* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied naval bombardments of Japan during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Invasion of Normandy wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
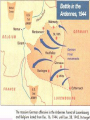
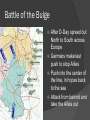
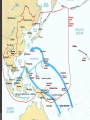
Objective: Analyze the US strategies and Major battles of WWII Std: 11.7.2 Prior Knowledge Importance Through the Atlantic Charter with Britain, the United States pledged to declare war against the Japanese. do everything it could to help defeat Germany. continue to stay completely neutral. pray for the war to end soon. D Day D-Day Significance Allies had been pushed off of Europe Needed to gain a foothold on the continent again Took a year to train and supply before attacking If failed, Russia could possible defeat Germany and control Europe Allies leave from Britain to attack Northern France Operation Overlord – D-Day Amphibious assault on the unsuspecting Germans Eisenhower supreme commander of Allied troops Land on the beach and take out the sea wall Normandy Battle of the Bulge After D-Day spread out North to South across Europe Germans make last push to stop Allies Push into the center of the line, in hopes back to the sea Attack from behind and take the Allies out Bulge 2 The Allies were able to make a stand and push the Germans back for their final defeat On the Eastern Front the Russians made their way into Berlin Objective: Analyze the US strategies and Major battles of WWII Midway • • • • • • • Japanese tried to eliminate American’s Naval power Surprise attack but US code breakers intercepted message Moved American aircraft carriers off the horizon and pulled Japan into a trap Japan lost 4 aircraft carriers and a heavy destroyer Turning point in Pacific Japan never recovered from defeat. America kept a base to launch attacks Island Hoping In the Pacific the US used Island Hoping. Jump islands that are heavily fortified but may not be key to the war Go to islands that are important because of proximity to Japan or resources Iwo Jima For 74 days, the U.S. pounded the small island with nearly 7,000 tons of bombs, and more than 20,000 shells 110,000 American soldiers (25,000 killed or wounded) Vs. 25,000 Japanese soldiers (only 216 surrendered) Okinawa • 180,000 American soldiers and more than 1,300 warships Vs. 100,000 Japanese soldiers • 2nd largest invasion in world history behind D Day • Japanese pilots flew 2,000 kamikaze attacks Okinawa • • • Americans: 50,000 dead or wounded – costliest battle of the war Japanese: Out of 100,000 soldiers, only 7,200 remained to surrender The importance of these battles was that the U.S. was able to bomb the Japanese islands at will Firebombing Europe and Japan Goal: destroy cities All major cities were “fair” game Some considered this to be war crimes Morale: left people undeterred, they wanted revenge Atlantic Charter Set up goals for Post War world No territorial gains by US or Britain People have human rights Lower Trade barriers Freedom of the seas World free of want and fear Roosevelt couldn’t promise declaration of war Do everything to “force an incident” Importance Through the Atlantic Charter with Britain, the United States pledged to declare war against the Japanese. do everything it could to help defeat Germany. continue to stay completely neutral. pray for the war to end soon. Closure During World War II, the Allied invasion of France on D-Day (June 6, 1944) was significant because it demonstrated the power of the atomic bomb. resulted in a successful German revolt against Hitler and the Nazi Party. led to the immediate surrender of German and Italian forces. forced Germany to fight a two-front war. Closure What tactic was used by the United States in the Pacific theater Blitzkrieg Surprise Attack Island Hopping Schlieffen Plan Closure The Battle of the Bulge was significant because it marked the last German offensive. liberation of the death camps. Allies' first victory in a land battle. Axis powers' first loss in a land battle. Closure Which nation was defeated at the Battle of Midway after its plans of an attack were intercepted? the Soviet Union the United States Japan Great Britain