* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Age of Discovery Early 15th Century to 17th Century
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
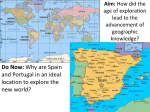
The Age of Discovery Early 15th Century to 17th Century Introduction to Exploration European Exploration was about: Power: • Wanted to dominate over the rest of the world Wealth: • Competed to become the richest country in the world. Trade : • Wanted to discover new trade routes between Europe and Asia. • (Trade=exchange of goods between two different countries) Causes of Exploration • Advanced Technology – Result of Renaissance – Able to travel great distances • New trade routes to Asia – Spices – Silk – Food • Three G’s – God- spread Christian beliefs – Gold- new riches & resources – Glory – become the greatest country in the world Major European Countries Involved 1. Portugal 2. Spain 3. England • Monarchies wanted to increase their wealth and power by controlling major trade routes • Provided funding to explorers to find direct trade routes – Middle East, India, and China Europe England Before Exploration Spain Portugal Africa After Exploration Cape of Good Hope Trade Routes to Asia & India New Technology/Innovations • Better and faster ship designs – Able to explore farther distances out into the oceans • Printing Press – Maps more widely available – Able to update more quickly • Reliable magnetic compass • New navigational methods – Astrolabe, sextant, compass – Realized the world was not flat – Increased accuracy of maps • Gun powder and new weapons – cannons/muskets/guns The Search For….GLORY! • Exploration sparked competition • 1st Place – Portugal = routes around Africa to India and China • Spices, silks, food, slaves/land • 2nd Place – Spain = routes to Americas and Caribbean • Land, slaves, sugar, food • 3rd Place – England = routes to North America (Canada) • Land, furs, slaves European Explorers • PORTUGAL: – Prince Henry the Navigator – Bartolomeu Dias – Vasco da Gama • SPAIN: – Christopher Columbus – Ferdinand Magellan – Amerigo Vespucci • ENGLAND: – John Cabot Prince Henry of Portugal • • • • Catalyst for European exploration Son of King John I of Portugal Often called Henry the Navigator Founded navigation school in 1419 – mapmakers, shipbuilders, scientists – Goals: • Discover new trade routes • Explore West African coast Bartolomeu Dias • First European to reach the southernmost tip of Africa – 1488 – Named it Cape of Good Hope Vasco da Gama • First to sail from Europe to India • Around 1498 sailed around Africa’s coast and across Indian Ocean to reach India • Portugal set up trade posts in Africa, India, and China. Christopher Columbus •Born in Italy, but sailed for Spain •Believed he could reach India by sailing west (not around Africa) •1492 -The King and Queen of Spain funded Columbus’ voyage •Made four voyages to the Americas Columbus 3 ships: Niña Pinta Santa Maria Columbus 1st Voyage = (RE)DISCOVERY • Thought he had reached India and named the land the “West Indies” • Called the natives “Indians” • Land was actually modernday Haiti/Dominican Republic in the Caribbean • Spain later discovers that Columbus had not reached the West Indies. Ferdinand Magellan • Born in Portugal • Sailed for Spain • Proved the new lands Columbus called “West Indies” were not India • First expedition to circumnavigate (sail around) the globe Amerigo Vespucci • Italian • Explored the Americas • Claimed the new lands were not part of Asia. – Route to Asia was blocked by two large continents – N. and S. America named after him. John Cabot • Born in Italy • Sailed for England • Made voyages to North America • Led to the founding of English colonies in America. England Spain Portugal Outcomes of Exploration Outcomes of Exploration • Lasting contact between Europe, Africa, and Americas • Columbian Exchange – exchange of goods, ideas, & diseases between Old World (Europe) and New World (Americas) • Devastated native American population • Atlantic Slave Trade – Forced movement of native Africans Columbian Exchange • Exploration led to an enormous exchange of: – People – Plants/crops & animals – Technology & ideas – Customs, traditions, & religions • Changed the lives of people in Asia, Europe, the Americas, and Africa Diseases • Diseases were exchanged from Europeans to natives • These included: – – – – Smallpox Malaria Plague Measles • Reduced native population by about 90% • Increased starvation • Lost native knowledge, customs, and religious traditions • Weakened tribal leadership – Allowed societies to be conquered The Slave Trade • Existed before the Europeans encountered Africa – Portuguese replaced European slaves with Africans • Traded goods with African leaders for slaves – brought slaves to the new world • Largest forced migration of people in history Global Impact of European Exploration in Europe and the Americas • Impact in Europe: – – – – – Power Wealth Trade Technological Advances Land • Impact in the Americas: – Spread of disease – Conversion to Christianity – Conquest of natives – Blending of cultural customs/traditions – Slavery – Colonization & imperialism Lasting Impact of Exploration • Globalization – international interchange of world views, culture, ideas, and products • Colonization/Imperialism – 17th century – Expansion of European empires – Slavery 2.0 • Interdependence – The Americas dependant on European countries for modern conveniences – Europeans dependant on Americas for resources and cheap labor • Transculturation – Blending of cultures to create a new culture