* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PRODUCTIONS/OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
Psychometrics wikipedia , lookup
Numerical weather prediction wikipedia , lookup
Perceptual control theory wikipedia , lookup
History of numerical weather prediction wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Computational electromagnetics wikipedia , lookup
Monte Carlo method wikipedia , lookup
Computational fluid dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Agent-based model wikipedia , lookup
Molecular dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Live, virtual, and constructive wikipedia , lookup
Military simulation wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
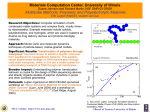
Simulation Lecture 6 Simulation Chapter 18S 1 Simulation Simulation Is … Simulation – very broad term methods and applications to imitate or mimic real systems, usually via computer Applies in many fields and industries Simulation models complex situations Models are simple to use and understand Models can play “what if” experiments Extensive software packages available ARENA, ProModel Very popular and powerful method 2 Simulation Examples Manufacturing facility Bank operation Airport operations (passengers, security, planes, crews, baggage) Transportation/logistics/distribution operation Hospital facilities (emergency room, operating room, admissions) Freeway system Business process (insurance office) Fast-food restaurant Supermarket Emergency-response system Military 3 Simulation A Simulation Model 4 Simulation Electronic Assembly/Test System Produce two different sealed elect. units (A, B) Arriving parts: cast metal cases machined to accept the electronic parts Part A, Part B – separate prep areas Both go to Sealer for assembly, testing – then to Shipping (out) if OK, or else to Rework Rework – Salvaged (and Shipped), or Scrapped 5 Simulation Part A Interarrivals: expo (5) minutes From arrival point, proceed immediately to Part A Prep area Process = (machine + deburr + clean) ~ tria (1,4,8) minutes Go immediately to Sealer Process = (assemble + test) ~ tria (1,3,4) min. 91% pass, go to Shipped; Else go to Rework Rework: (re-process + testing) ~ expo (45) 80% pass, go to Salvaged; Else go to Scrapped 6 Simulation Part B Interarrivals: batches of 4, expo (30) min. Upon arrival, batch separates into 4 individual parts From arrival point, proceed immediately to Part B Prep area Process = (machine + deburr +clean) ~ tria (3,5,10) Go to Sealer Process = (assemble + test) ~ weib (2.5, 5.3) min., different from Part A, though at same station 91% pass, go to Shipped; Else go to Rework Rework: (re-process + test) = expo (45) min. 80% pass, go to Salvaged; Else go to Scrapped 7 Simulation Run Conditions, Output Start empty & idle, run for four 8-hour shifts (1,920 minutes) Collect statistics for each work area on Resource utilization Number in queue Time in queue For each exit point (Shipped, Salvaged, Scrapped), collect total time in system (a.k.a. cycle time) 8 Simulation Simulation Models Are Beneficial Systematic approach to problem solving Increase understanding of the problem Enable “what if” questions Specific objectives Power of mathematics and statistics Standardized format Require users to organize 9 Simulation Simulation Process 1. Identify the problem 2. Develop the simulation model 3. Test the model 4. Develop the experiments 5. Run the simulation and evaluate results 6. Repeat 4 and 5 until results are satisfactory 10 Simulation Monte Carlo Simulation Monte Carlo method: Probabilistic simulation technique used when a process has a random component Identify a probability distribution Setup intervals of random numbers to match probability distribution Obtain the random numbers Interpret the results 11 Simulation Different Kinds of Simulation Static vs. Dynamic Continuous-change vs. Discrete-change Can the “state” change continuously or only at discrete points in time? Deterministic vs. Stochastic Does time have a role in the model? Is everything for sure or is there uncertainty? Most operational models: Dynamic, Discrete-change, Stochastic 12 Simulation Advantages of Simulation Solves problems that are difficult or impossible to solve mathematically Flexibility to model things as they are (even if messy and complicated) Allows experimentation without risk to actual system Ability to model long-term effects Serves as training tool for decision makers 13 Simulation Limitations of Simulation Does not produce optimum solution Model development may be difficult Computer run time may be substantial Monte Carlo simulation only applicable to random systems 14