* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hypersensitivity type I
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
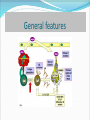
آلرژی چیست؟ مکانیسم القاء آلرژی چگونه است؟ آلرژی غذایی چیست؟ مهمترین آلرژن های غذایی ویژگیهای آلرژن های غذایی تولرانس نسبت به مواد غذایی تابع چه عواملی است ؟ hypersensitivity type I *Allergen Activation of Th2 B cell activation IgE binding of IgE to Fc receptor reexposure to Allergen pathologic reactions release of mediators General features Immediate hypersensitivity با ورود آلرژن ،سلولهای B آن راشناسایی وپس از فعال شدن ،آنتی بادی IgEترشح میکنند . Mast cell activation Factors involve in H.S type I Allergene Th2 cells Mast and basophil cells FcR-I Mediators Genetic predisposition cytokines Eosinophil and Basophil اين سلولها داراي گيرنده هاي high affinityبراي IgEبنام FCRمي باشند گرانولهايي سيتوپالسمي كه حاوي آنزيم ها و ساير مدياتورهاي فارماكولوژيك Mast cell activation Rapid release of granule contents (degranulation)such as Histamine,tryptase, chymase,proteoglycans(heparin ) Synthesis and secretion of lipid mediators(prostaglandines ,Leukotrienes) Synthesis and secretion of cytokines(IL-3,4,5,6,TNF-) Mediators actions Histamine= bronchoconstrictor,vascular leak,intestinal hypermotility PGD2=vasodilator and bronchoconstrictor , neut. Chemotaxis LTC4=bronchoconstriction,inflammation PAF=bronchoconstriction ,vasodilator, inflammation clinical and pathologic manifestations of Type increased vascular permeability Vasodilation smooth muscle contraction local inflammation Clinical and pathologic features Hay fever(allergic rhinitis) Increased peristalsis Bronchial asthma Anaphylaxis Wheal and Flare reaction Introduction to food allergies Actually, only about 2-10 % of adults and children have clinically proven true allergic reactions to food. food intolerance or other adverse reactions to food A true food allergy People who have food allergies must identify and prevent them because, although usually mild and not severe, these reactions can cause devastating illness and, in rare instances, can be fatal. Food intolerance refers to an adverse physiologic response to a food and may be due to inherent properties of the food a)toxic contaminant b)pharmacologic active component or to characteristics of the host a)metabolic disorders b)idiosyncratic responses c)Psychological disorder **** they may not be reproducible *** they are often dose dependent. Food allergy refers to an abnormal immunologic response to a food that occurs in a susceptible host. a)These reactions are reproducible each time the food is ingested b) they are often not dose dependent Histamine toxicity: Some natural substances (for example, histamine) in foods can cause reactions resembling allergy. Histamine can reach high levels in cheese, some wines, and certain fish Food additives: Another type of food intolerance is an adverse reaction to certain compounds that are added to food to enhance taste, provide color, or protect against the growth of microorganisms. The compounds most frequently tied to adverse reactions that can be confused with food allergy are : yellow dye number 5(tartrazine) monosodium glutamate (MSG) and sulfites. What are the most common food allergies? In adults, the most common foods that cause allergic reactions are shellfish, such as shrimp, lobster, nuts from trees, such as walnuts; fish; eggs and peanuts. In children, the pattern is somewhat different from adults, and the most common foods that cause allergic reactions are eggs, milk, peanuts, and fruits, particularly tomatoes and strawberries. Food allergy varieties Based on the immunological mechanism involved, food allergies may be further classified in : a)IgE-mediated b) Cell mediated c) mixed IgE mediated-cell mediated when both IgE and immune cells are involved in the reaction IgE-mediated classic food allergic reactions are those that are: immediate reproducible and readily diagnosed by detection of food-specific IgE Characteristics common to “major” food allergens are that : they are water-soluble glycoproteins, are 10 to 70kD in size and are relatively stable to heat, acid, and proteases. Frequent exposure High glycosylation In addition, the presence of immunostimulatory factors in the food may also contribute to such sensitization. However, the biochemical characteristics of a food allergen cannot explain alone , as only a minority of patient exposed to it develop allergy.