* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download RUMBLINGS OF CIVIL WAR 1845
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Antietam wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Namozine Church wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Roanoke Island wikipedia , lookup
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Missouri secession wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Seven Pines wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Missouri in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Lexington wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Gaines's Mill wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Wilson's Creek wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Jubal Early wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
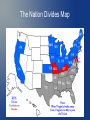
CAUSES OF THE CIVIL WAR 1820-1861 I. ESSENTIAL QUESTION... What issues and events shattered the nation's unity and led to the Civil War? James K. Polk 11th President of the U.S. Born in N.C. Attended UNC-Chapel Hill Oversaw the expansion of the US during the MexicanAmerican War and negotiated the addition of the “Oregon Territory” from Britain. II. CAUSES OF WAR 1. Regional divisions started to form after the Revolutionary War. 2. Economies in the northern and southern states were very different. 3. New land in the West created many arguments over the expansion of slavery. 4. New laws created hostility between politicians. 5. The election of Abraham Lincoln in 1860. III. MISSOURI COMPROMISE 1820- Maine becomes a “free state”, Missouri becomes a “slave” state. Henry Clay- Senator from Kentucky proposed the idea of drawing an imaginary line at latitude 36/30 north. (Pg. 322) Any new state north of the line would be “free,” any state south of the line would be “slave.” Missouri Compromise Map IV. THE COMPROMISE OF 1850 1850- California asks to enter the United States as a “free” state. Henry Clay asks Congress to reach a compromise: 1. CA be admitted as a free state, 2. Utah and New Mexico would decide for themselves whether to be slave or free. 3. Fugitive Slave Law- forced people in the North to return runaway slaves to the South. V. KANSAS-NEBRASKA ACT 1854- two new territories, Kansas & Nebraska became open to settlement. Both were north of the line established by the Missouri Compromise, so both would be free states. To compromise with the South, Congress declared that popular sovereignty (vote by local residents) would decide if each territory would be slave or free. VI. BLEEDING KANSAS Many Northerners flooded into Kansas to protest against slavery, while pro-slavery forces from the South also came. In all, 200 people died in Kansas over the issue of slavery. Newspapers labeled the territory, “Bleeding Kansas” and the “1st Civil War.” Bleeding Kansas VII. ATTACK IN CONGRESS 5/22/1856- Preston Brooks of S. Carolina attacked Charles Sumner of Massachusetts with a cane. Mr. Sumner suffered severe injuries that kept him out of Congress for 3 years! IX. THE ISSUE OF SLAVERY 1857- the Supreme Court ruled in Dred Scott v. Sandford, that slaves were “property” of their owners and did not have any rights. The court decided that Congress could not ban slavery in new territories. This leads to further division between the North and South. X. NORTHERN ABOLITIONISTS Abolitionists- those who wanted to rid the entire country of slavery. John Brown- a famous radical who killed 5 people in Kansas, and attempted to capture a federal weapons depot in West Virginia. Harriet Beecher Stowe- author of “Uncle Tom's Cabin,” an anti-slavery book that sold 400,000 copies, but was banned in the South. Brown & Stowe XI. ELECTION OF 1860 Abraham Lincoln (Republican) was elected as the 16th President of the U.S. Speaking on slavery, he said “A house divided against itself cannot stand. I believe this gov't cannot last permanently, half free and half slave.” Abraham Lincoln XII. THE SOUTH SECEDES Secede- to break away 1860- the South warned that if a Republican became President, it would secede from the union. The Confederate States of America- South Carolina is the 1st to secede and others follow. Jefferson Davis of Mississippi becomes President of the Confederacy. The Nation Divides Map NOTES QUESTIONS 1. How did the Missouri Compromise split the western territories in two? 2. What did the Compromise of 1850 do? 3. Why did the Kansas-Nebraska Act lead to violence? 4. Give an example of an abolitionist. 5. Other than slavery, what were two other causes of the Civil War? 6. What was the final event that led to the South seceding from the United States? CH. 15 NOTES FIGHTING IN THE CIVIL WAR 1861-1865 QUESTIONS TO THINK ABOUT… WHICH SIDE… Had a larger population (more soldiers)? Had more supplies (guns, ammunition, food, etc.)? Had better generals? Had a stronger navy? Had more railroads? Was more familiar to the battle ground fought on? Had stronger government control? Goals North’s Goals: The North wanted to restore the Union. South’s Goals: The Confederacy wanted to be an independent nation. It just needed to fight long enough and to convince Northerners that the war was not worth its cost. I. UNION ADVANTAGES 1. Experienced federal government and trade w/foreign nations. 2. Had 8 more states than the Confederacy. 3. 2x the population of the South. 4. Controlled 80% of the nation's factories and mills (more weapons, ammunition, etc..). 5. Better transportation. II. CONFEDERATE ADVANTAGES 1. Outstanding military officers. 2. More experienced soldiers. 3. Knew the land well in the South 4. Planned to fight a defensive battle. 5. Soldiers knew what they were fighting for: their homes, land, and loved ones. III. FIGHTING BEGINS April 12, 1861- S. Carolina troops fired on federal forces at Fort Sumter, SC. N.C.: the only southern state to form a peace movement during the war. FORT SUMTER (PRESENT DAY) IV. GATHERING ARMIES Draft- the requirement of all males, ages 18-35 to register for military service. North Carolina- supplied around 96 percent of the state's men (ages 20-60), and lost 40,000 men; more than any other southern state. V. ANACONDA PLAN Gen. Winfield Scott came up with the idea to block all southern ports, and attack the south from the west and east. Photo to the right-- VI. IMPORTANT BATTLES 1. 1st Battle of Bull Run (MD)- Confederates win, General Jackson gets the nickname “Stonewall” 2. Battle of Antietam (MD)- Union wins, Lincoln uses victory to issue the Emancipation Proclamation. 3. Chancellorsville (VA)- South wins, but Stonewall Jackson is shot by his own men and dies. 4. Gettysburg (PA)- Union wins, turning point of the war, Lee never invades the North again. VI. IMP. BATTLES CONT.. 5. Vicksburg (MS)- Union forces take control of the Miss. River. 6. Atlanta (GA)- Union forces win, victory helps Lincoln get re-elected. 7. Appomattox (VA)- Gen. Grant (North) forced Gen. Lee (South) to surrender. Gen. Jackson, Antietam Grave, Gettysburg, Surrender VII. POLITICAL DEVELOPMENTS The Emancipation Proclamation- 1863- freed all slaves living in Confederate states. It DID NOT outlaw slavery or free any slaves in Union states.