* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Civil War Technology - PHS
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Shiloh wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Lewis's Farm wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Perryville wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fredericksburg wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Forts Jackson and St. Philip wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Wilson's Creek wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Seven Pines wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Antietam wikipedia , lookup
North-South Skirmish Association wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Lexington wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Gaines's Mill wikipedia , lookup
Battle of New Bern wikipedia , lookup
Confederate privateer wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Hampton Roads wikipedia , lookup
Medicine in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
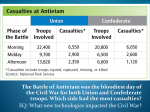
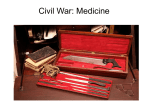
THE FIRST MODERN WAR Why is the Civil War called the“first modern war”? • • • • Technological advancements in weaponry Improved communication techniques Faster transportation methods Improved medical and sanitation techniques BATTLEFIELD TACTICS • Although weapons had improved battle tactic had not changed in hundreds of years. • Large armies were massed on opposite sides of a field. The advancing army moved across the field when they got close enough they charged (ran at) the enemy. • Usually, the battle ended with bayonets and hand-to-hand combat. BATTLEFIELD TACTICS (con’t) Because weapons advanced and tactics did not the Civil War was the deadliest war in American History. •More Americans died in the Civil War than all other wars combined. •More Americans died in the first day at the battle of Antietam than in all previous US wars. ADVANCES IN WEAPONRY: The minnie ball • The standard bullet used by troops during the Civil War • It is .57 caliber and made of soft lead • in combination with a rifled-musket it made traditional battlefield techniques obsolete The single most deadly advance in weapons Artillery: smoothbore vs. rifling • As with shoulder weapons, smoothbore cannons were not as accurate and could not shoot as far as rifled artillery. The three types of artillery • Cannons • Howitzers • Mortars Cannons • Cannons or guns, as they were sometimes called were fired in a relatively flat trajectory. • These were generally used as anti-personnel weapons. Howitzers • Howitzers were used against both personnel and field fortifications Mortars • Mortars came in sizes from small (2-man unit) to so large that they needed to be mounted on rail cars and could fire shells weighing more than 200 pounds. The high trajectory allowed these to shoot over field fortifications Other innovations in weapons… The first “Air Force”??? • Balloons were used by the North to spot enemy troops movements and to spot for artillery. • At a height of a mile of more, the balloonists “talked” to the ground via a light telegraph wire. Other innovations in weapons... • • • • hand grenade flame thrower machine gun anti-aircraft fire (see balloons) • land mines • railroad artillery • repeating rifles • Rotating gun turrets • use of periscopes • telescopic sight for rifles • Torpedoes • Portable bridges Other innovations in weapons… The Ketchum (left) and Excelsior hand grenades Other innovations in weapons... A Civil War “torpedo” (we would call them sea mines) The Gatling gunthe first workable machine gun Improvements in battlefield techniques….. • • • • • • Aerial reconnaissance field trenches on a grand scale military telegraph coded battle signals wire and spear entanglements Portable bridges The NEW Navy: The battle of the ironclads • Confederate engineers bolted on iron plates to the Merrimack, building a warship more powerful than anything the North had. Union cannon shells simply bounced off the Merrimack. • News of this monster quickly spread to the North. • The North responded by building the Monitor. • On March 8, the Merrimack attack and sunk or disabled three Union ships. • For one day, the Confederate navy ruled the seas. Battle of the ironclads (cont’d) • The next morning the Monitor appeared. • The two ships hammered away at each other, hull to hull, fighting at such close range that the two ships collided five times. • After four and a half hours , the Merrimack drew off. Battle of the ironclads (cont’d) • It was to be the Merrimack’s only fight. The Confederates blew her up two months later when the were forced out of Norfolk. • The Union set to building more Monitorlike ships while Europe watched in worried fascination. • From the moment the two ships opened fire that Sunday morning, every other navy in the world was obsolete. Battle of the ironclads (cont’d) • In London, Henry Adams cheered the Union triumph, but also saw in it an ominous fore-shadowing of things to come…”About a week ago, The British discovered that their whole wooden navy was useless…These are great times…Before many centuries more..science may have mankind in its power, and the human race commit suicide by blowing up the world.” The NEW Navy: Submarines • Naval attacks using a “submarine” had been attempted before. • The CSS Huntley was the first submarine to “successfully” sink an enemy ship. Care for the wounded…… • Generally speaking, if a soldier took a solid hit in an arm or a leg it was amputated. • “Gut shot” wounds were nearly always fatal. • The Civil War took place in what has been called “the medical middle ages”. • Physicians did not understand the germ theory as we know it today Care for the wounded…... • Surgeons would simply rinse their operating instruments off in cold water or wipe them off on their coats before moving on to the next patient. • A good surgeon could amputate an arm or a leg in about 10 minutes…one right after another…hour after hour. • Sometimes the pile of discarded limbs reached four to five feet high. Care for the wounded…... • Despite the crude medical care used, the Civil War is also credited with several “firsts” in battlefield medicine… • army ambulance corps • hospital ships • organized medical and nursing care • widespread use of anesthetics for battlefield wounded “Firsts” on the home front…... • Draft laws • photography of battle (brought the horror of the war home to the civilians) • a wide-ranging press corps in battlefield areas • American breadlines • American president assassinated Civil War Casualties…… • A casualty is when a soldier or sailor is lost for the duration of the war through death, wounds, injury or sickness. It does not include soldiers who were treated for wounds, etc. and then sent back to continue fighting. Civil War Casualties…... • Union dead 364,511 • Confederate dead 260,000 • Union • Confederate wounded 281,881 wounded 194,000 • Total Union • Total Confederate loss 646,392 Losses 454,000 A Civil War soldier’s chance of NOT surviving the war was about one in four Civil War Casualties… A quick comparison • 4,435 died in the American Revolution • 2,260 died in the War of 1812 • 13,283 died in the Mexican War • 2,246 in the Spanish American War • 116,516 died in WWI • 403,399 died in WWII • 33,746 died in Korea • 58,512 died in Vietnam • Up until the Vietnam War, the number killed in the Civil War surpassed all other wars COMBINED!!! CONCLUSIONS…... • The Civil War saw the beginnings of many methods of warfare that are still in use today almost 150 years later. • Although we would consider these innovations crude by today’s standards they proved deadly on the battlefield because technology was far ahead of tactics and care for the wounded.