* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download new Causes leading up to the Civil War
Survey
Document related concepts
Treatment of slaves in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Slavery in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
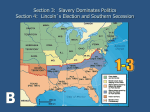
A Divided Nation Causes Leading Up to the Civil War Main Idea • Differences between the North and South led to growing tensions between the two regions. Differences Divide North & South Economy Population Feelings About Slavery North South Factories Wanted higher taxes on imported goods 19 Million Farming Wanted lower taxes on imported goods 11 Million (4 million slaves) Wanted to keep Wanted the right slavery in South to take slaves anywhere Farming • Most people in the southern states earned a living by farming: Cotton Tobacco Rice Wheat Slavery Slavery was allowed in the Southern States, where enslaved people grew crops such as cotton, tobacco, and rice. • Northern workers were free and were paid for their farm work. • As Southern plantations grew, so did the number of enslaved African Americans. • Different Views on Slavery • Abolitionists opposed slavery and fought to end slavery everywhere in the country. John Brown’ s raid- Brown and a group of 21 white and black men went to Harper’s Ferry, West Virginia on Oct. 16,1859 to seize weapons to give to slaves in Virginia to help them rebel against their owners. His group was surrounded by a force of U.S. Marines under Lt. Col. Robert E. Lee. Half of Brown’s men died and he was wounded and captured. ► Abolitionist John Brown • Southern slave owners continued to defend slavery because they needed workers for the large farms and plantations. • Slaves were given no choice. Slave Codes •All slaves were required to follow the slave code. They were not allowed to: •Leave their owners’ land •Hit a white person •Own property •Meet in groups •Buy or sell •Learn to read or write Slave pen where slaves were held before being auctioned to the highest bidder. Resisting Slavery Quiet Resistance •Refused to obey •Broke tools •Left gates open •Let boats drift away •Hid or destroyed goods Slave Rebellions •Ran away •Helped others escape •Took up weapons against owners •Nat Turner •The Amistad The Underground Railroad •Secret escape routes to help runaway slaves. •Conductors were people who helped slaves. •Not all conductors were African Americans. •Stations were secret hiding places for slaves. Harriet Tubman •Harriet Tubman was the most famous “conductor”. •She escaped from the South, she went back over 19 times to help other slaves runaway. •She led over 300 slaves to freedom, including her whole family! Free African Americans By 1860, there were 4.5 million African Americans living in the U.S. • 4.1 million of these African Americans lived in the South. • 1 out of every 9 African Americans were free. Most free African Americans lived in cities. • Without a certificate of freedom, even free African Americans could be sent back into slavery. • Missouri Compromise • • • In 1819, the U.S. was made up of 11 free states and 11 slave states. In 1820, Missouri was admitted as a slave state and Maine was admitted as a free state. After these two states were admitted, an imaginary line was drawn below Missouri. Any state admitted above that line would be a free state and any state below that line would be a slave state. Compromise of 1850 •Admitted California as a free state and divided up the rest of the western territory, allowing them to choose to be free or slave. •Fugitive Slave Laws returned runaway slaves to the South. Kansas-Nebraska Act of 1854 • • • Stephen Douglas Changed the Missouri Compromise to allow Kansas and Nebraska to choose if they would be slave or free (even though they were above the line and should have been free states.) Fighting broke out and over 200 people died. This event was called Bleeding Kansas. States’ Rights and Slavery •The North felt slavery should stay in the south, while the South felt that they should be able to take slaves wherever they wanted. •Southerners felt that if they lost their slaves, the economy would suffer. •They believed that each state should be able to decide the issue of slavery without the federal government making laws about it or having Congress decide for them. States’ Rights and Free Trade • • • • Southern states wanted to buy factory goods from Europe instead of from the North. Buying goods from Europe would hurt the economy of the North, which would also serve to punish them for fighting against slavery. The Northern states passed laws to tax goods from Europe, making them too expensive for Southerners to afford. The South felt these laws violated their rights. Uncle Tom’s Cabin The disagreements over slavery between the North and the South increased with the publication of Harriet Beecher Stowe’s novel, “Uncle Tom’s Cabin”. • The book was about the cruelty of slavery. People began to see that slavery was wrong after reading it. • It was the second highest selling book after the Bible in the 19th century. • Harriet Beecher Stowe Lincoln met Stowe later and remarked that she was “the little lady who started a big war.” Supreme Court Case Dred Scott - 1857 Judge ruled that Dred Scott was NOT a free man because he was property. • Judge ruled that the Missouri Compromise violated the constitutional rights of those who lived in the north because it didn’t allow them to own slaves. • Senate Race Illinois 1858 • Stephen Douglas was a democrat. He was short, fat, well-dressed, well educated, and he was a good public speaker. • Abraham Lincoln was a republican. He was tall, skinny, wore wrinkled clothes, was self-taught, and he was a good public speaker. • Douglas won the senate race, but it helped people to get to know Lincoln. Lincoln is Elected President 1860 • Stephen Douglas ran against Abraham Lincoln, but this time Lincoln won. • Lincoln was elected president of the United States on November 6, 1860. Southern States Secede • • • Many Southern states believed that the South should secede, or break away, from the United States. South Carolina was the first state to secede from the Union on December 20, 1860. From December to February, 6 more southern states seceded, including Alabama, Florida, Mississippi, Georgia, Louisiana, and Texas. Confederate States of America • • In February 1861, the Confederate States of America was formed and Jefferson Davis was elected as the president. The states that seceded were called the Confederacy. The states that remained loyal to the United States government were called the Union. President of the Confederacy Jefferson Davis Lincoln is sworn in • Abraham Lincoln was sworn in as president of the United States on March 4, 1861. Lincoln’s Inauguration The War Begins • • • After Lincoln’s inauguration, the Confederacy took over most of the forts and military property in the South. Fort Sumter was one of the forts under Union control. It is located in South Carolina, the first state to secede from the Union. Civil War • • • The Union was running short on supplies so they sent a letter to President Lincoln requesting help. Before Lincoln had a chance to send supplies, the Confederates began firing on Fort Sumter. The Union army was forced to surrender. The battle at Fort Sumter began the Civil War. This photograph shows Major Robert Anderson and soldiers praying around the flag in Fort Sumter on December 27, 1860