* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Other Characteristics Shared by Mammals
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
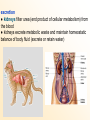
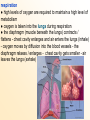
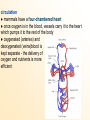
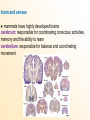
MAMMALIAN CHARACTERISTICS Chapter 30.1 OBJECTIVES: 1. Identify the characteristics of mammals. 2. Describe how mammals maintain a constant temperature to achieve homeostasis. 3. Compare the respiration in mammals to other vertebrates. Hair and Mammary Glands ● two characteristics that distinguish mammals from other animals mammary glands: glandular tissue that produce and secrete milk that nourishes developing young hair is to mammals as feathers are to birds... functions of hair 1. insulation 2. camouflage (bengal tiger blends into the jungle) 3. sensory device (whiskers) 4. waterproofing (sea otter) 5. signaling (white tailed deer) 6. defense (porcupine) Other Characteristics Shared by Mammals ● mammals are endotherms: produce body heat internally (high metabolic rates that require large amounts of energy) feeding and digestion ● energy created through the breakdown of food ● 4 trophic categories based on food source 1. insectivores 2. herbivores 3. carnivores 4. omnivores ● a mammal’s adaptations for finding, capturing, chewing, swallowing and digesting food influence the mammals structure and life habits... ● herbivores have a larger cecum and longer digestive tracts than carnivores excretion ● kidneys filter urea (end product of cellular metabolism) from the blood ● kidneys excrete metabolic waste and maintain homeostatic balance of body fluid (excrete or retain water) respiration ● high levels of oxygen are required to maintain a high level of metabolism ● oxygen is taken into the lungs during respiration ● the diaphragm (muscle beneath the lungs) contracts / flattens - chest cavity enlarges and air enters the lungs (inhale) - oxygen moves by diffusion into the blood vessels - the diaphragm relaxes / enlarges - chest cavity gets smaller - air leaves the lungs (exhale) circulation ● mammals have a four-chambered heart ● once oxygen is in the blood, vessels carry it to the heart which pumps it to the rest of the body ● oxygenated (arteries) and deoxygenated (veins)blood is kept separate - the delivery of oxygen and nutrients is more efficient brain and senses ● mammals have highly developed brains cerebrum: responsible for coordinating conscious activities, memory and the ability to learn cerebellum: responsible for balance and coordinating movement ● mammals carry out complex behavior like learning and remembering - get information about their environment and retain it ● importance of senses varies between groups of mammals glands A group of cells that secrete fluid to be used elsewhere in the body – helps regulate homeostasis (internal environment) reproduction Internal fertilization and development of the embryo takes place in the uterus , nourished by the placenta gestation: the amount of time the young stay in the uterus before they are born – varies between mammals