* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Civil War (1861-1865)
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Gettysburg Address wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Jubal Early wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
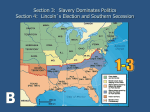
1861-1865 The Civil War (1861-1865) • a period of war between Northern + Southern states – The free states were called the Army of the Union (U.S.) and were compromised of 23 states; – The 11 slave states called themselves the Confederate States of America (C.S.A.) The Civil War (1861-1865) • By the end of the war, 600,000 soldiers had died – Which represents more than all the deaths of our other campaigns combined! – Over ½ die from disease than bullets A Deeply Divided America • Before the war, the country boasted 31,000,000 citizens and – 34 states (Minnesota, Oregon, Kansas) In the South, 4,000,000 were slaves – They made up ½ of the total population. – During this time, blacks are born & live in filth, disease, and ignorance. A Deeply Divided America • Taylor, Fillmore, Pierce, Buchanan were Presidents between 1849-1861 – They were largely ineffective, and their inactions helped further the cause for war. Differences between northern and southern states: __________ industrial economy “_____ free states” agricultural __________ economy “_____ slave states” A Deeply Divided America • Secession had been suggested many times as only way to deal with slavery • In their eyes slavery only way to preserve their economy - they didn’t know what to do without slaves • American Slavery had existed for so long (1619) that it was called “a peculiar institution” Society tried to end slavery several times during this period. • “Uncle Tom’s Cabin” (1852) - by Harriet B. Stowe told a violent story that moved many to join abolitionists Sold 300,000 copies in the first year. 2 million in a decade! Society’s Efforts to Stop Slavery • The “Underground Railroad” was created by Harriet Tubman + other conductors to evacuate slaves from South- nearly 50,000 saved by the “railroad.” • Tubman herself rescued over 300 slaves after her escape. The State of Slavery in America RACISM RULED throughout country – Even Northern Abolitionists were racist by modern standards. – Churches, schools, and even cemeteries wouldn’t accept them; workers didn’t trust them because they were worried about their own jobs The State of Slavery in America In the South, girl slaves were used and sold as breeders for more slaves. • Southerners saw their slaves as property, which could be moved with them to new lands. The Wilmot Proviso (1846) • The Wilmot Proviso (1846) unsuccessfully tried to end slavery by making it illegal in lands won during the Mexican War. An America Free, or Slave? –Several attempts made to deal with slavery – NONE WERE SUCCESSFUL –The Missouri Compromise (1820) – The nation kept an uneasy balance of power by admitting Missouri (SLAVE state) and Maine (FREE state) An America Free, or Slave? –The Compromise of 1850 – California statehood swung the balance to the North. –To maintain the balance, power and future states were allowed popular sovereignty. Path to War (1850-1856) • Several events placed the country on a path to war. • “Bleeding Kansas” (1856) proved that popular sovereignty was a failure in settling this issue. • As a result, Kansas collapsed into civil war and more than 200 people were killed. • The debate even spilled over into violence in the nation’s capital. Path to War (1850-1856) In 1856, Preston Brooks brutally attacked Charles Sumner with a cane over a speech Sumner had made. Path to War (1850-1856) In 1857, a slave named Dred Scott sued for his freedom and lost. The Supreme Court said that Scott was not a free man, and that Congress had no right to outlaw slavery in any territory. The Final Straws came in 1859-1860 • When John Brown’s Raid on Harper’s Ferry failed. • He was captured and hanged by the South. 1860 Election Results Abraham Lincoln’s Election •Finally, Lincoln’s election in 1860 pushed the South over the edge: slaveholders call him “The Black Republican” because he supported abolition. On December 20, 1860 South Carolina seceded from the Union, in response to Lincoln’s victory. Secession!: SC Dec. 20, 1860 • Abraham Lincoln won the election in 1860 over his longtime rival Stephen Douglas, who Lincoln debated several times in 1858. • With Lincoln’s election, the nation began to tear itself apart. Leadership during the War Abraham Lincoln (US) Jefferson Davis (CSA) The Union and Confederacy in 1861 Realities of the Campaign • Each side made critical errors in the early years of the War • Lincoln seriously underestimates the will of the South – not prepared for response his army receives in early years of the War • The South wrongly assumes Britain will come to its aid – all of Europe has banned slavery by 1860 Ranking North v. South: 1861 R e s o u r c e s •22 million population •Bank industry and factories •Value of goods increased •Horses and Railroad tracks •Firearms and munitions Production • 90% of industry – GOODS •Controlled the Navy • excellent generals -Robert E. Lee and Thomas Jackson • Familiarity with the land makes defending always easier than attacking • Farmers fight better than factory workers • Profitable economy based on cotton exports Weapons of the Civil War • Most soldiers were issued smoothbore muskets that were difficult to load and could be fired at an accurate range of only about 100 yards, (only three times in one minute.) Rifled muskets were much more accurate and deadly with a range of up to 500 yards. Destruction from Artillery • In the Civil War, some Cannons were rifled for better accuracy and more power. • Rifled cannons could accurately lob shells for almost 2000 yards; that is almost one mile!. • Smoothbore cannons were not as accurate and could be lobbed 500 yards. The Monitor Key Battles • Fort Sumter ( April 1861): Start of the War Battle of Bull Run (1st Manassas), July 1861 • Union defeat • Forces both sides to realize that the War will not end quickly Fort Donelson – February 1862 • Attacks by Ulysses S. Grant gave the Union its first victory of the War Shiloh - April 1862 • Union Victory (24,000 casualties) Antietam, 1862 • Union Victory – largest loss of life during the War (more than 25,000 casualties) • January 1, 1863 • Freed the slaves only in states that seceded from the Union. • It did not free slaves in border states. • Constitution forbid Lincoln to free slaves in the Union William Carney • After the Emancipation Proclamation blacks began to join the Union Army • Initially they were only used for manual labor • Eventually, Blacks saw live combat • 54th regiment out of Massachusetts African-Americans in Civil War Battles • Lee realized that the South was in dire straits and decided that it was crucial to attack the North on its own territory • July 1-3, 1863 - BATTLE OF GETTYSBURG, Pa. • Confed. bombardment; Union held firm • on July 3, General Pickett led 15,000 Confed. Troops across open fields - Union mowed them down (= "Pickett’s Charge") • Lee was defeated and retreated to Virginia • Gettysburg is the largest battle in the history of the Western hemisphere. • Over 100, 000 people died in 3 days It was the last time the South invaded the North. Vicksburg – July 1863 • won by U.S. Grant, cut South in 1/2 and gave the Union control of Mississippi River • Grant was then given control of all Union armies began a "scorched earth" policy to defeat the South Sherman’s ‘Total War’ – March 1864 • General Sherman given task of taking Atlanta; his "March through Georgia" saw total destruction from Atlanta to Savannah – tore up rail lines, destroyed crops, burned/looted towns Presidential Election of 1864 – Sherman’s Total War Assures Victory Surrender at Appomattox – April 1865 • April 3, 1865 - Grant took Richmond Va. - final blow to Lee's army • Lee surrenders on April 9, 1865 • Terms of surrender were lenient – Lincoln didn't want a humiliated South and further conflict Casualties on Both Sides Civil War Casualties in Comparison to Other Wars Effects of the Civil War • Creation of a single unified country (nationalism) • Abolition of slavery • Increased power of fed. gov't – killed the issue of state’s rights • To cover war debts, Union gov't issued war bonds and intro'd income tax • In a further illustration of fed. gov't power, Lincoln's gov't restricted civil liberties so nothing would detract from Union war effort (suspended Habeas Corpus) - free press/ speech also interrupted • U.S. now an industrial nation • W. lands increasingly opened to settlement • South was economically and physically devastated, w/ the plantation system crippled... Abraham Lincoln • Lincoln was an outspoken opponent of slavery • Abraham Lincoln’s speeches help define people’s perceptions of basic human rights & the role of government in protecting it Abraham Lincoln • “A house divided against itself cannot stand. I believe this government cannot endure permanently half-slave and halffree.” - (1858) Abraham Lincoln “The mystic chords of memory, stretching from every battlefield and patriot grave to every living heart and hearthstone all over this broad land, will yet swell the chorus of the Union, when again touched, as surely they will be, by the better angels of our nature." - 1st Inaugural Address (1861) Abraham Lincoln "...that we here highly resolve that these dead shall not have died in vain; that this nation, under God, shall have a new birth of freedom; and that this government of the people, by the people, for the people, shall not perish from the earth." - Gettysburg Address (1863) Abraham Lincoln "With malice toward none, with charity for all, with firmness in the right as God gives us to see the right, let us strive on to finish the work we are in; to bind up the nation's wounds; to care for him who shall have borne the battle, and for his widow and his orphan - to do all which may achieve and cherish a just and lasting peace, among ourselves, and with all nations." 2nd Inaugural Address (1865)