* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MATERNITY NURSING in the 21st CENTURY
Prenatal nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Patient safety wikipedia , lookup
Prenatal development wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and health care wikipedia , lookup
Licensed practical nurse wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal intensive care unit wikipedia , lookup
Maternal health wikipedia , lookup
Women's medicine in antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Long-term care wikipedia , lookup
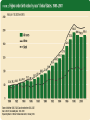
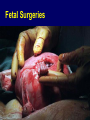
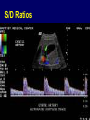
A GLIMPSE AT MATERNITY NURSING in the 21st CENTURY K. L. Ringgenberg, RNC, MSN, WHNP Shanghai Jiao Tong University SON April 5, 2006 Maternity Nursing in the 21st Century • Antepartum Care • Intrapartum Care • Technology in OB “Partum” • Parturition: birth • Partum: regarding time period to the birth • Antepartum: before birth or prenatal • Intrapartum: during the birth process • Postpartum: after the birth (usually regarded as the first 30 days) Antepartum Care in the 21st Century • Care beginning before the birth • “Prenatal” care History of Antepartum Care • Prior to 1925, no formal practice of antepartum care. • 2nd Century-warned against violent movements to prevent ROM, sexual intercourse harmful to pregnancy • 1513-first published OB text (Germany) • 1700s-forceps invented, male midwife developed theories for midwives in London • 1700s into 1800s-births attended by female community in US due to price History- continued • 20th Century-at the turn of the century, 50% of births in US conducted by midwives Home to Hospital-History • 1900 <5% USA babies born in hospital • 1940 50% • 1970 99% • 2005 99% Fast Facts-Maternal • 1900-maternal death rate 6-9/1000 USA • 40% of those deaths were due to infection • 2004-death rate at ~8-9/100,000 USA • 1989-maternal death rate in China 95/100,000 • 2004-48.3/100,000 Fast Facts-Infants • 1900-30% of infants in USA major cities died before 1st birthday • 2000s-infant mortality rate~7/1000 USA • <1950’s-infant mortality rate 300/1000 China • 2001-33/1000 in China (reportedly as low as 5/1000 in Beijing and Shanghai) 20th Century Influences • High infant & maternal mortality rates • 1914-coined term “nurse midwife” • Today-nurse midwife is defined as a RN with an advanced certification and master’s degree in midwifery • 1925-Children’s Bureau in the US recommended antepartum care to decrease mortality rates 20th Century Influences • 1965-Nurse Practitioner role (Peds) • 1972-NP role expanded to OB/GYN • 1989-US Public Health Panel examined prenatal care-recommendations made • 1950-2000-improvements in mortality due to changes in meds, antibiotics, blood products, nutrition-not prenatal care itself. 21st Century- Major Shifts caused by • Managed care • Rise of collaborative health care teams • Malpractice crises • Increased concerns for antepartum care and quality of care • Internet and computer technology 21st Century- more factors • Increased maternal age • ART-assisted reproductive technologies • Advances in genetic counseling and prenatal diagnosis • Evidence-based care • Efforts to meet goals of Healthy People 2010 and Safe Motherhood Initiatives in developing countries • Rising awareness of CAM (complimentary & alternative medicines) Twins 4/1000 West Triplets 1/7,000-10,000 Skopec Quads 1/600,000 Intrapartum Care in the 21st Century • Care provided during the birth process • Vaginal Delivery • Cesarean Section Where do delivers occur? • 96%-Hospital • 2.4%-Birthing Centers • 1%-Home *Delivers in US by CNMs Cesarean Sections • • • • • • • • • C/S rates are at an all time high. Rates vary from country to country. Some examples: Netherlands <10% Great Britain 20% USA 24-27% HK 50% in private hospitals China ~50% in some hospitals The jury is still out!!! Global Look • 70% on average-births attended by CNM in Western Europe • 85%-Holland (which WHO designates as ideal or #1 ranking) • 10%-United States • Refer to previous stats on mortality/morbidities. Nurse-Midwifery • Midwifery model-care that safeguard the birth process as natural and holistic. • Medical (or illness) model-care is based on birth is more of a disease state. • Intrapartum/neonatal mortality rate same for birth center or hospital (term/low risk) Certified Nurse Midwife • Registered Nurse • Advanced Practice Nurse (APN) • Master’s degree in Nursing • Specializing in Midwifery • Credentialing necessary for state licensing Defining Attributes • CNM-provides prenatal & gyn care to normal healthy (low risk) women; do delivers and postpartum care. • Practice in hospital setting, clinics, birthing centers and homes • May practice independently or in collaboration with a physician CNMs associated with• Personalized care • High-touch • Low-tech • Comforting care • Alternative approaches Competencies • Obtain admission history & physical • Assessments of mother and fetus • Order or initiate tests, medications or procedures • Perform ongoing exams of labor status • Attend the delivery Attending labor and birth • Provide safe, satisfying care • Patient and family are active participants • Informed consent • Appropriate use of technology Activities • Evaluation • Comfort • Assistance • Support • Reassurance • Management of complications Settings • Home • Birthing Centers • Hospitals-Labor, Delivery & Recovery Rooms (LDR), LDRP (post-partum), Single room maternity care, Birthing rooms Technology for the 21st Center • Birthing rooms • Delivery rooms • Operative suites Birthing Suite C-Section Rooms Latest Technologies • Electronic Fetal Monitoring (EFM) • Ultrasonography • Infusion pumps • Electronic monitoring devices: 1. Non-invasive 2. Invasive Fetal Surgeries Electronic Fetal Monitoring • Intermittent or continuous assessment of fetal heart rate (FHR) and uterine activity (UA) • Goal- to assist in identifying the fetus at risk EFM EFM • External (indirect) method • Internal (direct) Antepartum testing with EFM • NST-non-stress test • CST-contraction stress test • BPP-biophysical profile All assess fetal well-being Intrapartum EFM • External-tocodynamometer and transducer • Internal-spiral electrode and intrauterine pressure catheter • Fetal pulse oximetry Emerging EFM Technology • Computer analysis • Lack of clear definitions and standards at this point of fetal heart rate patterns, however, due to come out this year Electronic Health Record • Computers • Paperless charts • Integrates all aspects of assessment, intervention and evaluation Doppler Ultrasonography • Done at all stages of pregnancy • Transvaginal or transabdominal approach • Done for maternal or fetal indications • Done in office, clinic, mobile centers, ob unit, L & D Indications • Maternal diseases • Multiple gestations • Fetal growth • Establishment of fetal age • Placental location and grading • Assess fetal well-being (BPP) • Pre-term labor-cervical lengths It’s a Girl!!! 3-D & 4-D Ultrasound 3-D Early Gestation S/D Ratios Pulse Oximetry V/S Monitors Electronic B/P Monitor Critically Ill OB • Continuous cardiac monitoring • Invasive hemodynamic monitoring • CVP • Arterial lines • Pulmonary artery lines • Ventilator OB Critical Care Unit Flight Nurses Flight Nurse Genetics • Human Genome Project • Relationship to Maternity Nursing • Advanced maternal age • Patterns of inheritance • Prenatal testing • Genetic counseling • Ethics and other Telemedicine • Telemetry • Monitoring-FHR • Computer • Ultrasound images • Telephone Informatics • IT • Computers • Patient access to information • Nursing informatics Automated Medication Dispensing Machines • Cut down on errors • Bar codes • Chart medications • Labor saving • And more Summary • Past, present, future antepartum care aspects • Intrapartum care in the 21st Century as it relates to nursing and CNM • Technology today in maternity nursing with a glimpse into the future as well What is in your nursing future for the 21st Century? Questions or comments?