* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 9, Lesson 1 The World Divided.
Operation Anadyr wikipedia , lookup
Cuba–Soviet Union relations wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Containment wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Berlin Blockade wikipedia , lookup
1948 Czechoslovak coup d'état wikipedia , lookup
Allied-occupied Austria wikipedia , lookup
Eastern Bloc media and propaganda wikipedia , lookup
Berlin Crisis of 1961 wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Iron Curtain wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Culture during the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Yalta Conference wikipedia , lookup
Cold War (1962–1979) wikipedia , lookup
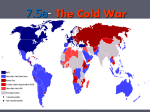
Chapter 9, Lesson 1 The World Divided. Mr. Julian’s 5th Grade Class Essential Question •What was the role of the United States as a superpower after World War II? Places • East Berlin • West Berlin • Moscow People • George C. Marshall Vocabulary • • • • • • • • • Aggressor Marshall Plan United Nations Communism Ideology NATO Berlin Airlift Cold War propaganda Europe and Japan After the War • The United States wanted to help the countries destroyed by the war rebuild. • Although, Germany and Japan had been the aggressors, the U.S. still wanted to help them. Europe and Japan After the War • In February 1945, Stalin, Roosevelt, and Churchill met in the Soviet Union to discuss what to do with Europe. • Stalin demanded that the Soviet Union have control over the countries on its borders, so that it could not be attacked again. Europe and Japan After the War • The U.S. did not like this demand but agreed anyway. • The U.S and the Soviet Union agreed to divide Korea to rid it of the Japanese. • The Soviet Union controlled most of Eastern and Central Europe including East Germany, Finland, and Poland Europe and Japan After the War • Victory, military strength, and resources made the Soviet Union and the United States the worlds most powerful nations or superpowers. Continuing Aid • The U.S. wanted to help Europeans recover for two reasons: – To show kindness – To become strong against the Soviet Union Continuing Aid • George C. Marshall, the U.S. secretary of state had an idea for making Western Europe stronger, provide funds, food, and materials to help the countries rebuild. • This plan became known as the Marshall Plan Continuing Aid • The plan helped promote democracy and helped form friendships with the U.S. • The U.S helped Asian countries too. The United Nations • The United Nations, or U.N. was formed to promote peace among countries of the world. • President Roosevelt was one of the main designers of the U.N. • Sadly he died just weeks before it became official. The United Nations • President Truman appointed Eleanor Roosevelt as the representative for the U.S to the U.N. • Mrs. Roosevelt helped adopt the Human Rights declaration. Troubling Differences • Although the Soviet Union and the U.S. had been allies during WW II the superpowers had little in common. • The Soviets used communism, or a political and economic system in which the government owns most everything. Troubling Differences • The United States and the nations of Western Europe had democratic governments that promoted personal freedoms and free enterprise. Troubling Differences • There were other important differences between the U.S.S.R. and the U.S. • The West valued human rights and wanted to work for peace, the Soviet Union did not share these ideas. • The differences in ideology, or beliefs, caused many problems. The Iron Curtain • Stalin made sure that each country controlled by the Soviet Union was communist. • These countries were no longer free to make laws or elect a government. • They were controlled by the government in Moscow. The Iron Curtain • The Iron Curtain described the closing off of Western influence to all countries controlled by the Soviet Union. • In reaction, the U.S. created N.A.T.O. (North Atlantic Treaty Organization) to help protect all of the countries involved. The Berlin Airlift • In June 1948 the Soviets stopped all traffic into Western Berlin. • No food, electricity, heating oil, or clothing were permitted. • Stalin hoped that this would break the will of Berliners and bring the entire city under Soviet control. The Berlin Airlift • The Americans and British would not leave the Western Berliners to starve or freeze. • They organized the Berlin Airlift where airplanes flew with food and supplies nonstop for 11 months. • The blockade did not work and was lifted in May 1949. The Berlin Airlift • The Soviets kept East Berlin closed off from West Berlin by building a wall dividing the two in in 1949 and completed in1962. A New Kind of War • In addition to establishing control in parts of Europe, the Soviet Union wanted to expand communism further. • In Asia, the Soviets backed governments in North Korea and China. • The Soviets made it clear they planed on doing away with democracy. A New Kind of War • The U.S. on the other hand was dedicated at stopping the spreading of communism. • The U.S. supported free elections and free enterprise. • The differences between countries became know as the Cold War, or a war fought with words, money, and sometimes, weapons. A New Kind of War • Propaganda was a key device in the Cold War. • Radio Free America would broadcast to people living behind the Iron Curtain telling them of democracy. • The Soviets would tell their people that Americans were poor and democracy did not work. A New Kind of War • One famous account happened when the Soviets showed their people Americans standing in line to buy Super Bowl tickets, they told them that we were standing in line to buy food. A World Divided • The world was divided into three groups, the West or Free World, Communist, or if you did not fit into either you were considered Third World. • In the Soviet Union, if citizens expressed their thoughts openly, they could be arrested or even worse. Time Line • 1945 - The United Nations was formed • 1946 - The Iron Curtain “fell.” • 1948 - The Marshall Plan went into effect.