* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Rotifer - I Love Science
Survey
Document related concepts
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Anatomical terminology wikipedia , lookup
Rotating locomotion in living systems wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
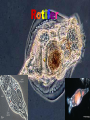
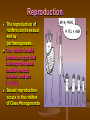
Rotifer Phylum Rotifera • From the Latin Rota a wheel and Ferre to bear or carry • Rotifera is divided into two classes, the Digononta and the Monogononta • The members of the class Monogononta constitutes 90% of the known species Characteristics of Rotifers • 1)Bilaterally symmetrical. • 2)Body has more than two cell layers, tissues and organs. • 3)Body cavity is a pseudocoelom[ second body cavity ]. • 4)Body possesses a through gut with an anus. • • 5)Body covered in an external layer of chitin called a lorica. 6)Has a nervous system with a brain and paired nerves. 7)Has no circulatory or respiratory organs. • 8)Reproduction mostly parthenogenetic [an asexual form of reproduction found in females where growth and development of embryos or seeds occurs without fertilization by a male.] , otherwise sexual and gonochoristic[ reproduction with two distinct sexes]. • • 9)Feed on bacteria, and protists, or are parasitic. 10)All live in aquatic environments either free swimming or attached. A Lil’ Video ! Physical Characteristics • The body is generally divided into a head, a trunk, and a foot region • The largest organ in the head is the wheel organ. • The trunk shape varies from long to spherical or baglike . • The foot has one or several sections, and it often has two toes with sticky glands at the tips. Habitat • Rotifers live in still water and flowing water environments such as lake bottoms, rivers, or streams. • Rotifers are also commonly found on mosses and lichens growing on rocks and aquatic insect larvae. Feeding The two wheels on rotifers are made of cilia that beat and create a current that draws water containing food into the gut of the rotifer. Rotifers eat bacteria (top left) , protists (bottom left) , and other small animals. Reproduction The reproduction of rotifers can be sexual and by parthenogenesis. The mictic female produces eggs that undergo the usual double meiotic division and are haploid. Sexual reproduction occurs in the rotifers of Class Monogononta Quiz Answers 1.The body is generally divided into a head, a trunk, and a foot region. The largest organ in the head is the wheel organ. The trunk shape varies from long to spherical or baglike . 2. Most Rotifers live in lake bottoms, rivers, or streams. 3. Mitic 4. Phylum Rotifera 5.The corona is the part of a rotifer that is used as a feeding device and locomotive device. Diagram The End • Tishana • Shanisa • Janasia