* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1 - Skyline R2 School
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
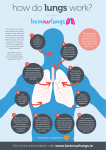
8. The Respiratory System 1 All your body cells need oxygen Without oxygen your body cells cannot produce energy 2 The main organ of the respiratory system is the lungs Vocabulary: Respiratory system A body system that brings oxygen into the body and gets rid of cell wastes 3 So how does your respiratory system work? To breathe you need the help of your muscular system 4 A large muscle called the diaphragm controls your lungs Vocabulary: diaphragm A large muscle that controls the lungs and breathing 5 When the diaphragm moves down, air is pulled into the lungs When the diaphragm moves up, air is forced out of the lungs 6 Air usually enters the body through the nose Inside the nose, tiny hairs clean the air by catching dirt and other particles 7 The clean warm air moves into the tube in your throat called the windpipe Vocabulary: windpipe A tube in the throat that moves air into the lungs 8 The air is warmed more by the windpipe (trachea) as the air moves toward the lungs The windpipe divides into two smaller tubes so air can go into both lobes of the lungs 9 The tubes continue to divide into the lungs and get smaller and smaller and end in tiny air sacs Vocabulary: Air sacs The end of the tubes that go into the lungs 10 The lungs are made up of about 300 million of these air sacs Air sacs are like little balloons and each are surrounded by capillaries 11 When you breathe in, oxygen enters the air sacs The oxygen passes through the thin walls of the air sacs and enters the capillaries 12 Then the oxygen is picked up by the red blood cells The blood cells carry oxygen to every cell in the body 13 At the same time, another process is taking place Carbon dioxide from the blood moves out of the capillaries 14 Then the carbon dioxide moves into the air sacs and leaves the body as you breathe out 15 Remember: Carbon dioxide is a waste produced by all body cells It is produced when body cells break down food and give off energy 16 In the lungs, carbon dioxide and oxygen are exchanged all the time Your body depends on this process to stay alive 17 If your body did not get enough oxygen, its cells would soon die The cells would also die if they could not get rid of carbon dioxide 18 The carbon dioxide would build up in the blood and become poisonous 19 Keep your digestive & excretory systems in working order by drinking lots of water Your body loses a lot of water through sweat and urine 20 It is very important for your systems to eat fruits, vegetables, and grains to help your body get rid of solid waste This helps you from getting “blocked” up! 21 Your respiratory system needs strong muscles and healthy lungs to bring lots of oxygen into the body Exercising helps to strengthen the muscles you use to breathe 22 Exercise also makes your lungs work harder It is very important for your respiratory system that you don’t smoke 23 Smoking harms the tissues of the lungs Damaged lungs cannot bring your cells all the oxygen they need which in turn weakens your body 24 25