion of the cochlea consists of what two membranes? 12. Assuming an average length of 2.5 cm for the external auditory meatus (EAM), what is the lowest resonant frequency of this canal? Draw the frequency-response for the EAM showing the two lowest resonances. SPPA 6030, Study Guide for Exam 2 2 13. What is the maximum firing rate that a neuron can sustain for a short period of time? What is the maximum firing rate that a neuron can sustain for an extended period of time? What do these firing-rate limits have to do with absolute and relative refractory periods? Why are these facts important for understanding frequency analysis by the auditory system? 14. How do the physical characteristics of the basilar membrane vary from the base of the cochlea to the apex? Why is this fact important for understanding frequency analysis by the auditory system? 15. What anatomical structure lies immediately above the superior surface of the tympanic cavity? 16. What portion of the malleus attaches to the tympanic membrane? 17. What effects do the contraction of the tensor tympani and stapedius muscles have on the structures of the middle ear? 18. How does the Eustachian tube of an infant or young child compare with that of an adult? Why are these anatomical differences important? 19. The __________________, a gap at the apex of the cochlea, allows the fluid in the vestibular canal to communicate with the fluid in the tympanic canal. 20. This material is a fatty substance that coats the fibers of some but not all neurons. Fibers that contain this substance transmit neural signals more rapidly than uncoated fibers. 21. Give an example that illustrates the difference between force and pressure. Why is this distinction important to the functioning of the auditory system? 22. Explain the two schemes that might be used by the auditory system to code frequency. 23. Draw graphs showing the amount of 8th-nerve electrical activity as a function of position along the basilar membrane for: (a) a high-frequency signal, (b) a mid-frequency signal, and (c) a low-frequency signal. What, if anything, does this graph have to do with Fourier analysis? 24. Draw a graph showing how voltage varies over time in the generation of a neural spike potential. Label your graph and provide a scale for the voltage axis. 25. What does it mean to say that the auditory pathway exhibits tonotopic organization? 26. The peripheral auditory system consists of everything from the pinna up to and including the _________________________. 27. The central auditory system consists of structures in the ______________________________ and the ______________________________. 28. What do neurons have in common with toilets? SPPA 6030, Study Guide for Exam 2 29. According to the Hallowell Davis model of hair-cell function, hair cells form part of an electrical circuit. Draw this circuit and briefly explain how it works. 30. A hair cell channel consists of ____________________________. 31. What specific component of the hair cell channel is responsible for transduction? 32. Most auditory nerve fibers are: (a) afferent, or (b) efferent. 33. Most auditory nerve fibers synapse on: (a) IHCs, (b) OHCs, or (c) IHCs and OHCs about equally. 34. The cochlea contains roughly this many channels __________________. 35. It is not uncommon for a disease process to affect both the sense of hearing and the sense of balance. Why might this be the case? Terms for Exam 2 (Anatomy and Physiology) Note: Items that are separated by slashes are alternate names for the same structure. transducer conductive mechanism sensorineural mechanism central auditory system acoustic nerve/auditory nerve/8th cranial nerve vestibular branch of the 8th nerve cochlear branch of the 8th nerve pinna helix antihelix tragus antitragus concha ear lobe external auditory meatus/ear canal sebaceous glands cerumen tympanic membrane/ear drum tympanic sulcus Shrapnell's membrane/pars flaccida pars tensa umbo tympanic cavity/middle ear cavity jugular vein 3 SPPA 6030, Study Guide for Exam 2 attic/epitympanic recess tympanic cavity proper oval window annular ligament round window internal tympanic membrane facial nerve/7th cranial nerve promontory pyramidal eminence stapedius muscle tensor tympani Eustachian tube/auditory tube malleus - manubrium, head, neck incus - short process, body, long process stapes - head, neck, posterior crus, anterior crus, footplate impedance (resistance, mass reactance, capacitive reactance) impedance mismatch force pressure acoustic reflex intensity control theory labyrinth bony labyrinth membranous labyrinth helicotrema internal auditory meatus vestibular mechanism otolith system semicircular canals ampulla utricle saccule cristae maculae angular acceleration/"head motion" linear acceleration perilymph endolymph cochlea vestibule basal, medial, and apical turns of the cochlea modiolus basilar membrane Reissner's membrane organ of Corti spiral lamina/bony spiral lamina 4 SPPA 6030, Study Guide for Exam 2 scala vestibuli/vestibular canal scala tympani/tympanic canal scala media/cochlear duct/cochlear partition stria vascularis tectorial membrane Dieter's cells phalangeal process limbus inner hair cells outer hair cells cilia cuticle/cuticular plate tunnel of Corti rods of Corti neuron dendrite axon cell body afferent process efferent process myelin spike potential depolarization absolute refractory period relative refractory period ganglion nucleus traveling wave place theory/place principle frequency theory/synchrony theory volley principle tonotopic organization 5