* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Powerpoint
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Missouri secession wikipedia , lookup
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Fort Sumter wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Sumter wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Secession in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
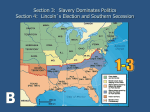
UNION IN PERIL American History I - Unit 8A Ms. Brown Review • Which political party believed in nativism and disliked immigrants and Catholics? • The Know-Nothing Party (American Party) • To which political party did Franklin Pierce belong? Did he support the Kansas-Nebraska Act? • Democrat – states’ rights and popular sovereignty • Pro-Kansas-Nebraska Act • Which party formed in response to the passage of the Kansas- Nebraska Act? • The Republican Party • By 1856, where are most Democrats and where are most Republicans? • North – Republicans • South - Democrats 8A.4 – SLAVERY AND SECESSION Scott v. Sandford (1857) • Dred Scott – slave from Missouri • 1834 – owner took him into Illinois and Michigan Territory (free areas), upon return to Missouri Scott claimed freedom because he lived in free areas for several years. Scott v. Sandford (1857) • Scott sued his owner (Emerson) in a Missouri court lost • Emerson died, Scott used his next owner, Sandford in a federal court lost but appealed to the federal circuit court chosen for consideration by the Supreme Court Scott v. Sandford (1857) • Was Dred Scott a free man or a slave? • Chief Justice Roger B. Taney issued a 3 piece decision. • Scott filed suit in Missouri, a state in which he was considered a slave. • Slaves are not citizens, therefore cannot sue in court. • The Missouri Compromise was unconstitutional. Slaves are property and thus Congress is not allowed to ban slavery because that would mean taking away private property. Effects of Scott v. Sandford (1857) • South – cheered the decision • By officially banning Congress from banning slavery outright, the expansion of slavery across the nation seemed easier. • North – stunned! • Many joined the Republican Party (anti-slavery expansion) in hopes of keeping slavery in check. Lecompton Constitution • 1857 – proslavery government in Lecompton, Kansas wrote a constitution and applied for statehood as a slave state. • Kansas’ residents had to approve the constitution in a vote more anti-slavery than proslavery settlers constitution was rejected. Lecompton Constitution • POTUS Buchanan publically supported the Lecompton Constitution angered Stephen Douglas because he believed in true popular sovereignty (rule by the people) • Douglas persuaded Congress to allow Kansas residents to vote on the Constitution again failed again • Northern Democrats – Douglas is a hero! • Southern Democrats – Douglas is a traitor! • Split in Democratic party grew. • Kansas’ fate concerning slavery up in the air. Douglas-Lincoln Debates • 1858 – Illinois seat in US Senate up for election • Douglas and Lincoln had a series of public debates. Douglas Lincoln • Current seat holder • Democrat – States’ rights, popular sovereignty • Well-known, charismatic • Argued slavery would die on its own over time; popular sovereignty should be used for now • Challenger • Republican – anti-slavery expansion • Not well-known, spoke solemnly and directly • Argued slavery was immoral; slavery would not end until the government intervenes Douglas-Lincoln Debates • During the debates, Lincoln questioned how Douglas could say he supported… • popular sovereignty in the Kansas-Nebraska Act AND ALSO • the Scott v. Sandford decision which claimed that slavery could not be banned officially by a government. • Douglas responded with the Freeport Doctrine • States could exclude slavery by refusing to pass laws that supported slavery. • Due to Scott v. Sandford, states could not ban slavery BUT Douglas said they could just not pass laws that supported it, thus finding a loophole in the SCOTUS decision. Douglas-Lincoln Debates • Douglas won the IL Senate seat, but his actions split the Democratic party further. • Lincoln lost, but gained national attention from Republicans possible presidential candidate for 1860? John Brown at Harpers Ferry • 1859 – John Brown and 21 men (white and black) attacked Harpers Ferry, VA (federal arsenal) • Brown wanted to steal the weapons in the arsenal, give them to slaves in the area, and start a rebellion • Brown held 60 slave owners hostage, but no slaves came forward to take weapons. John Brown at Harpers Ferry • US Marines captured Brown and he was tried and hanged for treason. • Northerners – saw Brown as a martyr (person who sacrifices themselves) for ending slavery • Southerners – scared the North was plotting more slave rebellions, discussed secession again Rise of Lincoln • May 1860 – Republican Convention to choose presidential candidate for later that year William Seward • NY Senator • Anti-slavery expansion • Financial support of wealthy NYers • Loved being the center of attention • Very confident he would get the nomination Lincoln • • • • No current office Anti-slavery expansion Relatively unknown nationally Seemed more moderate (no reputation to offend anyone) • Tried to reassure Southerners that he would not interfere with their existing slaves • Lincoln won the nomination for the Republican Presidential Candidate for 1860 • Southerners – Lincoln’s election would be “the greatest evil that has ever befallen this country.” Election of 1860 LINCOLN DOUGLAS BRECKINRIDGE BELL Republican Northern Democrats Southern Democrats Constitutional Union (Know-Nothings , Whigs) NO slavery Popular sovereignty Lincoln = 16th POTUS! YES slavery Ignored slavery Southern Secession • Lincoln’s victory increased discussion of Southern secession from the Union • Lack of a political voice in Congress • Slavery in danger • Threatened the Southern way of life that they had known for almost 200 years • December 20, 1860 – SC seceded from the Union • In the next few weeks, MS, FL, AL, GA, LA, and TX had also seceded. What is this picture conveying about the nature of the Election of 1860 and the political views of Americans? The Confederacy • Aka the Confederate States of America – formed in 1861, loose union of Southern states that seceded from the Union • Drafted a constitution that resembled the US Constitution, but… • “protected and recognized” slavery in states and new territories • Said that each state was “sovereign and independent” of other states • Elected Jefferson Davis as president of the Confederacy • “The time for compromise has now passed.” Calm Before the Storm • POTUS Buchanan tried to declare secession illegal, but there wasn’t much he could do. • Lincoln was not POTUS until his inauguration in March 1861 • Southern Congressmen and federal officials resigned, leaving half of DC empty… seemed as if the federal government would disappear. • Would the North let the South leave without a fight? Fort Sumter • Early 1861 – Southern Confederate troops took control of military forts in the states that had seceded, only 2 left • Fort Sumter (the more important fort left) faced an attack by Confederate troops • Lincoln had 2 choices… • Order Union troops to fire shots and protect Fort Sumter, but then he would be responsible for possibly starting a war • Let Fort Sumter fall into Confederate hands, but then he would essentially be legitimizing the Confederacy as a real and separate nation (which would make him look weak) Fort Sumter • Lincoln decided not to shoot AND not to surrender chose to send in “food for hungry men” • Left the hard decision up to Jefferson Davis • Davis had 2 choices… • Attack Fort Sumter and face starting a war • Do nothing and make the Confederacy look weak and not like a real nation First Shots at Fort Sumter • Davis chose WAR! • April 12, 1861 – Confederate troops attacked Fort Sumter and the Union troops inside surrendered. • By May 1861, VA, AR, TN, and NC had joined the Confederacy • The US was officially split in two halves… and in a Civil War.