* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Animal Body Systems
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
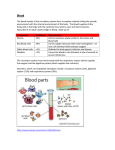
Animal Body Systems Objectives…(At the end of this lecture you should be able to): Summarize the functions of the digestive, respiratory, circulatory, nervous, skeletal and excretory systems. Compare a gastro vascular cavity with a one-way digestive system. Differentiate open from closed circulatory systems. Distinguish asexual from sexual reproduction. Body Systems are specialized to carry out different tasks Simple animals like sponges carry out the many tasks of living with little specialization in the cells of their body. More complex animals have evolved tissues and organs that are specialized to perform specific functions. Body Systems are specialized to carry out different tasks Seven important functions of these tissues and organs are : Digestion Respiration Circulation Conduction of nerve impulses Support Excretion Reproduction Digestion Purpose: Obtain energy & nutrients Sponges digest their food with their body cells Simple animals, such as flatworms, have a gastro vascular cavity: a digestive cavity with only one opening. More complex animals, like us, have a digestive tract with two openings: mouth and anus. Respiration Purpose: Exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide gases Can only take place across a moist surface. In simple animals like jellyfish gasses are exchanged directly with their environment through diffusion. More complex animals have specialized respiratory structures like gills or lungs. Circulation Purpose: Transport oxygen and nutrients to the other parts of the body There are 2 types of circulatory systems: Open: heart pumps fluid containing oxygen through a series of vessels & is dumped into the body cavity. Closed: heart pumps blood through a system of blood vessels. The blood stays in the vessels the whole time. OPEN: CLOSED: Conduction of nerve impulses Purpose: Coordinate the activities in an animal’s body and allow animal to sense and respond to environment. Simple animals, like hydra, have little coordination among their nerve cells. Complex animals, like grasshoppers, have nerve cords/ganglia & a brain. Support: Skeletal Purpose: Provide a framework that supports the body. Many soft-bodied invertebrates have a hydrostatic skeleton made of water like a filled water balloon. Other invertebrates, such as insects & crabs, have an exoskeleton: a rigid external skeleton. Complex animals, like dogs, have an endoskeleton: hard material such as bone embedded within the animal. Excretion Purpose: Removal of wastes from cellular metabolism (CO2, ammonia, etc.) Simple aquatic invertebrates & some fishes pass it through their skin/gills by diffusion. More complex animals have specialized excretory structures like kidneys. Reproduction Purpose: produce offspring to ensure that the species survives Two types of reproduction: Asexual: does not involve fusion of two gametes. EX: A sponge can reproduce by fragmenting its body. Sea anemones pull apart into 2 individuals Sexual: a new individual is formed by the union of a male and female gamete. EX: egg + sperm = fertilization = blastula Is this sexual or asexual reproduction? Fun & Funky Fact: Sea “horse” reproduction Pregnant sea horse fathers give birth. A female sea horse inserts her eggs into a pouch on the male’s abdomen, where they are fertilized. The male incubates the eggs until they are fully developed and then gives birth to tiny sea horses. Fertilization There are two types of fertilization: External: occurs outside the body EX: Most aquatic animals simply release the male and female gametes near one another in the water, where fertilization occurs…..think opening scene of Finding Nemo….they were outside the mom. Internal: occurs inside the females body EX: Animals that live on land don’t have water so the gametes would dry out. Internal fertilization allows it to take place in a moist environment. Objectives… (At the end of this lecture you should be able to): •Summarize the functions of the digestive, respiratory, circulatory, nervous, skeletal and excretory systems. •Compare a gastro vascular cavity with a oneway digestive system. •Differentiate open from closed circulatory systems. •Distinguish asexual from sexual reproduction. Quick Test Which two body systems in most animals are involved in taking up oxygen from the environment and transporting oxygen to body cells? a) b) c) d) Digestive & Respiratory Respiratory & Circulatory Circulatory & Nervous Nervous & Excretory The correct answer is: Today’s classwork: Directed Reading Worksheet (page 5) Use your notes &/or Chapter 27, Section 2 to complete this in full sentences. This is an independent assignment & Is due before you leave