* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Present
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
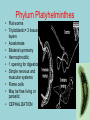
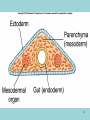
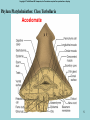
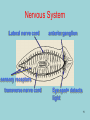
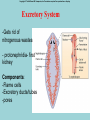
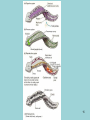
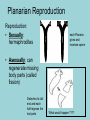
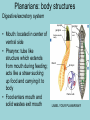
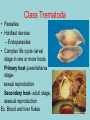
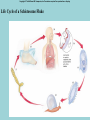
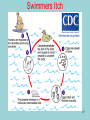
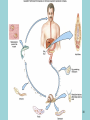
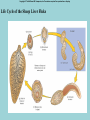
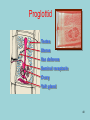
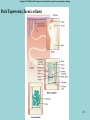
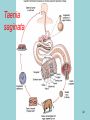
Phylum Platyhelminthes Zoology WCHS 1 Phylum Platyhelminthes • Flat worms • Triploblastic= 3 tissue layers • Acoelomate • Bilateral symmetry • Hermaphroditic • 1 opening for digestion • Simple nervous and muscular systems • Flame cells • May be free living or parasitic • CEPHALIZATION 2 Acoelomate Ectoderm Mesoderm Endoderm Digestive cavity is the only inner cavity 3 4 Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Phylum Platyhelminthes: Class Turbellaria Acoelomate 5 Other Body Plans: Pseudocoelomate Ectoderm Mesoderm Endoderm Fluid filled cavity between the endoderm and ectodermpseudocoelom Differs from a true coelom because…. • It is not entirely lined with mesoderm tissue • Organs are not suspended or attached to membranes 6 (mesenteries) Other Body Plans: Coelomate Ectoderm Mesoderm Endoderm Epithelial lined cavity between digestive tract and body wall 7 8 Flatworm Body Systems • No Circulatory or Respiratory systemssimple diffusion through body wall Systems Present• • • • Digestive Nervous Excretory Reproductive 9 Flatworm Body Systems: Digestive Incomplete• mouth • pharynx (to swallow food) • intestine(no anus) 10 Nervous System Lateral nerve cord anterior ganglion sensory receptors transverse nerve cord Eye spot= detects light 11 Cephalization=“Primitive Brain” Auricle Cerebral ganglion Paired nerve cords 12 Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Excretory System -Gets rid of nitrogenous wastes - protonephridia- first kidney Components: -Flame cells -Excretory ducts/tubes -pores 13 Reproductive System •Sexual and asexual reproduction sexual- eggs + sperm asexual- regeneration •Hermaphroditesboth male (penis and testis) and female organs(vagina and ovary) 14 15 Kingdom Animalia Phylum Platyhelminthes Classes: Turbellaria Trematoda Cestoda 16 Class Turbellaria • • • • Most free-living Aquatic Eye spots Regenerate if cut in two • Ex. Planaria 17 Planarians • Free-living flatworm • bilateral symmetry • Lives in fresh water usually under leaves and rocks • Usually feeds on dead or slow moving organisms Planarian Reproduction Reproduction: • Sexually: hermaphrodites each Planaria gives and receives sperm • Asexually: can regenerate missing body parts (called fission) Detaches its tail end and each half regrows the lost parts What would happen ???? Planarians: body structures • • • • Nervous/sensory system: Brain-like structure Nerve cord: carries impulses down body Eyespots: sense light and dark Sensory pits: line sides of head to aid in movement and sensing surroundings • Flame Cells: remove excess water and nitrogenous wastes Planarians: body structures Digestive/excretory system eyespot • Mouth: located in center of ventral side • Pharynx: tube like structure which extends from mouth during feeding; acts like a straw sucking up food and carrying it to body • Food enters mouth and solid wastes exit mouth ganglion ganglion Gastrovascular cavity Mouth Nerve cord pharynx Flame cells LABEL YOUR PLANARIAN!!! Class Trematoda • Parasites • Holdfast devices – Endoparasites • Complex life cycle- larval stage in one or more hosts Primary host-juvenile/larva stagesexual reproduction Secondary host- adult stage, asexual reproduction Ex. Blood and liver flukes 22 Flukes Blood fluke life cycle: • Eggs are released in water from wastes of infected host • Hatch in to swimming larvae in water • Larvae enter a host (like a snail) where they develop & mature • Enter water again and bore into skin of new host (man) • From the blood stream they bore into intestines where they attach and feed on blood Schistosoma • Blood flukes • 200 million people • 1 million deaths/year 24 Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Life Cycle of a Schistosome Fluke 25 Schistosome • Cercaria have forked tail 26 Swimmers Itch 27 Clonorchis sinensis human liver fluke Oral sucker Intestine Uterus Yolk gland Ovary Seminal recepticle Testes 28 Clonorchis sinensis • • • • • • Chinese liver fluke 50 million people Cirrhosis of liver Diarrhea Edema Pain 29 30 Fascioloa hepatica • Sheep liver fluke • Sheep, cattle and man – Weight loss • Eat contaminated vegetation 31 Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Life Cycle of the Sheep Liver Fluke 32 Paragonimus westermani • Lung fluke • Carnivores, pigs, rodents and man • May be fatal 33 34 35 Class Cestoda: “cess pool” • Tape worms • All parasitic • Live in intestines of vertebrates • No digestive system • 40 feet long 36 Tapeworm structures • Scolex= head • hooks and suckers to aid in attachment to intestine • Proglottids: individual parts of worm – Each one is detachable – Each proglottid may contain up to 100,000 eggs which fall off when full – When released, they exit with the host’s wastes Tapeworm life cycle • Eggs hatch in intestines of intermediate host (pig or cow) • Young worms burrow out of intestine into pig’s muscle tissue forming cysts • Secondary host (man) eats undercooked/raw meat containing worm larvae cysts • Larvae hatch and mature in intestines • Attach to intestines, soak up digested food of host • May enter bloodstream and infect other tissues Scolex 39 Proglottid Testes Uterus Vas deferens Seminal receptacle Ovary Yolk gland 40 Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Pork Tapeworm (Taenia solium) 41 Taenia saginata 42 Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Life Cycle of the Broad Fish Tapeworm Diphyllobothrium latum Source: Redrawn From Centers for Disease Control, Atlanta, GA. 43 Dipylidium caninum 44 Echinococcus granulosus • Parasite of dogs – Host • Juveniles in sheep, man and other mammals – Intermediate host • Hydatid cyst 45 46 Hydatid Cyst • Cysticercus – Juvenile stage 47 Ecinococcus granulosus • Adult stage in dog 48 49