* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Living system interactions
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
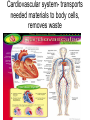
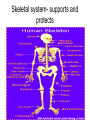
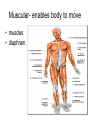
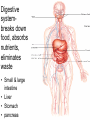
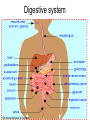
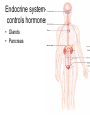
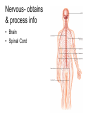
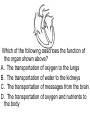
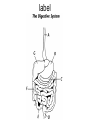
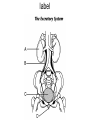
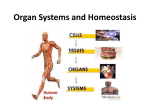
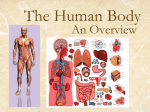
Living system interactions District Assessment Review Cell, tissue, organs, organ systems Cardiovascular system- transports needed materials to body cells, removes waste Skeletal system- supports and protects Muscular- enables body to move • muscles • diaphram What are smooth muscles and where are they located? Smooth muscles are involuntary muscles such as inside of many internal organs. Skin- protects the body- keeps water inside, sense external environ • Skin and Hair Digestive systembreaks down food, absorbs nutrients, eliminates waste • Small & large intestine • Liver • Stomach • pancreas Digestive system Reproductive- creates offspring • Female- ovaries • Male- testes Endocrine systemcontrols hormones • Glands • Pancreas Nervous- obtains & process info • Brain • Spinal Cord Respiratory- gets oxygen into the body, removes carbon dioxide Excretory system- removes wastes- regulate water Immune system- fights disease • Lymphoid organs include: • adenoids • blood vessels (the arteries, veins, and capillaries through which blood flows) • bone marrow • lymph nodes • spleen • thymus • tonsils Equilibrium • Balance • System is stable- parts function smoothly • Homeostasis Homeostasis • Process by which the body’s internal environment is kept stable in spite of change in the external environment • 1. Heart rate • 2. Breathing rate • 3. Temperature (body) • 4. Blood cell count Negative feedback • Living systems maintain internal equilibrium (homeostasis) process is turned off by the condition it produces • 1. Levels of sugar (glucose) • 2. Shivering • 3. Perspiring • 4. Turgor pressure in plants – helps give shape and firmness (wilts- less pressure) Hormone • Chemical produced by an endocrine gland (that affects the activity of a tissue or organ) • Insulin Diffusion • Substances move back and forth through cell membrane (high to low) Osmosis • Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane • Ms. May is not feeling well. She has a fever and has been vomiting. What type of internal stimulus would cause this type of response? A. Heat exhaustion B. Invasion of a virus C. Freezing temperature D. Lack of nutrients in the body Which of the following describes the function of the organ shown above? A. The transportation of oxygen to the lungs B. The transportation of water to the kidneys C. The transportation of messages from the brain D. The transportation of oxygen and nutrients to the body Which of the following happens to your eyes as you leave a dark movie theatre and walk in to a bright room? A. Your pupils dilate. B. Your pupils remain the same size. C. Your pupils constrict to limit the amount of light. D. Your pupils dilate to limit the amount of light. label label label label Example of stimulus and response • Within the context of the integumentary (skin) system: An ant crawling on your arm disturbs the hairs on your arm. You feel that stimulus and brush the ant away! Example of stimulus and response • Within the context of the circulatory system: If foreign invaders such as a bacteria enter your body, your body sounds an alert and dispatches an army of white blood cells to the wound site to attack the invaders. Example of stimulus and response • Within the context of the respiratory system: If you hold your breath (a conscious act), carbon dioxide begins to build up in the blood stream. Your body detects this; you faint and lose consciousness; you begin to breathe normally, your body receives the oxygen it needs, and you return to consciousness. Example of stimulus and response • Within the context of the endocrine system: If there is too much glucose in your blood stream, the pancreas will produce a chemical called insulin which enables body cells to take in glucose from the blood and use it for energy. If the glucose returns to the normal level, the production of insulin from the pancreas would stop. An organ where gas exchange occurs in the • A. Heart • B. lung • C. kidney • D. brain Which of these structures are most abundant in the human body? • A. systems • B. tissues • C. cells • D. organs Example of stimulus and response • Within the context of the excretory system: If you eat the fish with mercury in it, your liver will filter the poison out of your body.