* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Invertebrates
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
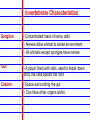
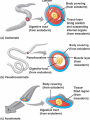
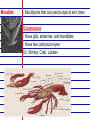
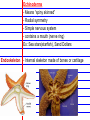
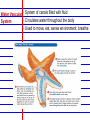
Invertebrates 8 major Invertebrate Phyla • • • • • • Porifera- sponges Cnidaria-sea anemones and jellyfish Nematoda- round worms Platyhelmenthes- Flatworms Mollusca- snails, slugs, squids, and octopi Annelida- segmented worms(repeated body segments) • Arthropoda- insects, shrimps, lobsters, and crabs • Echinodermata- sea stars, urchins, brittle stars Invertebrate - Organism without a backbone 3 Main Body Plans 1. Bilateral 2. Radial 3. Asymmetrical Bilateral - Two sides of the body mirror each other Radial - Symmetry is found all around the center point Asymmetrical - There is no line of symmetry Invertebrate Characteristics Ganglion - Concentrated mass of nerve cells - Nerves allow animal to sense environment - All animals except sponges have nerves Gut - A pouch lined with cells, used to break down food, the cells absorb the food Coelom - Space surrounding the gut - Can have other organs within Sponges- Porifera - Simplest invertebrates - Asymmetrical, no tissues, gut or neurons - Live in water - Can regenerate broken or missing parts Regeneration - Classified by their shapes - Ability to grow back a body part Pores -Holes on the outside of body -Water brings in food and oxygen Osculum -Hole on top of sponge that allows water to leave Cnidarians - Radial symmetry -complex tissue and a gut -simple nerve cells -stinging cells - Ex: Jellyfish, Anemones - Two body forms: Medusa or Polyp Medusa - Swims through water Polyp - Usually attach to a surface Classes of Cnidarians Hydrozoans -common cnidarians -live in both fresh and salt water -most spend lives as polyps Jellyfish -use tentacles to catch food -spend most of lives as medusas Sea anemones -brightly colored -spend lives as polyps Coral -polyps -brightly colored -made of calcium carbonate -live in colonies -build underwater reefs - Found in warm, tropical waters Nematoda Round Worms (long, slim, & round) - Bilateral symmetry - Simple nervous system - Simple brain is a ring of ganglia - Many are parasites Trichinella spiralis - Some infect humans pinworms and hookworms - decomposers Platyhelmenthes Flatworms (simplest worms) - Bilateral symmetry - Clearly defined head - Two large eyespots - Cannot see through eyespots, but sense light - parasitic - Microscopic Planarian Flukes - 3 major classes -Live in freshwater lakes and streams -predators -well developed nervous system -parasites-feed on a host organism -no eyespots -contain suckers and hooks to attach to other animals Tapeworm -parasites -no gut or eyespots -attach to the intestines of other animals Absorb nutrients -can infect humans Mollusks and Annelid Worms Mollusks -Most live in the ocean -some live in freshwater and land -complex ganglia-control breathing, movement, & digestion -contain a circulatory system- pump blood -Bodies are made of : -Muscular foot-used for movement -Visceral mass- contains gut, gills, and other organs -Mantle-covering used for protection if no shell, covers the visceral mass -Shell-hard covering used for protection from predators or land mollusks from drying 3 Classes of Mollusks Gastropods -slugs and snails -eat by using a radula tongue with curved teeth Bivalves - 2 shells -clams, oysters and other shellfish -use gills to filter food from water(tiny plants,bacteria) Cephalopods -Octopus and squid -use tentacles to get food and a powerful jaw to eat it -contain large brain connected to ganglia -most advanced nervous system, smartest inverte Annelid Worms -segmented worms -bodies are in segments identical repeating body parts -bilateral symmetry -circulatory system -Complex nervous system with brain -Live in salt water, freshwater or on land -3 major groups Earthworms -most common -decomposers -leave casting(waste product)in soil produce rich s Use stiff hairs or bristles to move Marine Worms -Colorful -Live in ocean -Polychaetes covered in bristles “Many bristles” -Eat mollusks or filter water for food Leeches -Parasites that suck blood produces a chemical that thins blood can be used medically -Scavengers that eat dead animals Arthropods and Echinoderms Four Characteristics Shared by Arthropods 1. Segmented and specialized body 2. Jointed limbs- “athro”(joint) “pod”(foot) - Body parts bend at joints 3. External Skeleton (Exoskeleton) 4. Well developed nervous system Segmented body Specialized structures -head, thorax, and abdomen Wings, antennae, gills, pincers, claws Exoskeleton – hard covering of the body Nervous system Antennae- feelers that sense touch, taste, and smell. Compound eye- several identical light sensitive units. Brain/nerve cord Mandible - Mouthparts that can pierce objects and chew Crustaceans - Have gills, antennae, and mandibles - Have two compound eyes Ex: Shrimp, Crab, Lobster Arachnids - 2 body parts: Cephalothorax and Abdomen - 4 pairs of legs, no antennae - Simple eyes -spiders, scorpions, mites, ticks Insects - Largest group of arthropods - Six legs - 3 main body parts-head, thorax, abdomen - 2 antennae Metamorphosis - Change from young to adult - Organism goes through a complete change Complete Metamorphosis - 4 stages: egg, larva, pupa, adult - No major changes in organism Incomplete Metamorphosis - Grows from smaller youth to larger adult - 3 stages: egg ,nymph, adult Echinoderms - Means “spiny skinned” - Radial symmetry - Simple nervous system - contains a mouth (nerve ring) Ex: Sea stars(starfish), Sand Dollars Endoskeleton - Internal skeleton made of bones or cartilage Water Vascular - System of canals filled with fluid - Circulates water throughout the body System - Used to move, eat, sense environment, breathe Types of Echinoderms Brittle Stars Basket Stars -long slim arms -smaller than sea star Sea Urchins Sand Dollars -round with no arms -shell-like structure -use spines and tube feet to move Sea Lilies Feather Stars Sea Cucumbers -have multiple feathery arms -no arms and worm-shaped -soft, leathery body