* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Civil War - Fort Bragg USD
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Frémont Emancipation wikipedia , lookup
Reconstruction era wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
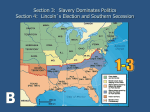
The Civil War 1861-1865 Questions for Reading • Who debated? What were they running for? What was the key issue they debated? Who won the election? • What happened at Harpers Ferry? Review • What were the two ways that the U.S. acquired territory west of the Mississippi River? • A = La. Purchase & War w/ Mexico. • What was the significance of Marbury v. Madison? • A = Established precedent of judicial review. Mo Review • Describe the Pro-slavery argument. • What was the Dred Scott case? • What were the three compromises arrived at as the country expanded west? • A = Missouri comp.; Comp. of 1850; and the Kansas-Nebraska Act. Some Mo Review • What was “Popular Sovereignty”? • What was “Bleeding Kansas”? • Who wrote Uncle Tom’s Cabin and why was it upsetting to people In the South? • Who were the two most famous abolitionists? • A = Frederick Douglass and William Lloyd Garrison Sectional Tension • Westward Expansion and slavery. • Remember: – Missouri Compromise – Compromise of 1850 – Kansas-Nebraska Act The Dred Scott Case (1857) • Slave who sued for his freedom because he had been taken by his master to free states. • Supreme Court ruled: – A. Slaves are not citizens. – B. Government does not have the right to prevent slavery in territories (Missouri compromise is thus unconstitutional). John Brown • Radical Abolitionist. • Leads a raid on Harper’s Ferry (1859). • Wanted to give weapons to slaves so they could rebel. • Is captured and hung. • Anti-slave people call him a martyr. • South considers him to be crazy. Lincoln-Douglas Debates • 1858 Senate race in Illinois. • Series of debates between the candidates—Republican Abe Lincoln and Democrat Stephen Douglas. • Main issue they debate is what to do about the issue of slavery in the western territories. • Douglas win the election, but Lincoln becomes famous throughout the country. Lincoln-Douglas Debates The Election of 1860 • Abraham Lincoln, the Republican candidate for President, is against the extension of slavery into the western territories. • Does not think blacks are equal to whites but thinks slavery is bad for white self-making. • Some in the South say that they will secede (leave the Union) If he is elected President. Election of 1860 Lincoln wins • The South secedes. • They form The Confederate Sates of America. • Some southern “Border” states stay in the union. The Beginning of the fighting • South Carolina attacks Fort Sumter April 12, 1861. Northern Advantages • More Manufacturing • More Railroads • Larger Population • Mo Money Southern Advantages • Better Military Leadership • Can fight a Defensive war • Fighting in cause they believe in. • Cotton Modern Warfare • First “modern War.” • Ironclads • Landmines • Repeating Weapons • Improved artillery • Railroad & Telegraph Northern Leaders • Pres. Abe Lincoln • Generals: – U.S. Grant – William T. Sherman Southern Leaders • President: Jefferson Davis • General Robert E. Lee Northern Goals • Preserve the Union— NOT TO END SLAVERY • Key Strategy—Naval Blockade Draft Riots • Both the Union and the Confederacy begin to draft soldiers. • Rich people could buy their way out of it or hire substitutes. • In New York, there were draft riots (mostly poor Irish). The Emancipation Proclamation • In 1862, Lincoln issued the Emancipation Proclamation that threatened to free slaves in any territory still in rebellion by 1863. • Only takes effect as the Union army captures Confederate territory. • Important symbolically because it now made the war about ending slavery. Andersonville • Southern Prisoner of War Camp Facts about the Civil War • 1861-1865— North Wins. • More than 600,000 Americans die. • Lincoln is assassinated • Slaves are freed by 13th Amendment • South Destroyed by “Total War.” Lee Surrenders to Grant at Appomattox Court House Review • What was the cause of sectional tension between the North and the South? • Who was John Brown and how was he viewed by the North and the South? • What political party did Abe Lincoln belong to? • What were Lincoln’s feelings about African Americans and Slavery? • Why did the Southern states begin to secede? • What was the beginning of fighting during the Civil War? • What were the Northern advantages when the war broke out? • What were the Southern advantages? • Who was the President of the South during the Civil War? • Why were there draft riots in the North? • What was Andersonville? • How did the “Emancipation Proclamation” change the purpose of the war? • Who won the Civil War and what years was it fought? • Describe the Dred Scott case.