* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
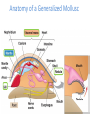
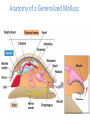
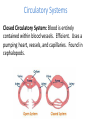
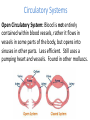
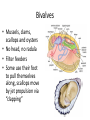
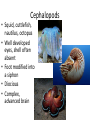
Cuttlefish Snail Nudibranch Chapter 16 Molluscs Scallop Limpet Protostomes that shed their exoskeleton Protostomes with spiral embryonic cleavage Anatomy of a Generalized Mollusc Mantle: The dorsal body wall that often extends beyond the visceral mass, often secretes calcium carbonate, forming a shell. Radula: A toothed chitinous ribbon used for scraping up food into the mouth. Unique to all molluscs except bivalves. Visceral Mass: Dorsal concentration of internal organs. Gills: A large surface-area tissue used for exchanging gases. Found in molluscs with open or closed circulatory systems. Anatomy of a Generalized Mollusc Circulatory Systems Closed Circulatory System: Blood is entirely contained within blood vessels. Efficient. Uses a pumping heart, vessels, and capillaries. Found in cephalopods. Circulatory Systems Open Circulatory System: Blood is not entirely contained within blood vessels, rather it flows in vessels in some parts of the body, but opens into sinuses in other parts. Less efficient. Still uses a pumping heart and vessels. Found in other molluscs. Mollusk Descriptions Baldomero Olivera is a Distinguished Professor of Biology at the University of Utah. He is also an Adjunct Professor at the Salk Institute, La Jolla, California and at the Marine Science Institute, University of the Philippines. Bivalves • Mussels, clams, scallops and oysters • No head, no radula • Filter feeders • Some use their foot to pull themselves along, scallops move by jet propulsion via “clapping” Gastropods • > 70,000 species of snails, conchs, whelks, slugs and sea hares • Large, flat foot for movement, one or two gills • Use shell for selfdefense, but some species have lost it • Most are herbivorous or scavengers Cephalopods • Squid, cuttlefish, nautilus, octopus • Well developed eyes, shell often absent • Foot modified into a siphon • Diocious • Complex, advanced brain Predator Molluscs Nova Cone Snail Video 35:20-42:40 Modern cephalopods just tip over and swim with the ancestral dorsal surface pointing in the direction that they travel. The result; the morphological anterior side is functionally dorsal, the morphological posterior is functionally ventral. The mouth and arms are now ventral, but it swims “up” (the new anterior). Anterior Ventral Dorsal Posterior Motion Squid Dissection