* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Choosing the right statistic
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
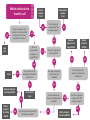
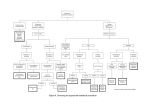
Statistical Reporting Format Statistic Letter (df) = obtained value, p decision Examples: A paired-samples t-test with 10 participants: t(9) = 3.54, p<.05 A one-way between-subjects ANOVA: F(2, 15) = 68.20, p<.05 If your results are NONSIGNIFICANT, you typically write p=NS. Example: F(2, 15) = 1.32, p=NS //\\//\\//\\//\\ //\\//\\//\\//\\ //\\//\\//\\//\\ //\\//\\//\\//\\ //\\//\\//\\//\\ //\\//\\//\\//\\ //\\//\\//\\//\\ //\\//\\//\\//\\ //\\//\\//\\//\\ //\\//\\//\\//\\ //\\//\\//\\//\\ //\\//\\//\\//\\ //\\//\\//\\//\\ //\\//\\//\\//\\ //\\//\\//\\//\\ //\\//\\//\\//\\ //\\//\\//\\//\\ //\\//\\//\\//\\ //\\//\\//\\//\\ //\\//\\//\\//\\ //\\//\\//\\//\\ //\\//\\//\\//\\ //\\//\\//\\//\\ //\\//\\//\\//\\ //\\//\\//\\//\\ //\\//\\//\\//\\ //\\//\\//\\//\\ //\\//\\//\\//\\ //\\//\\//\\//\\ //\\//\\//\\//\\ //\\//\\//\\//\\ //\\//\\//\\//\\ //\\//\\//\\//\\ //\\//\\//\\//\\ //\\//\\//\\//\\ //\\//\\//\\//\\ Which statistical test should I use? yes Are you counting up a number of events which have only one of two possible outcomes? yes Independent samples T-test Are the groups composed of the sample people? yes no yes BetweenSubjects TwoWay ANOVA MixedFactorial ANOVA Are you comparing two samples? yes no no yes Z-test no no Are you comparing a sample to a population? Sign test Pairedsamples T-test Do you know the population standard deviation? Are you comparing more than two samples? no yes Does each person experience only one condition? no Between-Subjects One-Way ANOVA One-Sample t-test no WithinSubjects One-Way ANOVA yes Are the groups composed of the sample people? Do you have more than one independent variable? no yes Are all the groups composed of the sample people? yes Within-Subjects Two-Way ANOVA Test Statistic df Use this test when: Sign Test N/A N/A Evaluating a series of repeated events, such that each event has one of two possible outcomes. Z-test Z N/A Comparing sample to a known population mean, when we know the population standard deviation One-sample t-test t N-1 Comparing sample to a known population mean, when we don’t know the population standard deviation Paired-Samples t-test t N-1 Comparing two samples, the data from which comes from the same participants Independent-Samples t-test t N-2 Comparing two samples, the data from which comes from completely different groups of participants One-Way ANOVA F num = k-1 denom = N-k Comparing more than two samples, the data from which comes from completely different groups of participants Between-Subjects Two-Way ANOVA F --- Evaluating the effect of two independent variables, such that each condition contains different participants Within-Subjects Two-Way ANOVA F --- Evaluating the effect of two independent variables, such that each condition contains the same participants Mixed-Factorial ANOVA F --- Evaluating the effects of two independent variables, one which is within-subjects, and the other between Chi-Square Homogeneity c2 k-1 Evaluating whether or not frequencies are equal Chi-Square Goodness of Fit c2 k-1 Evaluating whether or not a set of frequencies differs from some comparison set of frequencies Chi-Square Independence c2 (R-1)(C-1) Evaluating whether two sets of frequencies are different according to two levels of categorization