* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Foundations of individual behavior
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
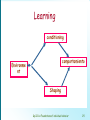
Dirección de Proyectos Informáticos Foundations of individual behavior Objective • • • • • Relacionar satisfacción y productividad ¿qué es la disonancia cognoscitiva? Relación entre actitud y comportamiento 5 variables de la personalidad y desempeño Porque dos personas pueden ver lo mismo e interpretarlo como cosas distintas • Teoría de la atribución • Proceso de aprendizaje. GpiIC-1A Foundations of individual behavior 1 Some psychology concepts Attitudes learning Personality Perception GpiIC-1A Foundations of individual behavior 2 Attitudes • Evaluative statements–either favorable or unfavorable- concerning objects, people or events • We are interested in attitudes about the work… – “I like my job” GpiIC-1A Foundations of individual behavior 3 Attitudes: Job satisfaction Positive Attitudes Negative Attitudes Job Satisfaction Job Dissatisfaction GpiIC-1A Foundations of individual behavior 4 Attitudes: …What determines job Satisfaction ? – – – – Mentally challenging work Equitable rewards Supportive working conditions Supportive colleagues- • People want jobs were: – They can apply their abilities an capacities – Task variety – Freedom and feedback GpiIC-1A Foundations of individual behavior 5 Attitudes: ..what determines Job Satisfaction? Satisfaction Frustration None objectives A lot GpiIC-1A Foundations of individual behavior 6 Attitudes: Job Satisfaction • People expect more than material… • People seeks: – – – – Personal communications Friendship Support from other people (socializes) GpiIC-1A Foundations of individual behavior 7 Productivity and job satisfaction • The more satisfaction are more productive? –… – It’s not clear… – Ti has same effects • Other factors have more influence… as working in a chain • But productivity provides satisfaction GpiIC-1A Foundations of individual behavior 8 Cognitive dissonance • Any incompatibility between two or more attitudes or between behavior and attitudes. • people will attempt to reduce the dissonance and, hence the discomfort • Way to reduce dissonance: – – – – – Change the job Change the behavior …it's unimportant Change the attitude Seek more consonant elements GpiIC-1A Foundations of individual behavior 9 Cognitive dissonance • Factors – uncontrollable… – Rewards… GpiIC-1A Foundations of individual behavior 10 Personality • The sum total of ways in which an individual reacts to an interact with others. • Sixteen primary traits: – Reserved - Outgoing – Less intelligent - More intelligent – Affected by feelingsEmotionally stable – Submissive - Dominant – Serious – Happy-go-lucky – – – – – – – – – – – Expedient - conscientious Timid - Venturesome Tough-minded - Sensitive Trusting - Suspicious Practical - Imaginative Forthright - Shrewd Self_assured apprehensive ConservativeExperimenting Group dependent – Self_sufficient Uncontrolled - Controlled Relaxed - Tense GpiIC-1A Foundations of individual behavior 11 Indicador de tipos MyersBriggs • • • • • • • • Extroverted - Introverted (E o I) Sensing - Intuitive (S o N) thinking - felling (T o F) Perceiving - judging (P o J) INTJ (Visionaries,… determined) ESTJ (Organizers,…) ENTP (Conceptualizer,…) NTs (Business people supersuccessful firms) GpiIC-1A Foundations of individual behavior 12 Personality: The big five model. • Extraversion: – sociable, talkative and assertive. • Agreeableness: – Good natured, cooperative and trusting. • Conscientiousness: – responsible, dependable, persistent and achievement oriented • Emotional stability: – Calm, enthusiastic, secure (positive) vs. tense, nervous, depressed, and insecure (negative). • Openness to experience: – Imaginativeness, artistic sensitivity and intellectualism GpiIC-1A Foundations of individual behavior 13 Major personality attributes influencing OB • Locus of control • • • • • • – Internals – Externals Machiavellianism self esteem Self monitoring Risk taking Type A personality Type B personality GpiIC-1A Foundations of individual behavior 14 Typology of personality • Realistic: – physical activities, require skill, strength, and coordination – Shy, genuine/ persistent, stable, conforming, practical – Mechanic, drill press operator, assembly line worker, farmer • Investigative – activities that involve thinking, organizing, and understanding – Analytical, original, curious, independent – Biologist, economist, mathematician, news reporter GpiIC-1A Foundations of individual behavior 15 Typology of personality • Social: – activities that involve helping and developing others – Sociable, friendly, cooperative, understanding – Social worker, teacher, counselor, clinical psychologist • Conventional: – rule-regulated, orderly, and unambiguous activities – Conforming, efficient, practical, unimaginative, inflexible – Accountant, corporate manager, bank teller, file clerk GpiIC-1A Foundations of individual behavior 16 Typology of personality • Enterprising: – verbal activities where there are opportunities to influence others and attain power – Self-confident, ambitious, energetic, domineering – Lawyer, real estate agent, public relations specialist, small business manager • Artistic: – ambiguous and unsystematic activities that allow creative expression – Imaginative, disorderly, idealistic, emotional, impractical – Painter, musician, writer, interior decorator GpiIC-1A Foundations of individual behavior 17 Matching personalities and Jobs GpiIC-1A Foundations of individual behavior 18 Perception • A process by which individuals organize and interpret their sensory impressions in order to give meaning to their environment • Factors influencing perception: – The perceiver, • Attitudes, motives, interest, experience, expectations – The target • Novelty, motion, sounds, size, background, proximity – The situation • Time, work setting, social setting GpiIC-1A Foundations of individual behavior 19 Attribution theory • When we observe people we attempt to develop explanations of why they behave in certain ways. • When individuals observe behavior, they attempt to determine whether it is internally or externally caused. • Internally: under control of individual. • Externally: outside causes. GpiIC-1A Foundations of individual behavior 20 Attribution theory • Determination depends on: – Distinctiveness • Different behaviors in different situations. – As usually or he don’t use to do this. – Consensus • Everyone do the same in this situation. – Consistency • Does the person respond the same over time? GpiIC-1A Foundations of individual behavior 21 Attribution theory • There is a tendency for individuals to attribute their own success to internal factors such as ability or effort while putting the blame for failure on external factors as luck. GpiIC-1A Foundations of individual behavior 22 Shortcuts in judging others • Selective perception – People selectively interpret what they see on the basis of their interest, background, experience, and attitudes. • Contrast effects – Comparison with otter people about same characteristic. • projection – Attributing one’s own characteristics to he other people. • Stereotyping – Perception of the group to which that person belongs. • Halo effect – Drawing a general impression about an individual on the basis or a single characteristic. GpiIC-1A Foundations of individual behavior 23 Learning • Any relatively permanent change in behavior that occurs as result of experience. • How do we learn? – Classical conditioning • Behavior depends on consequences (money, smiles,…) – Positive consequences: repeat. – Negative consequences: do no repeat. GpiIC-1A Foundations of individual behavior 24 Learning conditioning comportamiento Environme nt Shaping GpiIC-1A Foundations of individual behavior 25 Learning • Operant conditioning – slow, rewards, punishment. – Test and fail • Shaping – By observing what happens to other people. – Quick GpiIC-1A Foundations of individual behavior 26 Bibliography: • Robbins, Comportamiento Organizativo, Prentice Hall, 1999. GpiIC-1A Foundations of individual behavior 27