* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ns - Pattern
TCP congestion control wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Backpressure routing wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.1aq wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Serial digital interface wikipedia , lookup
Multiprotocol Label Switching wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
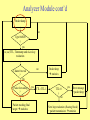
Pattern Project Area 3: Problematiche di instradamento Emulatore di Protocolli di Routing per reti Ad-hoc Alessandra Giovanardi DI – Università di Ferrara Scenario Campus: student informations, group studies, game activities Research activities Phase 1: Studies, theoretical and simulative (SAM), to investigate energy efficient routing protocols Phase 2: Emulation approach to investigate routing protocols for ad hoc networks and to give preliminary results on energy efficiencyinterface with SAM Test Environments Simulation •Cheap and quick to assemble, can do large-scale tests, tests are controlled and reproducible •Can be very slow, its implementation may differ considerably from real one Live tests •It is often difficult or too expensive to create a real test environment of any significant size •Real environment tests also tend not to be reproducible •May only be possible very late in development cycle Emulation •Involves hardware or firmware components of the systems •Can give a controlled, reproducible environment for running live code •Emulates any degree of "real-world badness" in a small, lab environment network •Provides a means for simulations to interact with a live environment Emulator Structure •Can check the performance of any kind of routing protocol, in a wireless environment. •Developed in the user space. •Created an interface to the SAM simulator, where many kinds of ad hoc routing protocols are implemented. •Based on the libpcap library and on the use of RAW sockets. •Integrated with a statistic module (performance indexes). •Two logical modules: send packet generation and transmission analyzer packet dump and forwarding (router) •Developed and tested on a cluster of Linux hosts with same filesystem •Hosts connected by an Ethernet network, but the framework is general (IEEE 802.11) Emulator Structure con’td Network Organization ns •N hosts identified by logical number n N •Packet generation can be activated in all hosts in the network or in a subset of them (Na < N) Na •All N hosts have router functions nd Analyzer Module cont’d Packet dump no Type 0x0020 ? yes ns, nd, TTL, Timestamp and nlast-hop evaluation no Channel test ok ? yes Packet forwarding ? no Packet reaching final target statistics yes TTL=TTL-1 Packet drop statistics TTL=0 ? no yes Error message + packet drop Next hop evaluation (Routing block) + packet transmission statistics Send Module •Selection of Na transmitting hosts •Generation of the frame: -arrival time (Poisson distribution or deterministic) -destination nd (uniform distribution) -timestamp (collection of the generation time) -TTL -payload •Evaluation of the next-hop (Routing block) •Creation of the frame and insertion on the network (RAW sockets) •Collection of statistics on packets effectively sent or dropped Implementation problems •Host synchronization (delivery time) •Kernel and interface packet drop •Transparent interface with SAM centralized structure (packet conversion, routing informations management, Temporization..) •... Synchronization •To collect the delivery times, hosts must be synchronized •NetworkTime Protocol (NTP) can gain in some cases an accuracy of 1ms, often it can cause a mismatch in the time synchronization up to 0.5s •We decided to compute the delivery time at the host having generated the timestamp, i.e., at the source node ns ns nd Time signalling packet (ns=0) •Time accuracy growths with the number of nodes relaying the packet Statistics •Each node can be involved in the collection of parameters needed to evaluate final performance •Many output files are created, characterized by a prefix identifying the logical number n of the node •Output files collect information on: -packets sent or dropped at the source -packets sent or dropped at each relaying node -packets correctly received or not (channel errors) by the destination •Performance indexes: -average success probability Psucc (correctly delivered packet fraction) -delivery time Tacc (end-to-end time) -average number of hops in the path Hop -number of isolated nodes Conclusions •Proposal of a general emulation framework for routing protocols in wireless environment •Work in progress: tests with a simple routing protocol (Dijkstra) without mobility •Future works: -investigation and emulation of ad hoc network routing protocols (DSR,AODV) -attention to energy efficiency, network life time etc.