* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Rheumatoid_Arthritis_Resident_Lecture
Focal infection theory wikipedia , lookup
Fetal origins hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Race and health wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Epidemiology of metabolic syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Epidemiology wikipedia , lookup
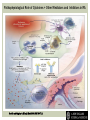
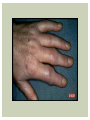
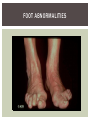
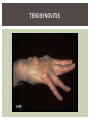
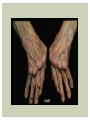
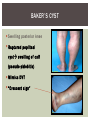
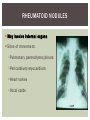
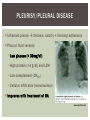
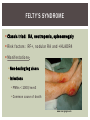
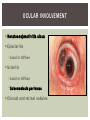
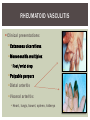
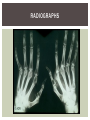
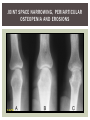
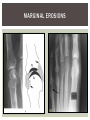
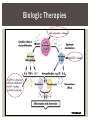
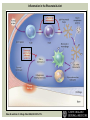
RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS INTRODUCTION Epidemiology/genetics Pathogenesis Clinical Features Laboratory Manifestations Diagnosis Management considerations and therapy RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Chronic, systemic inflammatory disease Unknown etiology Persistent inflammatory synovitis Synovial inflammation (pannus) cartilage destruction, bone erosion with subsequent deformity Peripheral joints in symmetric fashion Extra-articular manifestations also occur EPIDEMIOLOGY 2.5 million Americans (~1%), 165 million worldwide Females > males 3:1; all races Peak age onset: 4 th -5 th decade 80% develop between ages 35-50yrs Prevalence increases with age GENETICS Strongly associated with HLA -DR4 DRB1*0401/0404 severe and erosive disease “Shared epitope” on 3 rd hypervariable region of HLA DRB1 + HLA-DR4 seen in 20-30% of general population Other factors involved for disease to develop GENETICS T lymphocytes recognizing antigens in synovial tissue T cells, macrophages + fibroblasts produce proinflammatory cytokines Play a key role in synovitis and tissue destruction Pro-inflammatory cytokines: TNF alpha, IL-1 and IL-6 Pathophysiological Role of Cytokines + Other Mediators and Inhibitors in RA Scott D and Kingsley G. N Engl J Med 2006;355:704-712. RISK FACTORS FOR AGGRESSIVE RA HLA-DR4, High titer RF and + CCP ab Early radiographic erosions Constitutional symptoms Insidious onset Early appearance of rheumatoid nodules DISEASE ONSET Insidious: Most common presentation Small peripheral joints: MCPs, PIPs, wrists Abrupt: Acute polyarthritis Intense pain, swelling + limitation Slow monoarticular: Knees/shoulders progresses to small joints OVERVIEW: JOINT INVOLVEMENT TMJ: 20-30% C-spine: 40-50% Hips: 40-50% Shoulder: 50-60% Knees: 60-80% SC Joints : ? Ankles: 50-80% Elbow: 40-50% Foot : MTP 50-90% PIP 65-90% Wrist: 80-90% Hand: MCP 90-95% PIP 65-90% www.moviesyahoo.com CLINICAL FEATURES Symmetric inflammatory synovitis (palpable swelling) of small peripheral joints Tenderness to palpation and ROM Symptoms last > 6 weeks Useful indicator of disease activity Morning stiffness > 1˚ improves with activity CLINICAL FEATURES Symmetric polyarticular joint involvement (>3 joints) Small joint arthropathy: MCPs, PIPs, wrists, MTPs Knees, ankles and shoulders Typically spares: thoracolumbar spine + DIP joints Entrapment syndromes also commonly occur Carpal tunnel and tarsal tunnel BOUTONNIERE DEFORMIT Y www.medscape.com www.medscape.com SWAN NECK DEFORMIT Y www.medscape.com FOOT ABNORMALITIES TENOSYNOVITIS BAKER’S CYST Swelling posterior knee Ruptured popliteal cyst swelling of calf (pseudo-phlebitis) Mimics DV T “Crescent sign” AXIAL DISEASE AXIAL DISEASE Anterior alantoaxial subluxation of C1-2 common ≥ 3 mm separation between odontoid and atlas Recurrent HA, tingling in UE, unexplained dizziness Susceptible to trauma with endotracheal intubation Must get pre-op X-rays of neck (lateral flexion/extension) Symptomatic cervical myelopathy spinal fusion C SPINE X-RAY EXTRA-ARTICULAR MANIFESTATIONS 40% of patients Increased frequency: +RF, +CCP ab, HLA-DR1 +DR4 Environmental factors such as smoking Life expectancy loss of 18 yrs 5x mortality risk Organ System Systemic Extra-Articular Manifestations General Fever, LAD, weight loss and fatigue Bone Osteopenia and osteoporosis Cardiovascular CAD, MI, pericarditis, myocarditis, coronary vasculitis, nodules on the valves Dermatologic Palmar erythema, subcutaneous nodules, vasculitis Hematologic Anemia, thrombocytosis, Felty’s syndrome, LGL, NHL Neuromuscular Entrapment neuropathy, peripheral neuropathy, mononeuritis multiplex Ocular Keratoconjunctivits sicca, scleritis, episcleritis, peripheral ulcerative keratitis Other Sjogrens syndrome, amyloidosis, vasculitis Pulmonary Pleural Effusion, pleuritis, nodules, ILD, bronchiolitis obliterans, RHEUMATOID NODULES 20-40%of SPRA patients Reflects level of RA disease activity Develops on pressure areas Risk factors: +RF, subchondral cysts, Methotrexate(MTX) RHEUMATOID NODULES Single/multiple nodules Interfere with function/ulcerate Regress with DMARDS MTX may result in ↑ nodulosis RHEUMATOID NODULES May involve internal organs Sites of movement: Pulmonary parenchyma/pleura Pericardium/myocardium Heart valves Vocal cords CAPLAN’S SYNDROME Pulmonary nodulosis + pneumoconiosis Exposure to inorganic dusts (coal, asbestos, silca) Similar to simple rheumatoid nodules Modified tissue response to inhaled dusts May lead to progressive massive fibrosis (PMF) INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE Most common lung manifestation ↑ mesenchymal reactivity fibrosis PE: fine, diffuse dry rales; low DLCO CXR: Reticular/reticulonodular pattern honeycombing INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE Wide spectrum of findings on lung biopsy Histologic finding idiopathic interstitial pneumonia (IIP) Tx: “ground-glass” on HRCT good response to tx High dose steroids, imuran and cytoxan PLEURISY/PLEURAL DISEASE Inflamed pleura thicken, calcify + forming adhesions Pleural fluid reveals: Low glucose (< 30mg/dl) High protein (>4 g/dl) and LDH Low complement (CH 50 ) Cellular infiltrates (mononuclear) Improves with treatment of RA www.uptodate.com HEMATOLOGIC INVOLVEMENT Mild hypochromic normocytic anemia Thrombocytosis Lymphadenopathy Felty’s syndrome Large granular lymphocyte syndrome “Pseudo-Felty Syndrome FELT Y’S SYNDROME Classic triad: RA, neutropenia, splenomegaly Risk factors: RF+, nodular RA and +HLADR4 Manifestations: Non-healing leg ulcers Infections PMNs < 1000/mm3 Common cause of death www. knol.google.com FELT Y’S SYNDROME Treatment: DMARDs Methotrexate Splenectomy TNFi no studies in actual treatment of Felty’s Steroids improve neutropenia but ↑ risk of infection LARGE GRANULAR LYMPHOCY TE SYNDROME Variant of Felty’s Peripheral blood or bone marrow LGL cells Circulating LGLs, neutropenia, frequent infections, splenomegaly 3-14% leukemia unlike Felty’s. No splenectomy! OCULAR INVOLVEMENT Keratoconjunctivitis sicca Episcleritis Local or diffuse Scleritis Local or diffuse Scleromalacia perforans Choroid and retinal nodules RHEUMATOID VASCULITIS < 1% of RA pts Risk factors: High titer RF & long standing, severe disease (> 10yrs ) Male gender Smoking Prior DMARD use Hypocomplemetemia Circulating cryoglobins RHEUMATOID VASCULITIS Clinical presentations: Cutaneous ulcerations Mononeuritis multiplex Foot/wrist drop Palpable purpura Distal arteritis Visceral arteritis: Heart, lungs, bowel, spleen, kidneys COURSE OF RA Intermittent (15-20%) Long clinical remission (10%) Progressive disease (65-70%) RISK FACTORS FOR INCREASED MORBIDIT Y/MORTALIT Y Social factors: Physical factors: Early age at diagnosis Extra-articular features ↓ socioeconomic status Erosions on x-ray Psychosocial stress ↑RF + ↑ESR/CRP Low HAQ scores Duration of disease Disability at diagnosis > 20 swollen joints MORBIDIT Y/MORTALIT Y IN RA Median life expectancy decreased by 3 -18 yrs Mortality rates higher with extra-articular manifestions and women ~50% stop working within 5-10ys of diagnosis ~80% disabled to some degree after 20 yrs MORBIDIT Y/MORTALIT Y IN RA Infection: 70% more likely to have infection Don’t forget septic arthritis in RA patients arthocentesis NH lymphoma: 2-5 fold increased risk CAD: 3x the risk of sudden death/MI Cerebrovascular diseases: 70% more likely to have a stroke LABORATORY MANIFESTATIONS No lab test is specific for RA RF + Anti-CCP + (anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody) Increased ESR/CRP ANA + (25% of patients) Anemia +thrombocytosis RHEUMATOID FACTOR Usually IgM Ab recognizes Fc portion of IgG molecule 70% RF+ at onset, 85% overall in first 2 years High titer severe disease, extra-articular manifestations, increased mortality Normal 1-4%, 10-25% + over age 70 MNEMONIC FOR +RF CHronic: CH: Chronic diseases liver/pulmonary/sarcoidosis R: Rheumatoid arthritis O: Other CTDS (SLE, SS, MCTD) N: Neoplasms (XRT, chemotherapy) I: Infections (SBE, HIV, Hepatitis B+C, TB, Parvovirus B19) C: Cryoglobinemia ANTI-CCP Autoantibody directed at cyclic citrullinated peptide Sensitivity 65-70%, specificity (95%) RF and CCP ab combination specificity 99.5% Detectable in early RA May antedate onset of inflammatory disease Predictor of aggressive + erosive disease 1987 ACR CLASSIFICATION CRITERIA FOR RA Must have 4 of 7 criteria: Morning stiffness at least 1 ˚ Swelling in 3 or more joints Swelling of MCP, PIP or wrist joints At least 6 weeks Symmetric joint swelling Radiographic erosions or periarticular osteopenia SQ rheumatoid nodules Positive RF Differential Diagnosis for RA Comments Connective tissue diseases SLE, Systemic sclerosis, Sjogren’s Hemochromatosis 2nd /3rd MCP joints, distinctly asymmetric Check iron studies and skin changes Infectious endocarditis R/o murmurs, high fever and IVDA Polyarticular gout Joints often erythematous, rarely coexists with RA PMR Unlike PMR, RA rarely presents with proximal extremity pain Sarcoidosis Granulomas likely, as are hypercalcemia and chest X-ray findings common Seronegative spondyloarthopathy Tends to be more asymmteric than RA and typically involves the spine. Still’s disease Fever, leukocytosis, sore throat, liver dysfunction and salmon colored rash Viral arthritis Parvovirus B19, hepatitis B and C PARVOVIRUS B19 Symmetrical polyarthritis of peripheral small joints May resemble RA as well as SLE More common in adults (60%) > children (5-10%) Daycare worker or mother of small children Check B19 IgM antibodies or viral B19 DNA Self limited but may require further treatment WORK-UP FOR AN INFLAMMATORY ARTHRITIS CBC, CMP, UA, RF/CCP, ESR/CRP Uric acid, HIV, chronic hepatitis, Parvovirus B19 IgM, TSH, ANA, PPD X-rays: bilateral hands/feet + chest X -ray Arthrocentesis: Inflammatory WBC 5,000-50,000 (N 60-80%) IMPORTANCE OF EARLY DIAGNOSIS RA is progressive Structural damage occurs within first 2-3 years of disease 70% have radiographic damage with in first 3 years MRI reveals erosions earlier in disease Early aggressive treatment slows progression +disability RADIOGRAPHS RADIOGRAPHIC FEATURES A: abnormal alignment B: bones C: cartilage D: deformity E: erosions S: soft tissue swelling JOINT SPACE NARROWING, PERIARTICULAR OSTEOPENIA AND EROSIONS MARGINAL EROSIONS RA TREATMENT Step up or step down approach achieve remission Treat early disease aggressively and alleviate pain Maintain function for essential daily activities Maximize quality of life Slow progression/rate of joint damage OVERVIEW OF RA TREATMENT Patient education Modify CAD RF and Stop smoking !!! NSAIDs + low dose corticosteroids Disease modifying agents (DMARDs) Biologics Physical/occupational therapy Surgery for structural joint damage Keys to Optimizing the Outcome of Treatment O'Dell J. N Engl J Med 2004;350:2591-2602 NSAID THERAPY Pros Cons Controls inflammation Does not modify ↓ pain/swelling disease progression Improves mobility, ROM GI toxicity Improve quality of life Renal complications Low cost CNS toxicity CORTICOSTEROID THERAPY Pros Cons Anti-inflammatory + Disease progression? immunosuppressive effects Bridge to initiation of DMARD therapy Dose of < 10 mg/day CSI used for joint flares Tapering + discontinuation difficult Skin thinning, Cushingoid appearance, cataracts Steroid induced osteopenia/osteoporosis DISEASE MODIFYING ANTI-RHEUMATIC DRUGS Slows disease progression Decreases radiographic progression Improves functional disability Decreases pain + interferes with inflammatory processes METHOTREXATE Pros Cons Gold standard DMARD Labs q 2 months Improves survival Bone marrow suppression Proven ef ficacy and Alopecia, stomatitis durability in moderate to severe RA Used in combination with other DMARDs Lung + liver toxicity Contraindicated: pregnancy, pre-existing renal + liver disease (hepatitis) LEFLUNOMIDE (ARAVA) Pros Cons Early onset of action (~4 Black box warning: weeks) Targets autoimmune lymphocytes antiinflammatory Effective for moderate/severe RA Hepatotoxicity HTN, alopecia GI side effects diarrhea, weight loss Contraindicated: severe liver disease, pregnancy OTHER DMARDS Hydroxycloroquine (HCQ) aka plaquenil Ocular toxicity (eye examination every year) Sulfasalazine (SSZ) Reversible oligospermia Minocycline Cyclosporine Gold COMBINATION THERAPY Does not increase toxicity significantly Long term outcome more favorable Superior efficacy to monotherapy Combinations: MTX/SSZ/HCQ MTX and biologics Biologic Therapies www.ispub.com ANTI-TUMOR NECROSIS FACTOR THERAPY FDA approved: Infliximab (Remicaide) IV infusion Given with MTX to reduce human anti-chimeric ab (HACAs) Adalimumab (Humira) Etanercept (Enbrel) Certoluzimab pegol (Cimzia) Golimumab (Simponi) ANTI-TNF SUMMARY Rapid onset of action with improvement in symptoms Disability and quality of life Inhibition of radiographic progression Sustained efficacy of at least 5 years Class effect 1 st line therapy with MTX for high disease activity SAFET Y DATA FOR TNF Serious infections (opportunistic fungal, TB) Infusion, injection reactions Malignancy potential Neurologic/demyelinating disease Autoab (ANA + DS DNA) and lupus like syndrome CHF worsening, new onset OTHER BIOLOGICS Anakinra (Kineret) IL-1 receptor antagonist Rituximab (Rituxan) Chimeric monoclonal IgG1 anti-CD20 antibody B lymphocyte depletion Abatacept (Orencia) CTLA-4Ig Support or abrogate activation of T-cells Tocilizumab (Actemra) Humanized monoclonal antibody against IL-6 receptor INITIATING BIOLOGIC THERAPY Basic labs: CBC, CMP PPD (TB screen) or quantiferon gold Chronic hepatitis panel and HIV Routine health screening and vaccinations: Flu and PNA No live vaccines after initiation of therapy Ensure routine cancer screening UTD CONCLUSIONS Recognize and treat RA early RA is progressive disability Newer agents and aggressive therapy offers great hope for the future of most patients ANY QUESTIONS??? BIBLIOGRAPHY Feldmann M. Development of anti -TNF therapy for rheumatoid arthritis. Nature Review. 2002; 2:364-371. Turesson C, et al. Extra-articular disease manifestations in rheumatoid arthritis: incidence of trends and risk factors over 46 years. Ann Rheum Dis 2003; 62: 722-727. Turesson C, et al. Rheumatoid factor and antibodies to cyclic citullinated peptides are associated with severe extra articular manifestations in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2007; 66:59-64. Turesson C, Matteson E. Vasculitis in Rheaumatoid Arthritis. Current Opinion in Rheumatology. Feb 2009. Levesque M. Systemic Extra -articular manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis. Medscape 2008. BIBLIOGRAPHY Scott et al. Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitors for Rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 2006; 355: 704-12. Olson et al. New Drugs for Rheumatoid Arthritis. N Engl J Med 2004; 350:2167-79. Odell, J. Therapeutic Strategies for Rheumatoid Arthritis. N Engl J Med 2004; 350: 2591-602. Harris E, et al. Overview of the systemic and nonarticular manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis. Uptodate June 09. Odell JR et al. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with methotrexate alone, sulfasalazine and hydroxychloroquine, or a combination of all three medications. N Engl J Med 1996; 334: 1287-91. Feldmen M. Nature Reviews 2002; 2:364-371. Inflammation in the Rheumatoid Joint Olsen N and Stein C. N Engl J Med 2004;350:2167-2179.