* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Stats handouts
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
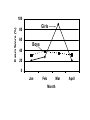
STATISTICS David Pieper, Ph.D. [email protected] Types of Variables Categorical Variables • • • • Organized into category No necessary order No quantitative measure Examples • • • • male, female race marital status treatment A and treatment B Types of Variables Ordinal Data • Ranked or ordered • Examples: – strongly agree, agree, disagree – worse, no change, better – 1st place, 2nd place, 3rd place Types of Variables Continuous Variables • Have specific order • Examples: – – – – weight temperature blood pressure time • May be converted to categorical or ordinal Types of Statistics • Descriptive – summarize data for clearer understanding • Inferential – generalize results from sample to population – make probability decisions Descriptive Statistics • Measures of central tendency – mean – mode – median • Measures of variability – – – – range variance standard deviation standard error Research Hypothesis • Null hypothesis: relationship among phenomena does not exist • Example: kids who attend daycare have no greater incidence of colds than kids who do not attend daycare Probability and p Values • p < 0.05 – 1 in 20 or 5% chance groups are not different when we say groups are significantly different • p < 0.01 – 1 in 100 or 1% chance of error • p < 0.001 – 1 in 1000 or .1% chance of error Type of Statistical Test to Use • Continuous variable as end point – 2 groups: t-test – 3 or more groups: ANOVA • Relation between 2 categorical variables: – Chi-square test – Fisher’s Exact test (2 x 2) • Relation between 2 continuous variables: – Regression analysis or correlation T-test • When comparing 2 independent groups and end-point variable (dependent variable) is continuous • Purpose is determine if the difference between the 2 groups is unlikely due to chance • May be paired or unpaired T-test • Example: • Blood pressure before and after exercise program (paired t-test) • Compare blood pressure in a group undergoing cardiac rehab to a control group not undergoing rehab (unpaired t-test) Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) When comparing 3 or more groups (independent variables) and end-point (dependent variable) is continuous. Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) Treatment A Treatment B Treatmnet C Patient 1 25 10 23 Patient 2 30 13 28 Patient 3 32 15 30 Patient 4 26 14 32 Patient 5 24 15 25 Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) mean SE Treatment A Treatment B Treatmnet C 27.4 1.5 13.4 0.9 27.6 1.6 p < 0.001 overall there is a difference between groups - does not tell us which groups are different from one another Post-hoc analysis with Tukey’s multiple comparison test A vs B p < 0.001 A vs C p > 0.05 (not significantly different) B vs C p < 0.001 Chi-square Test • When comparing 2 or more groups and the dependent variable is categorical • Minimum frequency in any cell must be at least 5 • If less than 5 and a 2 x 2 analysis - use Fisher’s Exact Test Male Female Hypertensive 35 17 Not Hypertensive 22 68 Is there a relationship between hypertension and gender? Chi square analysis - p < 0.001 Correlation or Regression • When determining if there is a linear relationship between 2 continuous variables • Ranges from -1 to 1 • Assumptions: – Relationship is linear – Random variables Pearson’s Correlation Coefficien Diastolic BP (mm) Weight (kg) 90 82 140 114 68 56 110 62 100 83 95 110 Is Diastolic BP related to Weight? r = 0.805 p < 0.01 Pearson’s Correlation Coefficient • r = 0.805 does not mean weight gain causes increase in BP or vice versa • Correlation does not prove cause and effect Type of Variable Descriptive Statistics Central Tendency Nominal (Categorical) (Non-parametric) Variability Compare Groups 3 groups 1 or 2 groups 2 2 Mode Relationship of Groups Fisher’s Exact Test Mode Ordinal (Ranks) Standard deviation Kruskal-Wallis Spearman’s Rank Order Confidence Interval t-test ANOVA Pearson’s r Median Mean (Continuous) (Parametric) Mann-Whitney Wilcoxon Median Mode Interval or Ratio Range Standard error Variance Range Regression Name the Statistical Test Do students improve their knowledge after a lecture, as measured by the number of correct answers on a quiz before and after the lecture? a. b. c. d. ANOVA Chi-Square Paired t-test * Unpaired t-test Name the Statistical Test Is there an association between smoking status and 3 levels of socioeconomic status? a. b. c. d. Mann-Whitney U-test Pearson’s correlation Turkey’s test Chi-Square * Name the Statistical Test Is there a relationship between length of hospitalization and number of medications prescribed when patient is discharged? a. Logistic regression b. Pearson’s correlation * c. Repeated measures ANOVA d. Chi-Square Free Statistics Software http://freestatistics.altervista.org/click/fclick.php?fid=4 Illustrations • • • • Graphs - not tables Replace keys with direct labels Use color Each axis must have a label with units • Each graph must have a legend 4 3 p < 0 . 0 1 CFR 2 1 0 B a s e l i n e A f t e r C o r o n a r y I n t e r v e n t i o n Exam Score (%) 100 Girls 80 60 Boys 40 20 0 Jan Feb Mar Month April