* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Powerpoint Presentation (P3)
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
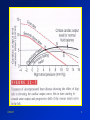
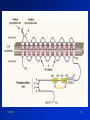
K 305 27 June 03 03/06/27 1 Contractile Dysfunction Reversible •stunning •hibernation Irreversible •necrosis •apoptosis 03/06/27 2 03/06/27 3 Contractile Dysfunction This cell damage produces: • hypocontractility • enhance the likelihood of arrhythmias • both of which can be lethal 03/06/27 4 03/06/27 5 03/06/27 6 Etiology of Ischemia - Reperfusion Injury •osmotic overload •number of particles in cytosol as lactate accumulates and ATP is broken down •immune response •neutrophils and complement system •pH paradox 03/06/27 7 Etiology of Ischemia - Reperfusion Injury •pH paradox • pHi which increases: •Na+-H+ activity •[Na+]I •Na+-Ca2+ exchange reverse activity •[Ca2+]i overload •contractile dysfunction 03/06/27 8 Regulation of Intracellular H+ H+ extrusion (acidosis) NHE-1 •pH paradox 03/06/27 9 03/06/27 10 03/06/27 11 EKG changes with ischemia/ MI Subendocardium •results in ST segment depression •injury current at rest causes baseline elevation •during plateau causes ST segment depression •observe a J point at the point between the QRS complex and the ST segment and this point represents zero current in the heart as all parts of the ventricles are depolarized •ST segment depression is usually due to imbalance between supply and demand and will reverse when exercise is stopped during a stress test 03/06/27 12 EKG changes with ischemia/ MI 03/06/27 13 EKG changes with ischemia/ MI Subepicardium or transmural •immediately results in heightened T waves •may be followed by T wave inversion • T wave inversion problems with directionality of repolarization •ST segment elevation occurs due to injury current during plateau phase of the action potential which is moving towards epicardium •deep (dirty, pathological) Q waves reflect scarring 03/06/27 14 EKG changes with ischemia/ MI 03/06/27 15 Plasma markers of MI 24-72 hours after MI - increases in: •CK •LDH •TnI 03/06/27 16 Radionuclide Imaging of Heart Technetium-99m-MIBI •MIBI - 2-methoxy isobutyl isonitrile •MIBI travels via CBF becomes trapped within healthy, active muscle cells in the heart •radioactivity monitored with a gamma camera •during an MI, some muscle cells will not trap the MIBI •also occurs with CAD except the lack of MIBI in some of the muscle cells is due to inadequate CBF 03/06/27 17 Cardiac Ischemia 03/06/27 18 Ischemic Preconditioning 03/06/27 19
























![Cardiology [MYOCARDIAL ISCHEMIA]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007911470_1-7356e719c8c909cc4cde0ff2f8cd782a-150x150.png)

