* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Circulation
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
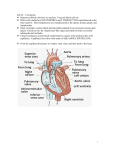
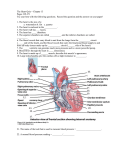
Chapter 42 No Circulatory System Exchange across PM directly with environment Gastrovascular cavity Digestion and distribution Open Circulatory System Bathes organs Minimizes diffusion distance Pumps hemolymph No pigment = move nutrients only Body movements circulate Closed Circulatory System Vessels enter organs Capillaries Hemoglobin pigments Allows higher pressure Larger, more complex organisms Control flow Cardiovascular System Heart, vessels, and blood Direction determines type of vessel Natural selection modified according to activity levels Number of loops and heart chambers Cardiovascular System Types 2 chambers Single circulation 3 chambers Partial 4 chambers Double circulation 4 chambers Heart pulmonary (tricuspid) aortic (bicuspid) Cardiac Cycle Systole = contract Diastole = relax Beating to its Own Rhythm Bundles of His Electrocardiogram measures activity conducted to skin via body fluids The Working Heart Lub-dub, lub-dub, lub-dub AV-semilunar contraction alternates Cardiac Output is volume of blood/min Heart rate X stroke volume (ventricle contraction) Heart murmurs Blood moves backward Myocardial infarction (heart attack) Lack of O2 kills muscle fibers Stroke Artery blockage kills nervous tissue Blood Vessels Endothelium Simple squamous Middle layer Smooth muscle Outer layer Connective tissue and Elastin Types of blood vessels Arteries and arterioles Thicker walls, smaller diameter High pressure Capillaries Lowest velocity Allows diffusion Regulate pressure Venules and veins Thinner walls, larger diameter Lowest pressure One way valves The Little Blue Pill Arterioles Vasoconstriction ○ BP effect? Vasodilation ○ BP effect? Hormonal and neural control Fight or flight, exercise Nitric oxide Capillaries Provide blood to all tissues Sphincters regulate flow patterns Thoroughfare channel is always open Active or inactive tissues Digestive Organs While eating Arteriole regulation too While exercising Human Cardiovascular System Process is continuous Circuits are simultaneous Be able to diagram/explain Blood Pressure and Flow Blood flows from high to low pressure Smaller vessels resistance Velocity slows in vessel number area Velocity and pressure slow Allows time for diffusion in vessel number area Velocity speeds up Toll booth or accident examples Pulse and artery stretch Circulation and Gravity Blood pressure highest at heart level Fainting Raising wounds Veins Valves and skeletal muscles ○ Standing on mats ○ Cool downs ‘Cankles’ Fluid Exchange B/w capillaries and interstitial fluid Blood components to large to leave vessel Blood pressure vs. osmotic gradient Blood Connective tissue Plasma is matrix Cellular Elements Erythrocytes Leukocytes Platelets Blood Composition (90%) w/o nuclei With nuclei infections B- and T-cells histamine macrophages phagocytes Fragmented cells w/o nuclei Blood Clotting Damaged vessel constricts Platelets form a temporary plug Fibrin threads trap cells to seal