* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Intro To Biology
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified organism containment and escape wikipedia , lookup
Taxonomy (biology) wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
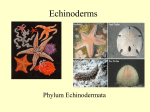
TAXONOMY Taxonomy is. a branch of science that deals with the classifications of living things Carolus Linnaeus 1753 Father of Taxonomy Three Interrelated Parts of Taxonomy • Classification Arrangement into groups • Nomenclature Assignment of Names • Identification Determining Identity Five Kingdom System • • • • • Animalia Plantae Fungi Protista Procaryote/Monera Monera (Bacteria) Fungi 1. Absorptive Chemoheterotrophs 2. Decomposers Protista 1. Unicellular 2. Autotrophic or Heterotrophic Examples: Amoeba Paramecium, Euglena Animalia 1. Multicellular 2. Heterotrophs The 5 Classes of Vertebrates Reptiles • • • • • They breathe with lungs. They are cold-blooded. Their bodies are covered with dry scales. They lay eggs. Black snakes, Bearded dragons, Turtles, Crocodiles, and Alligators are reptiles. Reptiles • Geckos and Skinks are unusual reptiles. • Frogs and Toads are non examples. Amphibians • • • • • They breathe with lungs and gills. They are cold blooded. Their skin is smooth and moist. Their birth of young is eggs. The examples are frogs, salamanders, newt, and mud puppies. Amphibians • African clawed frog is a unusual example. • The lizard is a non-example. Fish • They breathe with gills. • They are cold blooded. • Their skin is covered with scales and bony plates. • They lay eggs and have live births. • An example of a fish is a gold fish and sharks. Fish • A unusual example would be a sea horse and an eel. • A non-example would be a dolphin, whale and starfish. Mammals • • • • • Mammals breathe with lungs. They are warm blooded. They have hair/fur. Most give birth to live young. Some examples are bears, lions, tigers, and people. • Some unusual examples bats, whales, and dolphins Mammals • Non-examples are sharks and penguins. Birds • • • • • Birds breathe with lungs. They are warm-blooded. They are covered with feathers. They give birth to eggs. Examples of birds would be a red bird, hawk, and chicken. • Some unusual birds are the ostrich, flamingo, and penguin. Birds • Some non-examples are the bat and the dragonfly. Invertebrates 8 Phyla of Invertebrates Phylum Porifera (sponges) • asymmetrical • Body has canal and pores • sessile (attached to object, cannot move) Phylum Coelenterata (stinging cell) • Stinging cells and hollow bodies • tentacles that surround a mouth Examples: • • • • Jellyfish sea anemone coral hydras Phylum Echinodermata (spiny skin) • 5 part body • spines • Tube Feet (with Suctions) • Examples • Sea star or starfish Sea urchins, sand dollars Phylum Platyhelminthes (Flatworm) • flattened body • One body opening • Many are parasites, some are FreeLiving • Can regenerate Examples: • Planaria, Tapeworm Phylum Nemathelminthes (Nematoda/roundworm) • Round bodies with pointed ends • Males & females are separate Examples: • Hookwork • Ascaris Phylum Annelida (segmented worm) • Body divided into segments (with setae) • Most are hermaphrodites & free living • Examples Earthworms Ragworms Leeches Phylum Mollusca (soft-bodied) • Soft body usually protected by a shell • Body covered by mantle • Have muscular foot • Most have separate sexes • Examples: snails, slugs, octopus, cuttlefish, chitons, tusk shells, oysters, clams, and squids Phylum Arthropoda (joint-legged) • Jointed appendages • Segmented bodies • Exoskeleton that sheds by molting • Head, thorax, abdomen are main parts • Some separate sexes, hermaphrodites, parthenogenesis • Examples: • scorpion, caterpillar, • shrimp, lobster, crabs, insects Plantae 1. Multicellular 2. Photoautotrophs Classifying Plants Plants • Plants do not have fur, scales, or blood, so how are they classified? Like animals, plants are divided into two main groups. Then these two groups are divided into smaller groups. The ways that plants get their food and the ways that they create new plants will help you classify them. Who studies plants? A botanist is a scientist who specializes in the study of plants. They classify plants based on their characteristics (vascular and nonvascular). You could call them “Plant Explorers.” How are they classified? • One way that plants can be classified is by how they carry water. Plants can either be Vascular or Nonvascular. • Vascular means “having tubes” • Nonvascular mean “not having tubes” Vascular Plant Plants that have tubes, roots, stems, and leaves. These plants stand up tall. Why are these trees vascular? They have tubes, roots, stems, and leaves. They also stand up tall. More Vascular Plants Nonvascular Plant Plants that do not have tubes, roots, stems, or leaves. These plants soak up water and food from the soil, like sponges. They are also much smaller than vascular plants. Vascular or Non-Vascular? Vascular or Non-Vascular? Vascular or Non-Vascular? Vascular or Non-Vascular? Vascular or Non-Vascular?