* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Anxiety Disorders Some Practical Questions & Answers
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
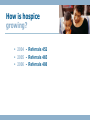
SOMC Hospice New name Same special kind of caring Dr. Suzann Bonzo February 2007 What is hospice? • Emphasis of comfort care, rather than curative • Holistic, addressing physical, emotional and spiritual well-being • Hospice regards the entire family, rather than the patient alone, as its “unit of care” • Supportive services offered to family What services are offered by hospice? • • • • • • Pain and symptom management Emotional and spiritual support Home health aides and trained volunteers Respite for family caregivers Medications, equipment and supplies Grief support for loved ones Where are hospice services provided? • • • • In the home In the hospital In the long-term setting In the Hospice Center (March 2007) How many families are served by hospice? • We serve over 100 patients and their families every day. • 2004 - 22,254 patient days • 2005 - 31,425 patient days • 2006 - 39,579 patient days What is the average length of stay? • 2004 - Average length of stay 41 days • 2005 - Average length of stay 65 days • 2006 - Average length of stay 63 days How is hospice growing? • 2004 - Referrals 452 • 2005 - Referrals 465 • 2006 - Referrals 488 What are typical diagnoses? • Acute Respiratory Failure • • • • • • • • Cirrhosis Liver Alzheimer’s Disease Anoxic Brain Damage CHF Coronary Artery Anomaly CVA Dementia Failure to Thrive • • • • • Debility Parkinson Disease Renal Failure HIV Cancer Pulmonary Disease • 1. Disabling dyspnea at rest resulting in decreased functional capacity (may be documented by FEV1 post bronchodilator <30%) – AND • 2. Progression documented by increasing ED visits or hospitalizations or decreasing FEV1>40cc per year – AND • 3. Hypoxemia with PO2<=55 or O2 sat <=88 on supplemental oxygen – OR • 4. Hypercapnia with PCO2>=50 Heart Disease • 1. Optimal treatment with diuretics and vasodilators – AND • 2. Significant symptoms of recurrent congestive heart failure at rest, classified as NYHA Class IV. (May be documented by an ejection fraction <=20%) Dementia • 1. Stage 7 or beyond of the Functional Assessment Staging Scale (as follows): – a. Unable to ambulate without assistance – b. Unable to dress without assistance – c. Unable to bathe without assistance – d. Urinary and fecal incontinence, intermittent or constant – e. No meaningful verbal communication, stereotypical phrases only, or ability to speak is limited to six or fewer intelligible words; Dementia (Cont’) – AND ONE OF THE FOLLOWING IN THE LAST 12 MONTHS: » Aspiration pneumonia » Pyleonephritis or other upper urinary tract infection » Septicemia » Decubitus ulcers, multiple, stage 3-4 » Fever, recurrent after antibiotics • Inability to maintain sufficient fluid and calorie intake with 10% weight loss during the previous 6 months or serum albumin <2.5. Stroke & Coma • Stroke and Coma: (Chronic phase patients) • 1. Meet the criteria for DEMENTIA – AND • 2. Karnofsky score <=40 – AND • 3. Poor nutritional status evidenced by weight loss > 10% over the last 6 months or serum Albumin <2.5 Liver Disease • 1. Prothrombin time prolonged more than 5 seconds over control , or INR > 1.5 – AND • 2. Serum albumin < 2.5 – AND • 3. Endstage disease showing at least one of the following: – – – – Refractory ascites or ascities with noncompliance Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis Hepatorenal syndrome Refractory hepatic encephalopathy or due to noncompliance – Recurrent variceal bleeding, despite intensive therapy What is the role of the medical director? • • • • • Available for consultations Medical coverage for hospital stays Medical coverage for Hospice Center stays Coverage for pain management After hour back-up for Hospice team What is the SOMC Hospice Center? • Facility designed to offer hospitality to those who enter, a building which can allow the staff to take care of seriously ill people in an efficient manner, yet appear non-institutional and comforting to those entering as patients or as their caregivers. Who is admitted to the SOMC Hospice Center? • • • • • Pain and symptom management Medication change and observation Caregiver crisis Imminent death Respite care What does the SOMC Hospice Center include? • Patient and family suites – each containing patient room, family room w/ sleeper sofas, and kitchenettes • Facility kitchen with the ability to prepare meals in the patient and family room • Family kitchen • Meditation room with digital baby grand piano • Family gathering area with pool table and entertainment center • Patient and family library What does the SOMC Hospice Center include? • Courtyard area with gazebo, fish pond and waterfall and fire pit • Internet access for patients and families • Private patio area • Children’s room • Interior waterfall feature • Family laundry room • Homelike décor Who provides care at the SOMC Hospice Center? • All physicians welcome to Center to provide care for their patients. Medical Director available to provide temporary coverage while patient is in the Center. • Scheduled Open House - March 4th, 2007 • Staffing: • • • • • Physicians LPN Chaplain Dietary Volunteers • • • • RN Aides Social Work Pharmacy Any Questions?