* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Presentation to Chapter, F5 Networks, 20 Sep 2013
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
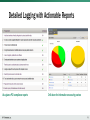
WEB APPLICATION FIREWALL 9-20-13 Tony Ganzer F5 SE Who Is Responsible for Application Security? Clients Network Infrastructure Applications Engineering services Developers Storage DBA How Does It Work? Security at application, protocol and network level Request made Security policy checked Content scrubbing Application cloaking Enforcement Response delivered Server response Security policy applied Actions: Log, block, allow BIG-IP enabled us to improve security instead of having to invest time and money to develop a new, more secure application. Start by checking RFC compliance 2 Then check for various length limits in the HTTP 3 Then we can enforce valid types for the application 4 Then we can enforce a list of valid URLs 5 Then we can check for a list of valid parameters 6 Then for each parameter we will check will check for max for max value value length length 7 Then scan each parameter, the URI, the headers GET /search.php?name=Acme’s&admin=1 HTTP/1.1 Host: 172.29.44.44\r\n Connection: keep-alive\r\n User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1)\r\n Accept:text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9\r\n Referer: http://172.29.44.44/search.php?q=data\r\n Accept-Encoding: gzip,deflate,sdch\r\n Accept-Language: en-GB,en-US;q=0.8,en;q=0.6\r\n Accept-Charset: ISO-8859-1,utf-8;q=0.7,*;q=0.3\r\n Cookie: SESSION=0af2ec985d6ed5354918a339ffef9226; \r\n Scope of Problem • Website Proliferation • Vulnerabilities introduced • Automated attacks • Changing the attack patterns • Risk of brand, $ and IP losses high How long to resolve a vulnerability? Website Security Statistics Report Unknown Vulnerabilities in Web Apps • • • • Customers want…… • Reduce Window of Exposure • Reduce Operational Cost • Assured Security real-time assessments & patching • Integrated with SDLC processes 8 Recent Application and Network Attacks • And the hits keep coming: Source: http://spectrum.ieee.org/static/hacker-matrix Concept– Simple as your ABCs Assess Block Correct (VA Partner) (F5) • Persistent Assessment vs 1/yr. • Mission Critical+ • All External • All Internal • 80% of Vulns • Remediate all Technical Vulns (Customer, SI or VAR) • • • • 20% Vluns fix Fix via iRules Code correction WAS Lifecycle Mgnt. Traditional Security Devices vs. WAF Network Firewall Known Web Worms Unknown Web Worms Known Web Vulnerabilities Unknown Web Vulnerabilities Illegal Access to Web-server files Limited IPS X Limited Limited Partial X Limited Limited X X X X Limited Buffer Overflow Limited Limited Cross-Site Scripting Limited Limited Limited Brute Force Login Attacks X X X X X X App. Security and Acceleration X X Forceful Browsing Look into the SSL traffic SQL/OS Injection Cookie Poisoning Hidden-Field Manipulation Parameter Tampering Layer 7 DoS Attacks X X X X X WAF-ASM Identify, Virtually Patch, and Mitigate Vulnerabilities • Scan applications with: – – – – WhiteHat Sentinel (F5 Free Scan Partner) Cenzic Hailstorm (F5 Free Scan Partner) QualysGuard Web App. Scanning IBM Rational AppScan • Configure vulnerability policy in BIG-IP ASM • Mitigate web app. attacks Data Center Protection from Vulnerabilities Enhanced Integration: BIG-IP ASM and DAST Customer Website White Hat Sentinel • Finds a vulnerability • Virtual-patching with one-click on BIG-IP ASM • Vulnerability checking, detection and remediation • Complete website protection BIG-IP Application Security Manager • Verify, assess, resolve and retest in one UI • Automatic or manual creation of policies • Discovery and remediation in minutes Benefits of Assessments with WAF • Narrows window of exposure and reduces operational costs: – Real-time assessments and virtual patching – Operationalizes admin. and simplifies mitigation • Assures app security, availability and compliance: – Assurance no matter vulnerabilities or policies built – OWASP protection, compliance, geo blocking • Improves app performance: – Availability improves cost effectiveness • Low risk of false positives: – Laser focused rules are generated automatically • Easily integrates with SDLC practices: – Ongoing website security program WAF and the Software Development Lifecycle • Policy Tuning • Pen tests • Performance Tests • • • • • • WAF “offload” features: Cookies Brute Force DDOS Web Scraping SSL, Caching, Compression • Final Policy Tuning • Pen Tests • Incorporate vulnerability assessment into the SDLC • Use business logic to address known vulnerabilities • Allow resources to create value Multiple Security Layers RFC enforcement • Various HTTP limits enforcement Profiling of good traffic • Defined list of allowed file types, URIs, parameters Each parameter is evaluated separately for: • • • • Predefined value Length Character set Attack patterns • Looking for pattern matching signatures Responses are checked as well Three Ways to Build a Policy Security policy checked Security policy applied Dynamic policy builder Automatic – • No knowledge of the app required • Adjusts policies if app changes Integration with app scanners Manual – • Advanced configuration for custom policies • Virtual patching with continuous application scanning Detailed Logging with Actionable Reports At-a-glance PCI compliance reports Drill-down for information on security posture DDoS MITIGATION Increasing difficulty of attack detection Physical (1) Data Link (2) Network (3) Transport (4) F5 mitigation technologies Network attacks Session (5) Presentation (6) Session attacks Application (7) Application attacks SYN Flood, Connection Flood, UDP Flood, Push and ACK Floods, Teardrop, ICMP Floods, Ping Floods and Smurf Attacks DNS UDP Floods, DNS Query Floods, DNS NXDOMAIN Floods, SSL Floods, SSL Renegotiation OWASP Top 10 (SQL Injection, XSS, CSRF, etc.), Slowloris, Slow Post, HashDos, GET Floods BIG-IP AFM SynCheck, default-deny posture, high-capacity connection table, fullproxy traffic visibility, rate-limiting, strict TCP forwarding. BIG-IP LTM and GTM High-scale performance, DNS Express, SSL termination, iRules, SSL renegotiation validation BIG-IP ASM Positive and negative policy reinforcement, iRules, full proxy for HTTP, server performance anomaly detection Packet Velocity Accelerator (PVA) is a purpose-built, customized hardware solution that increases scale by an order of magnitude above software-only solutions. OSI stack F5 mitigation technologies OSI stack RAPID VIRTUAL PATCHING SOFTWARE DEV. LIFECYCLE (SDLC) Project planning Requirements definition Installation & acceptance • Incorporate vulnerability assessment into the SDLC • Use business logic to address known vulnerabilities Integration & test Design Development • Decouple security from the SDLC • Address new vulnerabilities immediately • Ensure PCI compliance • Allow resources to create value Conjecture of relative breach impact is based on publicly disclosed information regarding leaked records and financial losses 2011 Sampling of Security Incidents by attack type, time and impact 178.com Size of circle estimates relative impact of breach in terms of cost to business Bethesda Software Epson Korea Nortrop Grunman IMF Fox News X-Factor Attack type Finnish Government Sites PCS Consulting Duowan Norway MSN Italy PM Site Italian Ministry Hemmelig.com Citigroup SQL injection CSDN Spanish Nat Police URL tampering Sega Diginotar Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Valve Steam Trion Epsilon Gmail Accounts Spear phishing PBS Third-party software HB Gary DDoS Sony PBS Booz Allen Hamilton Nexon Vanguard Defense SOCA 7K7K.com TGKK Monsanto Malaysian Gov Site Peru Special Police SecureID Trojan software Lockheed Martin RSA Brazil Gov L3 Communications Sony BMG Greece SK Communications Korea Turkish Government Stratfor Adidas United Nations NetNames DNS Service Nintendo Unknown Sony Hong Kong Stock Exchange US Law Enforcement Israeli and Palestinian Sites AZ Police Tian.ya NetNames DNS Service US Senate NATO Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Figure 1: 2011 Sampling of Security Incidents by Attack Type, Time and Impact Source: IBM X-Force 2011 Trend and Risk Report March 2012 Thank You! www.F5.com