* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chronic Illness and Emotional Distress in Adolescence
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
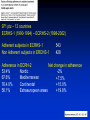
Adherence to treatment: How can it be improved? Non-Adherent patient Fulvio Braido Allergology & Respiratory Diseases University of Genoa Factor influencing the clinical outcomes of therapy Thorsson & Geller Respiratory Medicine 2005; 99: 836-849 The extent of Non-Adherence WHO report 50% of patients from developed countries with chronic disease do not use their medications as reccommended. 971 ptz – 12 countries ECRHS-1 (1990-1994) – ECRHS-2 (1998-2002) Adherent subjects in ECRHS-1 Non Adherent subjects in ERCHS-1 543 428 Adherence in ECRH-2 Net change in adherence 53.4% Nordic -2% 67.6% Mediterranean +7.5% 76.4.0% Continental +15.0% 56.1% Extraeuropean areas +19.8% Drug Disease Cognition Effectiveness = Efficacy Inhaler X Clinical effects Side effects Patient Satisfaction Adherence Patient Behaviour Treatment Schedule Patient-Physician Relationship J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol 2006 Vol. 16(4):218-223 The concerns about the adverse effects of ICS, is not necessarly related to actual experience, but rather to beliefs about the link between regular use and dependency or other perceived side effects. Barriers to Adherence Osterberg L. & Blasche T. N.E.J.M. 4 August 2005 Allergic Rhinitis and Asthma ad hoc survey: Clinical and Psychological perspectives F. Braido, I. Baiardini, S. Brandi, A. Porcu, G.W. Canonica Allergy and Respiratory Diseases, DIMI, Genoa University, Genoa, Italy 504 asthmatic patients 27.8% of asthmatic patients experience three or less rhinitic symptoms, 41% from 4 to 6 symptoms, 31.2 % more than 6 symptoms. These symptoms deeply interfere with daily life causing sleep problems (87.3%), lack of concentration (78.9%), difficulties in spare time (71.8%) and sport (71.7%). Rhinitis symptoms are responsible of the worsening of asthma, with an increase of dyspnoea (86.3%), cough (73.9%) wheezing (59%). Improving Asthma Control Study (IMPACT) – post hoc analisys