* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Amphibians
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
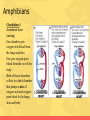
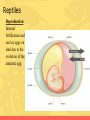
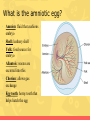
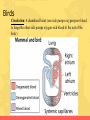
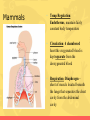
Animal Kingdom What are the charctersitics of an animal? • Eukaryote • Sexual reproducers • Heterotrophs • Locomotion • Multicellular What are the 2 major divisions in animals? Animals without a backbone Animals with a backbone • These include insects, worms, sponges, mollusks, and etc. • Known as chordata • Lack bones, some have hard outer shells or exoskeletons • Make up only 5% of animals. • Make up approximately 95% of all animals. • Insects make up 80% of all animals. • There are five divisions of animals with backbones. Phylum Chordata What is the phylum Chordata? Includes 5 Classes 1.Fish 2.Amphibians 3.Reptiles 4.Birds 5.Mammals What are fish? • Habitat: nearly every aquatic environment • Respiration: use gills to breathe • Circulation: 2 chambered heart • Reproduction: sexual (mostly external) • Nervous System: lateral line system that can detect movement What are the three types of fish? • 3 Major Types of Fish • Jawless Fish • Cartilaginous Fish • Bony Fish What are amphibians? • Examples: frogs, salamanders, toads • Habitat: live on land and water • Respiration: lungs in adults, gills in tadpoles, but mostly through the moist skin • Reproduction: External reproduction (water needed to transport sperm and eggs must be kept moist) Amphibians • Circulation: 3 chambered heart (mixing) • One chamber gets oxygen-rich blood from the lungs and skin • One gets oxygen-poor blood form the rest of the body • Both of those chambers collect in a third chamber that pumps a mix of oxygen-rich and oxygenpoor blood to the lungs, skin and body Amphibians • Temperature Regulation: Ectotherms, variable body temperature – gets heat from outside source • Metamorphosis – eggs, tadpoles, adult • Tadpoles – fins, gills, 2chambered heart • Adult – legs, lungs, 3chambered heart What are reptiles? • Examples: snakes, crocodiles, turtle, lizards • Habitat: Land mostly • Respiration: No exchange thru skin bc it is scaly MUST use lungs • Circulation: most have 3 chambered heart • Obtain food: claws, legs directly under body makes running easier • Temp Regulation: ectotherms Reptiles • Reproduction: Internal fertilization and can lay eggs on land due to the evolution of the amniotic egg What is the amniotic egg? • Amnion: fluid that cushions embryo • Shell: leathery shell • Yolk: food source for embryo • Allantois: wastes are excreted into this • Chorion: allows gas exchange • Egg tooth: horny tooth that helps hatch the egg What are birds? • Examples: pelican, penguin, blue jay • Respiration: lungs and air sacs for extra oxygen for flight • Temp Regulation: Endotherm (internally regulates body temp so it is constant) • Reproduction: internal fertilization and lay amniotic egg with a hard shell, must incubate eggs • Adaptations: hollow bones for flight, feathers are lightweight, wings Birds • Circulation: 4 chambered heart (one side pumps oxygen-poor blood to lungs the other side pumps oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body) What are mammals? Must haves to be a mammal: Hair Mammary glands that secrete milk to nurse young Diaphragm to expand and contract chest cavity to get more oxygen Specialized teeth (ex. Molars, canines, incisors) Can learn! Mammals • Temp Regulation: Endotherms, maintain fairly constant body temperature • Circulation: 4 chambered heart the oxygenated blood is kept separate from the deoxygenated blood • Respiration: Diaphragm – sheet of muscle located beneath the lungs that separates the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity What is the role of hair for mammals? • Why is HAIR important? • Insulation • Waterproofing • Conserves body heat • Mammals cool off by panting and sweating How are mammals classified? Mammals are classified into 3 groups based on their method of reproduction 1. Placental Mammals 2. Marsupials 3. Monotremes What are Placental Mammals? • Carries baby in the mother’s uterus until development is almost complete • Placenta provides food for the baby, allows gas exchange, and removes waste • 95% of mammals are placental What are Marsupials? • After a baby has grown to a certain size, the mom carries the baby inside a pouch made of skin and hair on the outside of the mom’s body • Most are found in Australia What are Monotremes? • Reproduces by laying eggs • Found only in Australia, Tasmania, and New Guinea • 3 species of monotremes alive today (platypus, spiny anteater and longbeaked echidna