* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Respiratory System Cornell Notes
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic resistance to malaria wikipedia , lookup
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
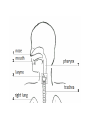
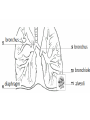
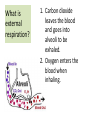
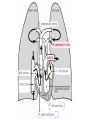
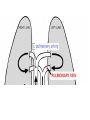
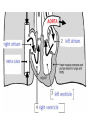
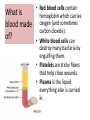
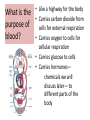
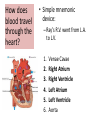
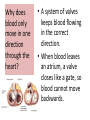
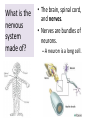
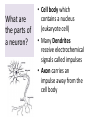
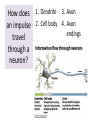
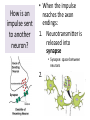
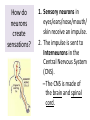
Respiratory System Cornell Notes How does air get into the lungs? • Your respiratory system is made of two lungs and a series of tubes • Inside the lungs, at the end of the tubes are alveoli (pr: Al-vee-o-lee) Destination: Alveoli 1. Nose or mouth 2. Pharynx 3. Larynx (vocal chords/Adam’s apple) 4. Trachea 5. Bronchus (bronchi) 6. Bronchioles 7. Alveoli What are alveoli? • Alveoli are the location of external respiration. – Respiration means exchanging gases • Alveoli are surrounded by tiny blood vessels called capillaries. What is external respiration? 1. Carbon dioxide leaves the blood and goes into alveoli to be exhaled. 2. Oxygen enters the blood when inhaling. What is cellular respiration? • Cellular respiration is what cells do to make ATP. • Materials needed: Oxygen and glucose • Materials produced: ATP, carbon dioxide, and water How is breathing possible? • You use your diaphragm and intercostals (muscles between your ribs) to breathe. – Exhale: breathing out – Inhale: breathing in • When you exhale, diaphragm moves up and curves toward your head. • When you inhale, diaphragm contracts in order to be a flat shape. Circulatory System Cornell Notes What color is blood? • Blood can be different shades of red. – Red blood cells • It is never blue. – In textbooks, blue means “high in carbon dioxide, low in oxygen” – Red means “high in oxygen, low in carbon dioxide” What is blood made of? • Red blood cells contain hemoglobin which carries oxygen (and sometimes carbon dioxide). • White blood cells can destroy many bacteria by engulfing them. • Platelets are sticky fibers that help close wounds. • Plasma is the liquid everything else is carried in. What is the purpose of blood? • Like a highway for the body • Carries carbon dioxide from cells for external respiration • Carries oxygen to cells for cellular respiration • Carries glucose to cells • Carries hormones— chemicals we will discuss later— to different parts of the body • Arteries are usually high in How are arteries and oxygen because they carry blood away from the heart veins – Exception: pulmonary different? arteries • Veins are usually high in carbon dioxide because they carry blood toward the heart – Exception: pulmonary veins How does blood travel through the heart? • Simple mnemonic device: – Ray’s R.V. went from L.A. to L.V. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Venae Cavae Right Atrium Right Ventricle Left Atrium Left Ventricle Aorta Why does blood only move in one direction through the heart? • A system of valves keeps blood flowing in the correct direction. • When blood leaves an atrium, a valve closes like a gate, so blood cannot move backwards. Nervous System Cornell Notes What is the nervous system made of? • The brain, spinal cord, and nerves. • Nerves are bundles of neurons. – A neuron is a long cell. What are the parts of a neuron? • Cell body which contains a nucleus (eukaryote cell) • Many Dendrites receive electrochemical signals called impulses • Axon carries an impulse away from the cell body • Axon endings contain neurotransmitter • Myelin sheath keeps the impulse from leaving the cell’s membrane; keeps it moving in the direction toward the axon endings. What is an impulse? • An impulse is a signal started by neurotransmitters –It is like a chain reaction. How does 1. Dendrite 3. Axon an impulse 2. Cell body 4. Axon endings travel through a neuron? How is an impulse sent to another neuron? • When the impulse reaches the axon endings: 1. Neurotransmitter is released into synapse • Synapse: space between neurons 2. Neurotransmitter lands on receptors of nearby dendrites. How do neurons create sensations? 1. Sensory neurons in eyes/ears/nose/mouth/ skin receive an impulse. 2. The impulse is sent to Interneurons in the Central Nervous System (CNS). –The CNS is made of the brain and spinal cord. How do neurons move our muscles? 1. Interneurons in our CNS receive an impulse. 2. The impulse is sent to motor neurons in the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS). – The PNS includes all the nerves that carry messages to/from the CNS 3. The impulse is sent to a muscle cell (effector). Which neurons are used during thinking? Choose one of the following: a) Sensory neurons b) Interneurons c) Motor neurons The correct answer is b. What are the parts of the PNS? • The Somatic Nervous System sends impulses to and from skeletal muscles (neck, arms, fingers, legs, etc.) • The Autonomic Nervous System sends impulses to and from your internal organs (heart, diaphragm, liver, kidneys, etc.) Which neurons are used during a reflex? 1) a sensory neuron – OUCH! You touch a cactus needle. 2) A spinal cord interneuron — NOT a brain interneuron, because you don’t think about what to do next 3) a motor neuron – You move your hand away quickly. 2.6 Paragraph The urinary system contains kidneys, which are made of nephrons. Humans have two kidneys. Their job is to filter blood. Each kidney is made of about one million nephrons. A nephron can filter out waste and make sure body fluids are balanced. This describes the role of kidneys and their basic units, nephrons. 4.10 Paragraph In my study of abused drugs, I learned about stimulants, depressants, narcotics, and hallucinogens. Stimulants increase the activity of the Central Nervous System and the sympathetic .…