* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ppt - Cynosure Health
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
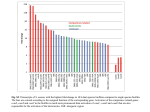
Tailoring Patient Support To Levels of Activation Application of the Patient Activation Measure® To Achieve Better Care, Improved Health & Lower Costs Cynosure Health Summit “The Great Quality Swap Meet” © Insignia Health 2012. Proprietary & confidential Chris Delaney Insignia Health May 21, 2012 The Patient Activation Measure® (PAM) Developed at the University of Oregon by Dr. Judith Hibbard and Dr. Bill Mahoney More than 200 studies of health activation in academic and medical centers, with 80+ peer reviewed published studies thus far Measures an individual’s knowledge, skills and confidence for managing their health and healthcare Survey instrument assigns an individual to an activation level (1 - 4) based on and a numeric score (0 – 100). Most individuals score between 30 and 80. 10 to 12 points separate activation levels Provides insight into an wide array of health-related attitudes and behaviors Hospital and clinic clients in roughly 25 states © Insignia Health 2012. All rights reserved 2 Activation is developmental -- four segments along a continuum General population 10-20% of the population 20-35% of the population © Insignia Health 2012. Proprietary & confidential 20-30% of the population 20-30% of the population 3 Worldwide research validates the PAM’s validity and reliability More than 80 published studies across conditions and populations provide pivotal health activation guidance © Insignia Health 2012. Proprietary & confidential 4 Low activation signals problems (and opportunities) © Insignia Health 2012. Proprietary & confidential 5 A PAM score is predictive of future utilization and outcomes © Insignia Health 2012. Proprietary & confidential 6 How capable is this individual at managing his or her health and healthcare decisions? © Insignia Health 2012. Proprietary & confidential 7 Understanding Patients From the Perspective of Activation © Insignia Health 2012. All rights reserved 8 Hundreds of patient characteristics – motivators, behaviors, outcomes, have been mapped to activation levels © Insignia Health 2012. All rights reserved 9 Emotional disposition plays a profound role in activation and how best to communicate with patients © Insignia Health 2012. Proprietary & confidential 10 Achieving best practice self care or evidence based guidelines is developmental. A PAM score guides the journey Data Source: RWJ Aligning Forces ©11Insignia Health 2012. Proprietary & confidential 11 Medication taking is a struggle for the low activated Source: 2010 – 2011 Care Transition QIO Program © Insignia Health 2012. Proprietary & confidential 12 The low activated find much less value in their clinical interactions © Insignia Health 2012. Proprietary & confidential 13 Tailoring Support to Levels of Activation © Insignia Health 2012. Proprietary & confidential 14 Activation level insights guide support toward what is realistic and achievable for a given level © Insignia Health 2012. Proprietary & confidential 15 A PAM score can play a pivotal role in resource allocation Source: PeaceHealth’s Team Filingame Uses Patient Activation Measure to Customize the Medical Home, Center for the Health Professions Research Brief, May 2011 © Insignia Health 2012. Proprietary & confidential 16 Targeting the low activated is a key strategy in care transitions Source: QualityNet Conference Dec 2010. Alabama Quality Assurance Foundation (QIO) © Insignia Health 2012. Proprietary & confidential 17 Coaching for Activation® online & print resources guide patient support ACTIVATION LEVEL BASED COACHING GUIDE PAM LEVEL 1 ! ! " #$%&' ( &) * +) , +( - ' &$. /+' . ( &" * ( + ) ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! “My doct or t akes care of me.” “I don’t underst and t he cause”! ! SPECIFIC GOALS & RELATED ACTION STEP OPTIONS TO CONSIDER Condition Knowledge & Symptom Awareness (example goals & steps) ! Build skill in problem solving around managing symptoms Step: Write down symptoms, how they felt, and what might have triggered the symptoms. Discuss findings w/member of health care team ! Build basic knowledge about condition Step: Explain what their condition is in one or two simple sentences ! Learn important targets/numbers related to their health condition Step: Be able to explain their numbers and where they fall Medications (example goals & steps) ! Learn how medications work, their risks, benefits, and side effects. Step: Identify concerns and knowledge gaps related to medications and close these gaps ! Identify barriers to taking meds and problem solve together Step: Observe for a week when and how medications are taken. Spot missed days/does and what might have gotten in the way ! Begin to work toward taking medications as part of daily routine Step: Together, fill out a medication chart that includes all prescribed and over-the-counter medications + dosing directions Insignia Health, LLC | Proprietary and Confidential | 0" %. %$1 &* 2+$ ) . $1 &* 2+2 ) . /#+ ! May not understand that they need to play a role in their own health Lacks basic knowledge about their condition May not understand treatment options, or self-care expectations May not feel in charge of own health and healthcare Use to failure Feels very overwhelmed with regard to self-care and healthcare. Experiences a lot of negative emotion that makes it hard to cope Poor problem solving skills Low confidence in their ability to impact their health Difficulty following through on treatment regimens Has trouble connecting behavior to health 30%-40% Rx adherent; High rate of ERuse/hospitalization Build confidence through small step goals that they can make a difference in their health and how they feel Overcome feelings of being overwhelmed by giving permission to take it one step at a time. Don’t overwhelm with too much information Increase self-awareness by connecting his/her behaviors to their health, and how he/she feels Help member see that through their own actions they can have a positive impact on their health Focus on current (not long-term) health issues Use positive messages, avoid disagreements, and show empathy Don’t “jump the gun!” asking them to do behaviors beyond their level Begin to problem solve around small issues to overcome barriers to behavioral change. Let the individual choose the area to work on, and then guide toward appropriate goals/steps SPECIFIC GOALS & RELATED ACTION STEPS OPTIONS TO CONSIDER Diet & Nutrition (example goals & steps) ! Pay attention to the habits & stressors that promote poor diet, identify an opportunity to improve, and try it out Step: Keep track of the food that is eaten for at least a few days in the coming week. What is eaten and how much? Try taking pics with a phone camera. Are there triggers that lead to certain food behaviors? ! Develop basic knowledge of ‘good’ and ‘bad’ foods. Understand the characteristics of each. Reflect on portion sizes and how full he/she feels after meals Step: Make a small diet “upgrade” in the next week – replace high calorie/fat snack w/ fruits/veggies; go LF or NF with some foods; reduce portion size, try a new fruit/veggie rich in color Physical activity (example goals & steps) ! Start to develop an understanding of the specific benefits of physical activity, Step: Keep track of the types and amounts of activity he/she gets in a day, and how it makes them feel. Discover where there may be some opportunities to fit in more activity, and try adding a few extra minutes to something that they already do © 2010 | For use with a valid copyright license only! ! ! ! ! * CareMap guides support diabetes, COPD, CHF, care transition and a general chronic condition version 18 © Insignia Health 2012. Proprietary & confidential Coaching Model Impact: National DM Firm Coaching tailored to levels improves outcomes and reduces cost Clinical Indicators Medications: intervention group increased adherence to recommended immunizations and drug regimens to a greater degree than the control group. This included getting influenza vaccine. Blood Pressure: Intervention group had a significantly greater drop in diastolic as compared to control group. LDL: Intervention group had a significantly greater reduction in LDL, as compared to the control group. Hibbard, J, Green, J, Tusler, M. Improving the Outcomes of Disease Management by Tailoring Care to the Patient’s Level of Activation. The American Journal of Managed Care, V.15, 6. June 2009 © Insignia Health 2012. Proprietary & confidential 19 Coaching Model Impact: PeaceHealth Medical Home • Statistically significant improvement in 8/10 clinical measures • Improved adherence • Increase in controlled blood pressure from 56% to 76% • Improvements in A1c & LDL • 47% of patients improved PAM scores • 24% increase in office appointments Source: PeaceHealth’s Team Filingame Uses Patient Activation Measure to Customize the Medical Home, Center for the Health Professions Research Brief, May 2011 © Insignia Health 2012. Proprietary & confidential • Increased patient satisfaction 20 PAM as a Key Vital Sign Activation requires supporting individuals where they are and moving away from a uniform approach that pushes guideline behaviors for all The lower activated (levels 1 & 2) are poor self-managers and account for 75%+ of healthcare costs The low activated (levels 1 & 2) have accounted for 80% to 100% of readmits in care transition programs Coaching support tailored to levels consistently demonstrates the ability to improve patient self-management and reduce healthcare costs Tailoring to activation levels helps to align resource to were the need is greatest © Insignia Health 2012. All rights reserved 21