* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human Anatomy body Systems
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
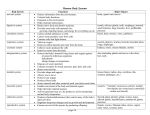
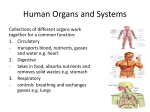
Human Anatomy body Systems Integumentary system 1. Organs 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Skin Hair Nails Sweat glands Sebaceous glands Integumentary System 1. Functions 1. 2. Protect underlying tissue Regulate body temperature 1. 3. Sweat glands (sudoriferous gland) Synthesize products that lower pH, and carry away urea, sodium chloride, lactic acid, products broken down from garlic and spices Skeletal System 1. Organs 1. 2. 3. Bones Ligaments Cartilages Skeletal System 1. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Framework Attachment place for muscles Protect internal organs Blood cell production (Hemopoeisis) Reservoir for salts Muscular System 1. Organs 1. Skeletal 1. 2. 2. Smooth 1. 2. 3. Quadriceps femoris Biceps brachii Diaphragm Lining of Intestines Cardiac 1. Heart Muscular System 1. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Move your bones Maintain posture Create heat Pump blood Allow us to breathe Move food and waste along digestive and urinary tracts Nervous System 1. Organs 1. 2. 3. Brain Nerve cord Sensory and Motor Nerves Nervous System 1. Functions 1. An intricate network of structures that activates, coordinates,and controls all the functions of the body. Endocrine System 1. Organs 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Thyroid Parathyroid Anterior pituitary Posterior pituitary Pancreas Adrenal glands Testes Ovaries Pineal Gland Endocrine System 1. Functions 1. Network of ductless glands that secrete hormones into the blood or lymph fluid and affect particular target tissues, altering metabolism, growth and secretions from other organs. Digestive System 1. Organs 1. Primary Organs 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 2. Mouth Teeth Tongue Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small intestines Large intestines Accessary Organs 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Salivary glands Gastric glands Liver Pancreas Gall bladder Digestive System 1. Functions 1. Receive food and convert large molecules into smaller molecules that can be absorbed and used by the bodies cells Respiratory System 1. Organs 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Nasal cavity Oral cavity Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchi lungs Respiratory system 1. Functions 1. 2. 3. 2. 3. Pulmonary ventilation of the body and exchange of O2 and CO2 between air and blood Warms the air Assists in speech formation Breathe? Respire? Circulatory System 1. Organs 1. 2. 3. Heart Arteries (away) Veins (toward) Circulatory System 1. Functions 1. Transport 1. 2. 3. Nutrients from digestive system to all cells of the body Wastes from cells to kidneys Oxygen from lungs to cells and Carbon dioxide away from cells to lungs Lymphatic System 1. Organs 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Lymph nodes Thymus gland Tonsils Liver Spleen Appendix Bone marrow Lymphatic system 1. Functions 1. 2. Transports fats, proteins and other substances to the blood system Aids in defending your body against various microorganisms. 1. 2. T-cells (lymphocytes) B-cells (lymphocytes) Urinary System 1. Organs 1. 2. 3. 4. Kidneys Ureters Urinary Bladder Urethra Urinary System 1. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Remove nitrogenous wastes from the blood stream in the form of UREA Maintain water balance Maintain electrolyte balance Maintain blood pressure Reproductive System 1. Organs 1. Male Reproductive 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 2. Testes Vas Deferens Prostate Gland Seminal Vescicle Bulbourethral Gland Penis Urethra Female Reproductive 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Ovaries Fallopian Tubes Uterus Vagina Clittoris Vulva Reproductive System 1. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Producing and maintaining sex cells (ovum, spermatazoa) Transporting sex cells from origin to the female reproductive system Providing a place for the development of the fertilized zygote. Producing hormones 1. 2. 3. Testosterone Progesterone Estrogen Body Cavities 1. Dorsal 1. 2. 2. Cranial Spinal Ventral 1. 2. Throacic Abdominopelvic Planes of Reference 1. Sagittal 1. 2. Transverse 1. 3. median Horizontal Frontal Directional terms Cranial 2. Superior 3. Caudal 4. Inferior 1.